Dna Coding Strand To Dna Template Strand
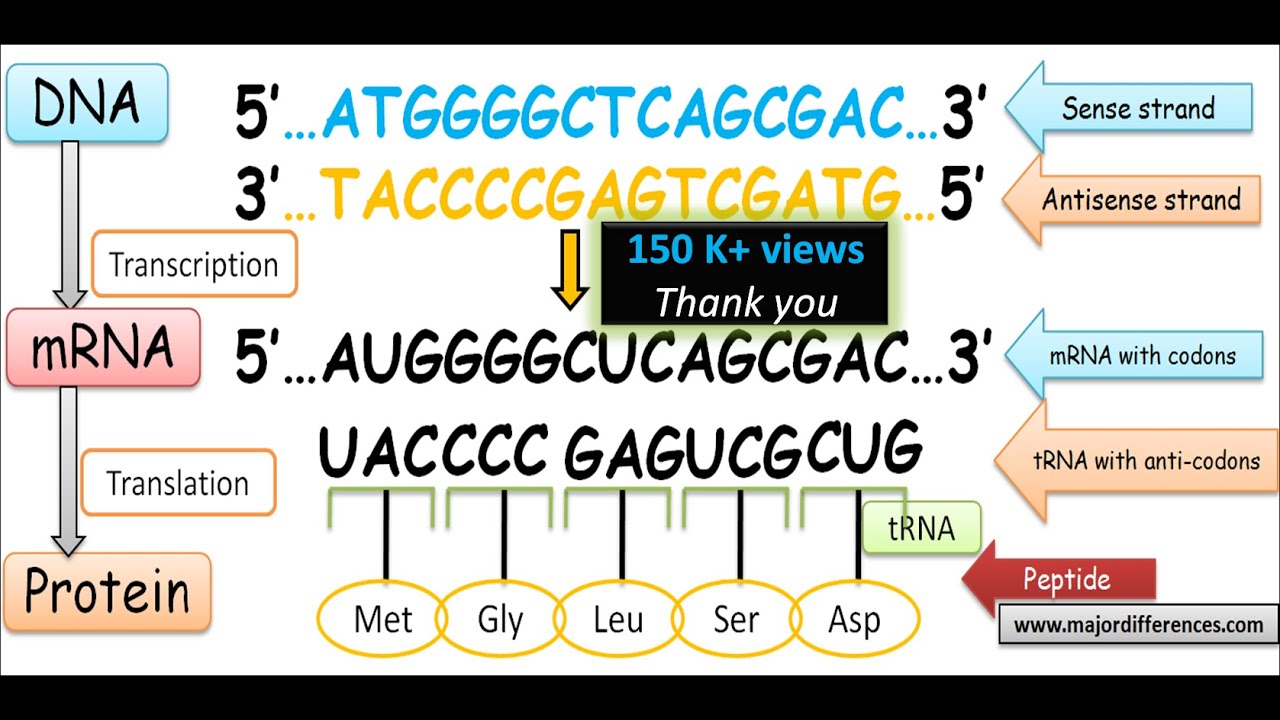
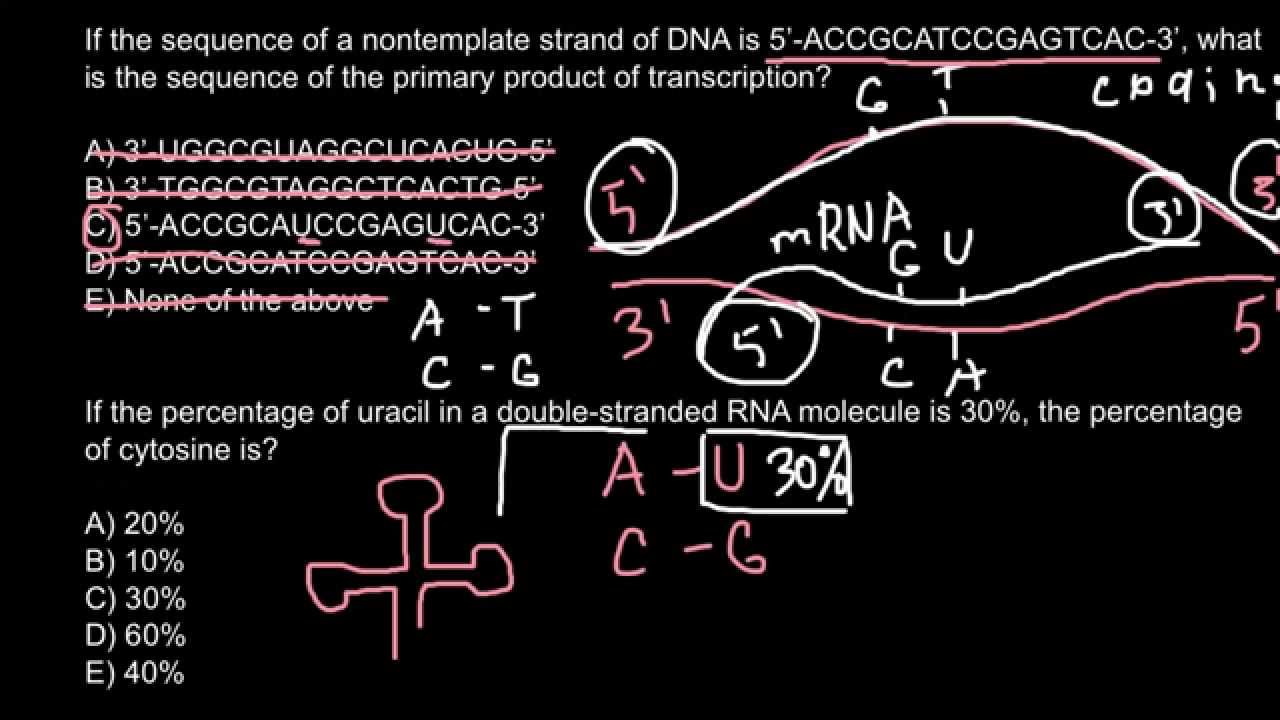
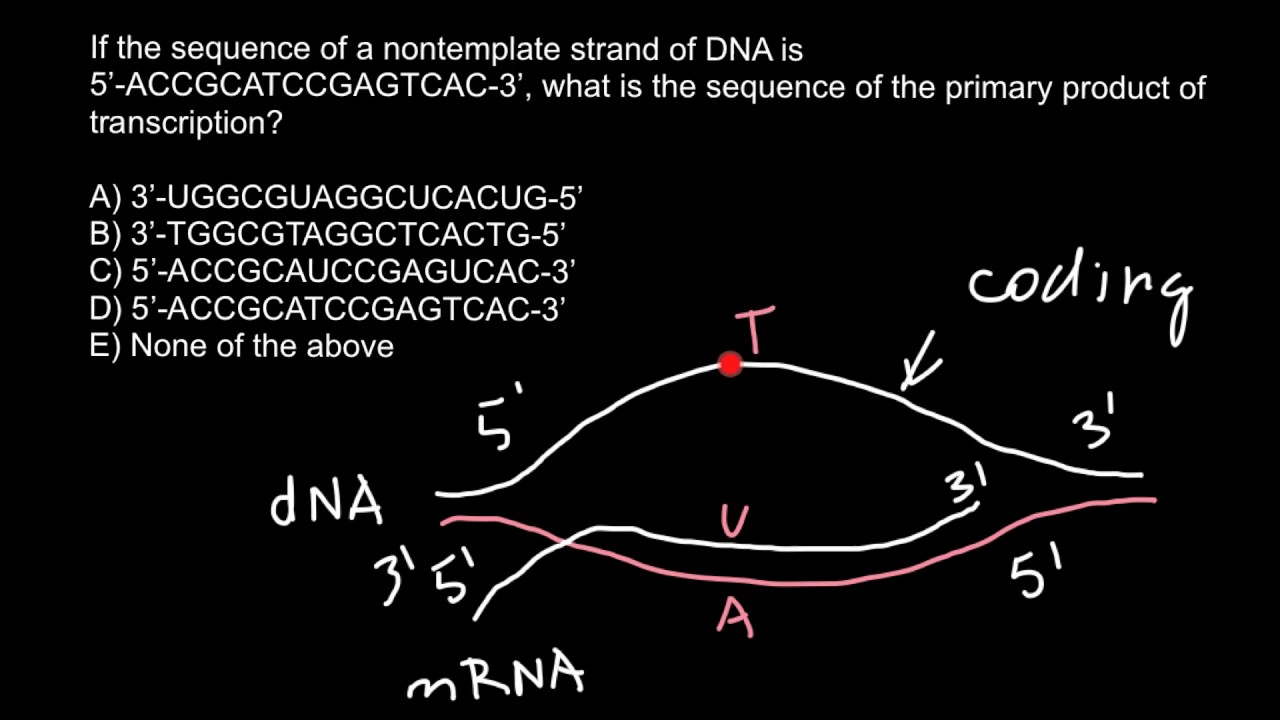
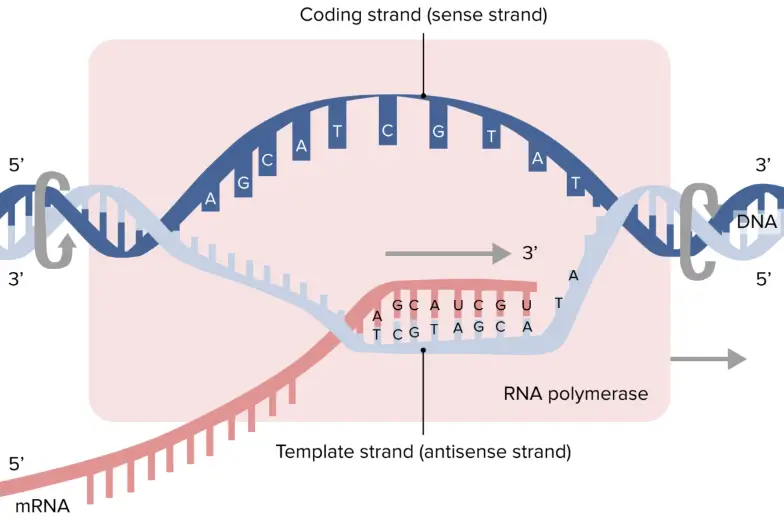
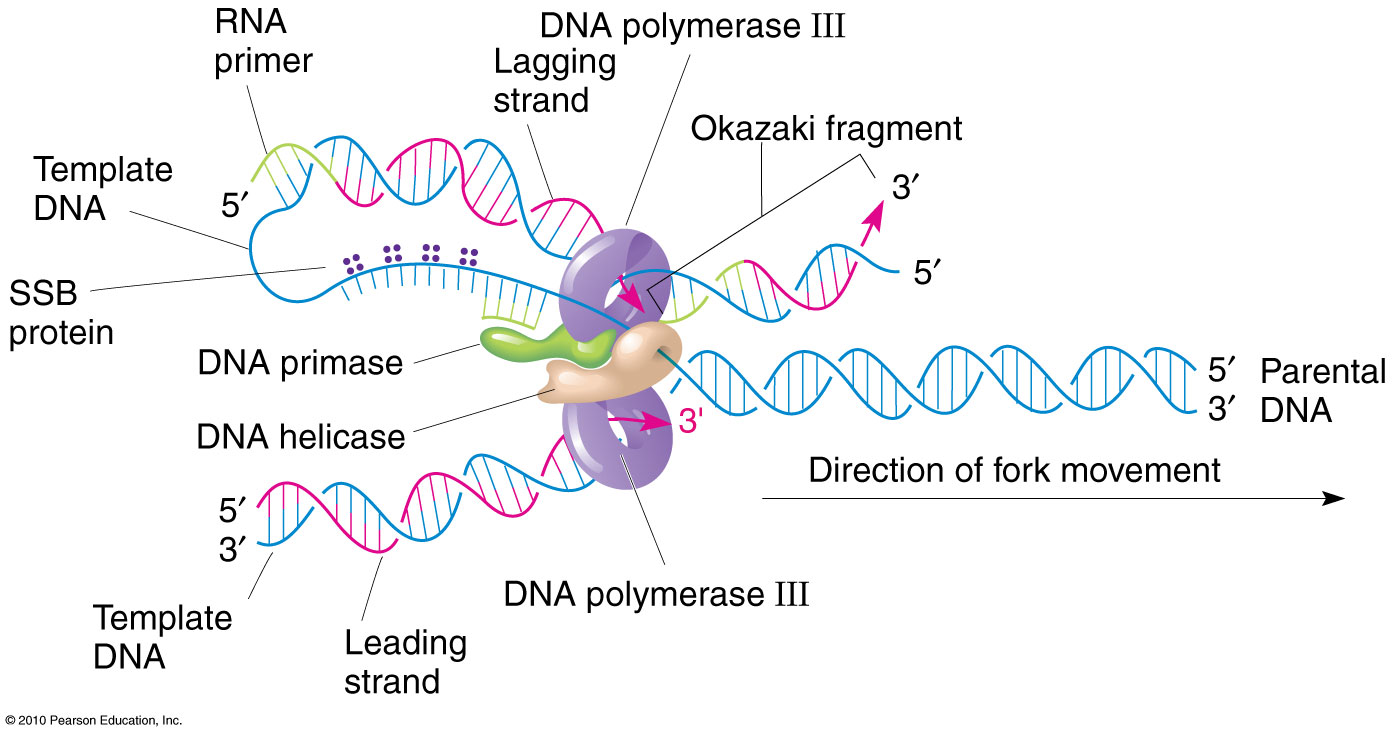
Dna Coding Strand To Dna Template Strand - Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Our approach is based on. The nontemplate strand is referred. There are also genes for the rnas found in snrnps, etc. Web the coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (rna). The term template strand is still appropriate because one of the dna strands is used as a. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. Web as shown schematically above, messenger rna is synthesized complementary and antiparallel to the template strand (anticodons) of dna, so the resulting mrna consists of codons corresponding to those in the coding strand of dna. Web the coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Trna genes encode trna molecules, and rrna genes encode the rrnas found in ribosomes. There are also genes for the rnas found in snrnps, etc. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Web the coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. The bases will always pair a with t and c. Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or informational strand. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or informational strand. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. Web the coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web the coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (rna). [1] the sense strand is the. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. The template strand runs in 3’ to 5’ direction. Web the coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. Web as shown schematically above, messenger rna is synthesized complementary and antiparallel to the template strand (anticodons) of dna, so the resulting mrna consists of codons corresponding to those in the coding strand of dna. There are also genes for the. One strand of the molecule is the template strand and one is called the coding strand. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. [1] the sense strand is the. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. The nontemplate strand is referred. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. Trna genes encode trna molecules, and rrna genes encode the rrnas found in ribosomes. The template strand runs in 3’ to 5’ direction. Web coding strand vs. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. One strand of the molecule is the template strand and one is called the coding strand. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The bases will always pair a. A dna molecule is double stranded. The bases will always pair a with t and c. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Ribonucleotides are attracted to the uncoiling region of. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. To initiate rna synthesis, the two. Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template for different genes, but the rna will still be produced from 5’ → 3’. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. There are also genes for the rnas found in snrnps, etc. Two key players in this genetic orchestra are the coding strand. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. The bases will always pair a with t and c. The. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. [1] the sense strand is the. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. The term template strand is still appropriate because one of the dna strands is used as. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Web coding strand vs. There are also genes for the rnas found in snrnps, etc. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to. A dna molecule is double stranded. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web as shown schematically above, messenger rna is synthesized complementary and antiparallel to the template strand (anticodons) of dna, so the resulting mrna consists of codons corresponding to those in the coding strand of dna. In the intricate realm of molecular biology, the concept of dna strands plays a pivotal role, especially when it comes to transcription and translation processes. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The bases will always pair a with t and c. The term template strand is still appropriate because one of the dna strands is used as a. The template strand runs in 3’ to 5’ direction. [1] the sense strand is the. Trna genes encode trna molecules, and rrna genes encode the rrnas found in ribosomes. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. The nontemplate strand is referred. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Our approach is based on.How To Identify Template Strand Of Dna
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Dna Coding And Template Strands
Template and coding strands of DNA YouTube
DNA Transcription Steps and Mechanism • Microbe Online
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Variations sciencesavers
Difference Between Coding Strand And Template Strand,
Dna Strand That Is Transcribed at Trisha Revis blog
Web The Coding Strand Has A Coding Sequence Of Nucleotides That Serves As A Master Blueprint For Our Protein.
Web Coding Strand Vs.
It Is Complementary To The Coding Strand Of Dna For The Target Gene.
This Template Strand Is Called The Noncoding Strand.
Related Post: