Django Template Render
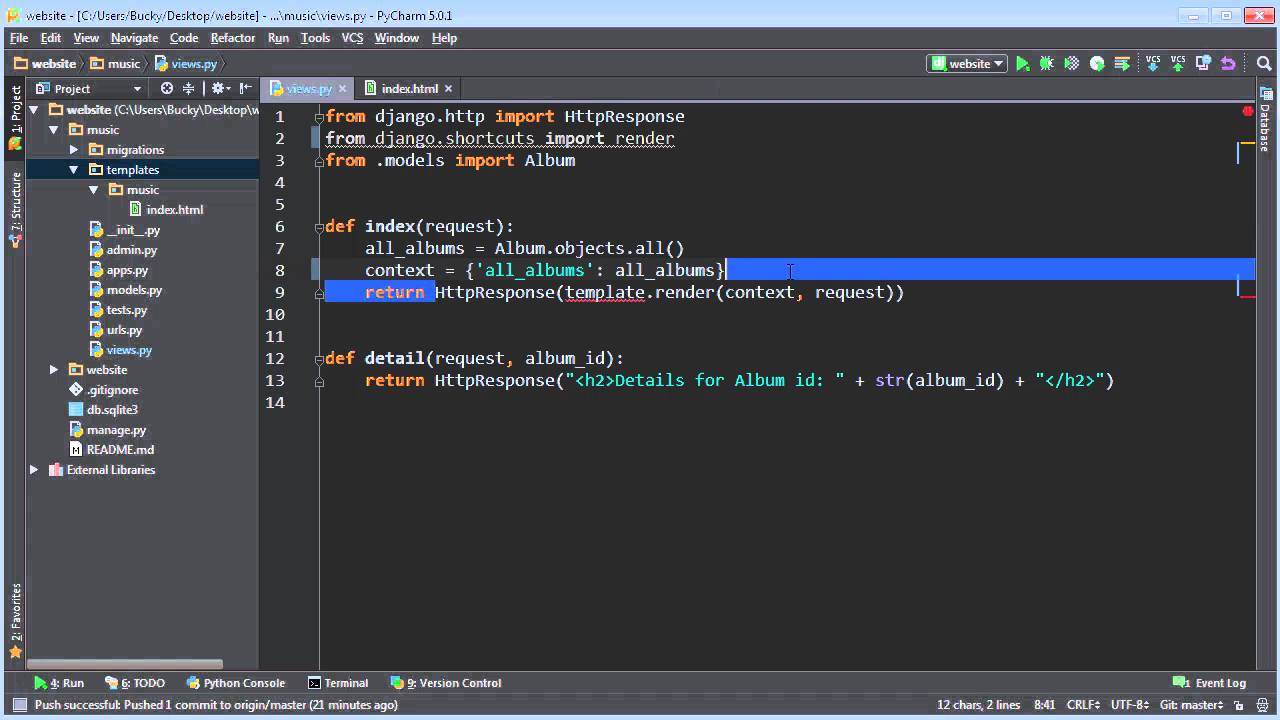
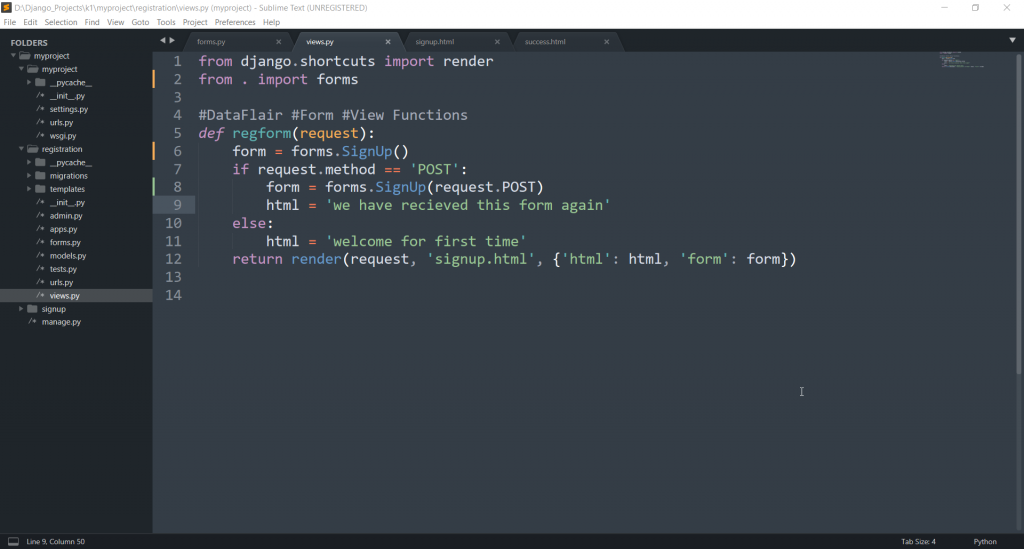
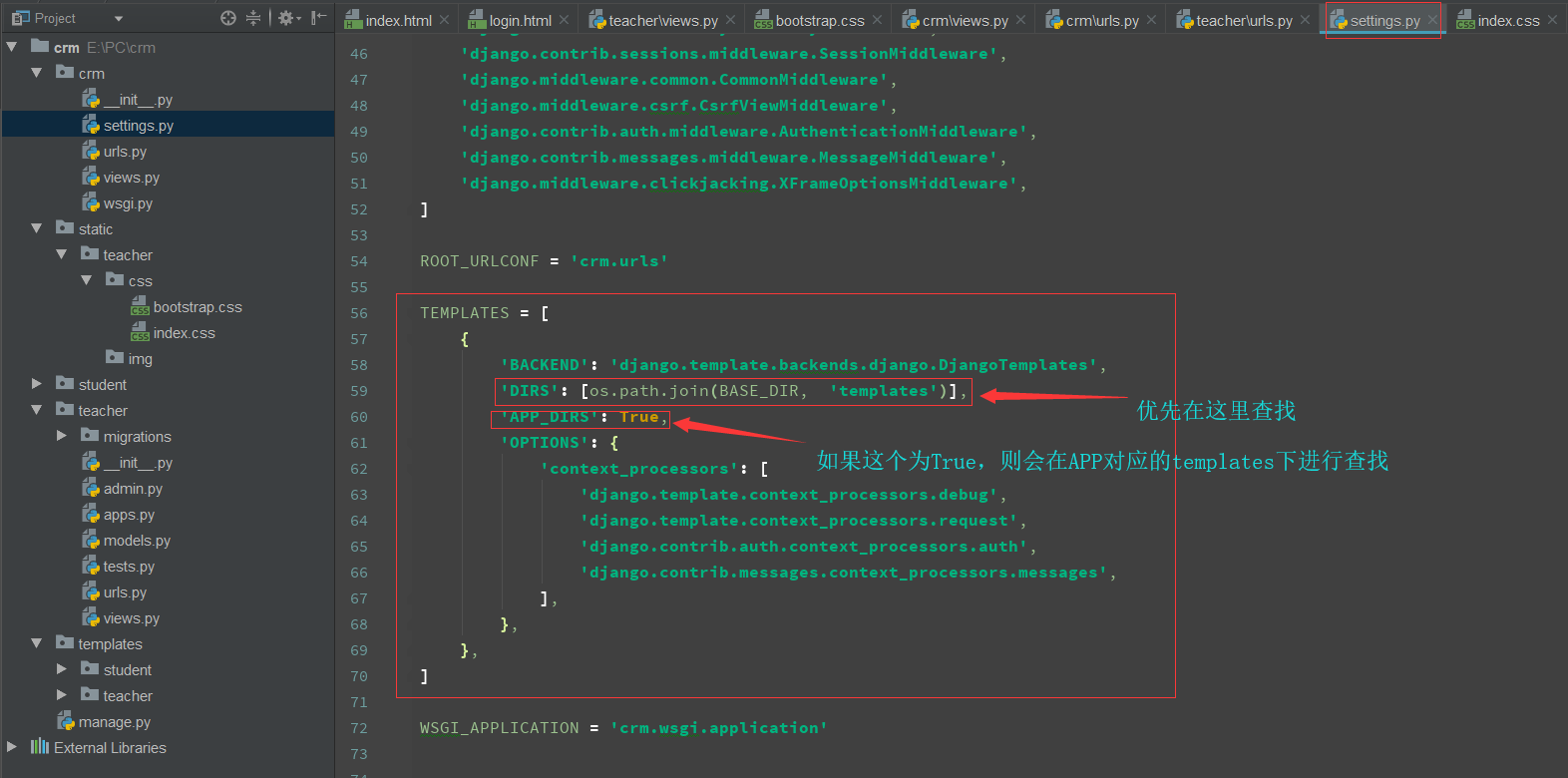
Django Template Render - The main ones are variables and tags. Web django’s form widgets are rendered using django’s template engines system. Web in django, it is easy to render the html templates by setting urls of respective html pages. This tutorial covers how to write django custom template tags and filters, including simple tags, inclusion tags, block tags, and different types of filters. To render a template in a view, you’ll need to use django’s render function. When django compiles a template, it splits the raw template text into ‘’nodes’’. Web this code demonstrates using render() to render a template named my_template.html and passing a dictionary named context containing a message to the template. From django.template import context, template t = template('this is your {{ message }}.') c = context({'message': First things first, open up views.py in the. If you’re looking for reference on the language syntax, see the django template language. Web your project’s templates setting describes how django will load and render templates. Update your view like this: Modify the presentation of your data through template filters. Web rendering templates in views. I will then show you how to access that data in the template and display it to the user. Web based on the the docs for using the template system: A compiled template is a list of node objects. Each node is an instance of django.template.node and has a render() method. Web how would i go about speeding up django template rendering? Render (request, template_name, context=none, content_type=none, status=none, using=none) [source] ¶. By convention djangotemplates looks for a “templates” subdirectory in each of the installed_apps. There are three circumstances under which a templateresponse will be rendered: Each node is an instance of django.template.node and has a render() method. Render (request, template_name, context=none, content_type=none, status=none, using=none) [source] ¶. The main ones are variables and tags. Reading the docs and other sources, it should be done in 3 steps: This template folder is that which django provides in default, it's not available inside my app. To render a template in a view, you’ll need to use django’s render function. The django template engine renders templates that contain variables, constructs, tags, and filters. Web server = bob. Each node is an instance of django.template.node and has a render() method. Web rendering templates in views. Web how would i go about speeding up django template rendering? This tutorial covers how to write django custom template tags and filters, including simple tags, inclusion tags, block tags, and different types of filters. Web this code demonstrates using render() to render. What’s even more curious, i have multiple other templates which are essentially the. Binddn} that is enough for it to break the extend. Forms and widgets can specify custom renderer classes. Web to generate the dynamic parts of the webpage, django uses its specific template language called django template language or dtl. Web i use the wmd.js to store the. The default settings file configures a djangotemplates backend whose app_dirs option is set to true. The main ones are variables and tags. Update your view like this: Reading the docs and other sources, it should be done in 3 steps: The django template engine renders templates that contain variables, constructs, tags, and filters. You can use django’s template engine to display data in very powerful ways. Render (request, template_name, context=none, content_type=none, status=none, using=none) [source] ¶. A widget’s template can be overridden by a project. Web the rendering process takes the intermediate representation of template and context, and turns it into the final byte stream that can be served to the client. Templates =. This template folder is that which django provides in default, it's not available inside my app. Reading the docs and other sources, it should be done in 3 steps: Django templates not only allow passing data from view to template, but also provides some limited features of. To render a template in a view, you’ll need to use django’s render. Web your project’s templates setting describes how django will load and render templates. The django template engine renders templates that contain variables, constructs, tags, and filters. Web you can render a template in your code like so: Web django’s form widgets are rendered using django’s template engines system. Web in django, it is easy to render the html templates by. Web this code demonstrates using render() to render a template named my_template.html and passing a dictionary named context containing a message to the template. In the django intro page, we learned that the result should be in html, and it should be created in a template, so let's do that. Web your project’s templates setting describes how django will load. Render (request, template_name, context=none, content_type=none, status=none, using=none) [source] ¶. The request object is automatically included in the context. A widget’s template can be overridden by a project. Web how would i go about speeding up django template rendering? Update your view like this: Web server = bob. From django.template import template, context t = template(my name is {{ my_name }}.) c = context({my_name: Create reusable templates with inheritance and inclusion. The main ones are variables and tags. Web based on the the docs for using the template system: Web the rendering process takes the intermediate representation of template and context, and turns it into the final byte stream that can be served to the client. Reading the docs and other sources, it should be done in 3 steps: Widgets can specify custom template names. Create reusable templates with inheritance and inclusion. There are three circumstances under which a. Web to do so, first i am trying to render a simple varable in a template. What’s even more curious, i have multiple other templates which are essentially the. Web rendering templates in views. When django compiles a template, it splits the raw template text into ‘’nodes’’. Each node is an instance of django.template.node and has a render() method. Modify the presentation of your data through template filters. A widget’s template can be overridden by a project. Web to generate the dynamic parts of the webpage, django uses its specific template language called django template language or dtl. I've already attempted to perform all database access in the view, such that the template only hits ram and not the db engine. Web server = bob. Django templates not only allow passing data from view to template, but also provides some limited features of. A template is rendered with a context. The request object is automatically included in the context. By convention djangotemplates looks for a “templates” subdirectory in each of the installed_apps. Widgets can specify custom template names. Use the render() shortcut in views to quickly use templates.Django Template Render
Django Tutorial for Beginners 15 Render Template Shortcut YouTube
Django Templates, Django App, Django Project , How to render HTML page
5 How to Render template in our Django Project Render Templates in
Django Tutorial for Beginners 4 Django Templates + How to Render a
Django Template Render
How to render template in Django Life Coach
How to render template in django django template django full
Django Template Render
CodeWithGagan Programming Language and IT Lectures Render a basic
It Assumes An Understanding Of Templates, Contexts, Variables, Tags, And Rendering.
'Your Message'}) Html = T.render(C)
This Template Folder Is That Which Django Provides In Default, It's Not Available Inside My App.
A Compiled Template Is A List Of Node Objects.
Related Post: