Dna Template Strand To Mrna
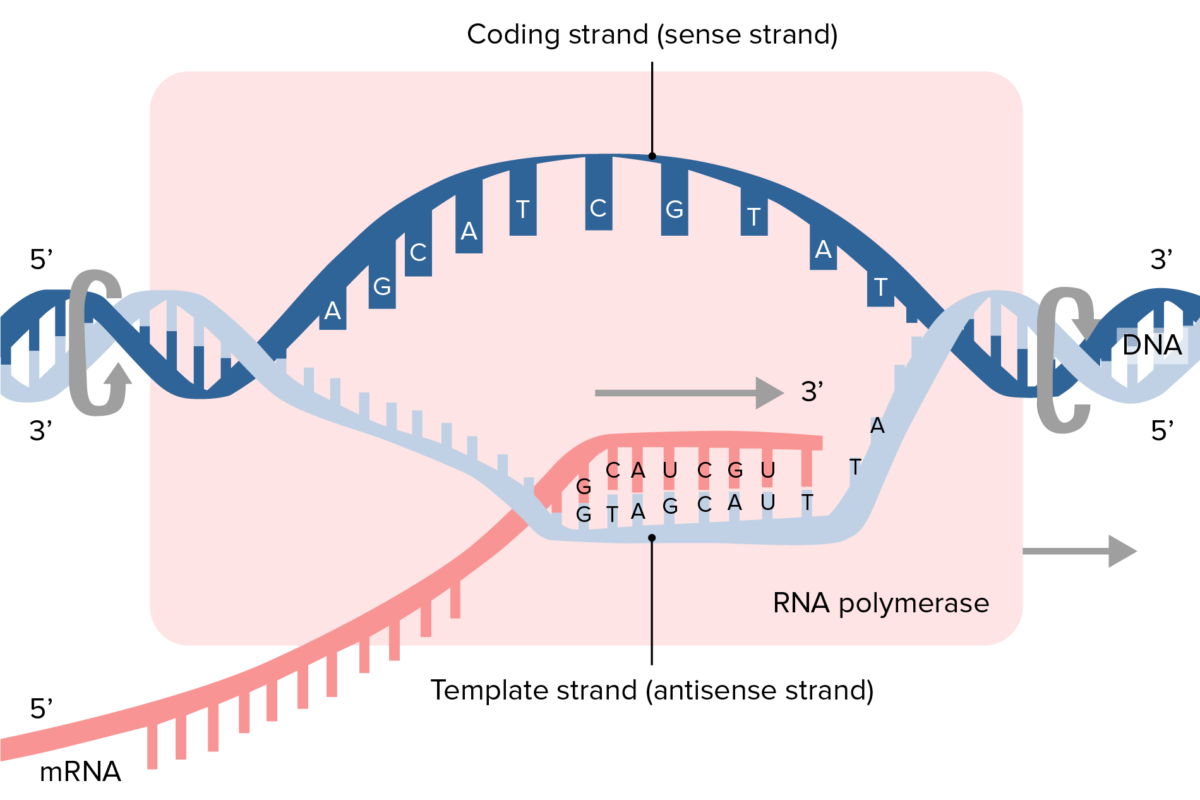
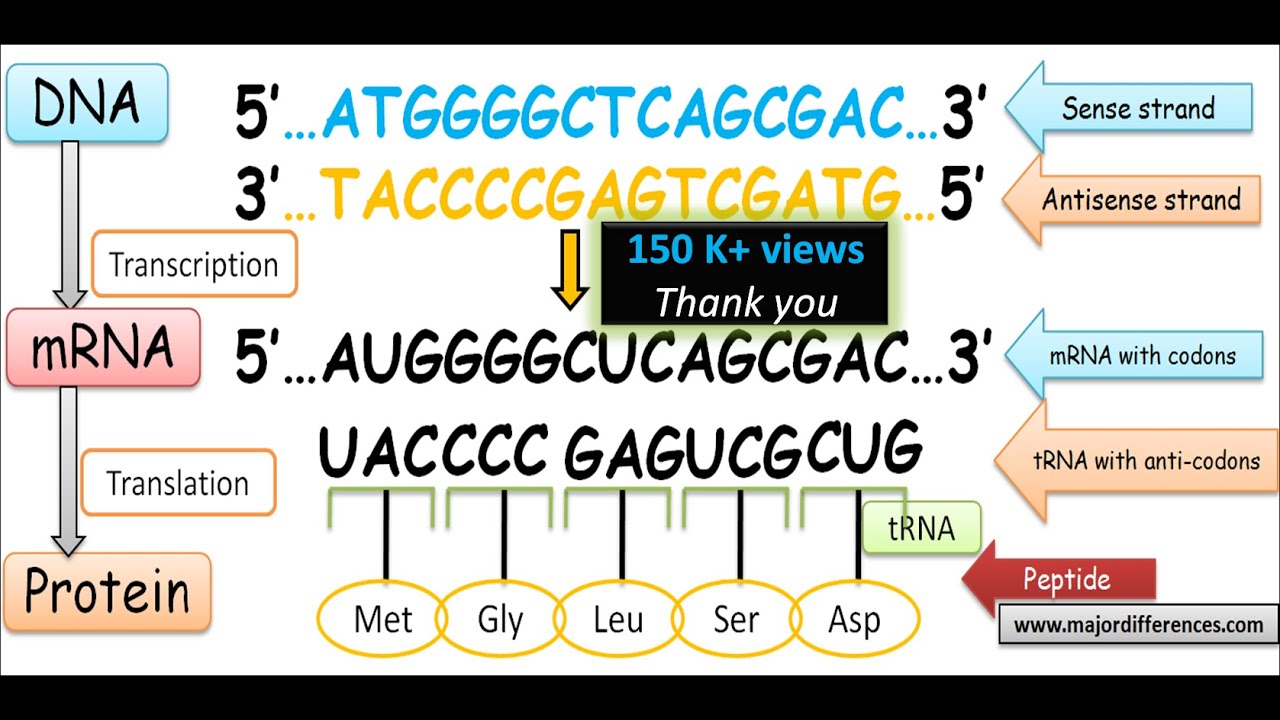
Dna Template Strand To Mrna - As the polymerase nears the end of the gene being transcribed, it encounters a region rich in cg nucleotides. Each ribonucleotide is inserted into the growing rna strand following the rules of base pairing. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. It is the transfer of genetic instructions in dna to messenger rna (mrna). Although rna polymerase traverses the. During transcription, a strand of mrna is made that is complementary to a strand of dna. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. Although rna polymerase traverses the. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). A dna molecule is double stranded. Simple bootstrap web creator software download. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Our approach is based on. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web as shown schematically above, messenger rna is synthesized complementary and antiparallel to the template strand (anticodons) of dna, so the resulting mrna consists of codons corresponding to those in the coding strand of dna. The mrna folds back on itself, and the complementary cg nucleotides bind together. Web dna to mrna to protein converter restriction site finder hamming calculator. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Simple bootstrap web creator software download. Figure below shows how this occurs. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. It is the transfer of genetic instructions in dna to messenger rna (mrna). Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. During. As the polymerase nears the end of the gene being transcribed, it encounters a region rich in cg nucleotides. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. One. A dna molecule is double stranded. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. As the polymerase nears the end of the gene being transcribed, it encounters a region rich in. Although rna polymerase traverses the. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. The bases will always pair a with t and c. As the polymerase nears the end of the gene being transcribed, it encounters a region rich in cg nucleotides. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're. Translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web as shown schematically above, messenger rna is synthesized complementary and antiparallel to the template strand (anticodons) of dna, so the resulting mrna consists of codons corresponding to those. A dna molecule is double stranded. Simple bootstrap web creator software download. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different mrna. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Web as the rna polymerase travels. A dna molecule is double stranded. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. As transcription proceeds, rna. The bases will always pair a with t and c. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Figure below shows how this occurs. Our approach is based on. Web as shown schematically above, messenger rna is synthesized complementary and antiparallel to the template strand (anticodons) of dna, so the resulting mrna consists of codons corresponding to those in the coding strand of dna. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different mrna. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Dna to mrna to protein converter. Although rna polymerase traverses the. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. The nontemplate strand is referred. It is the transfer of genetic instructions in dna to messenger rna (mrna).Mrna Template Strand
Mrna Template Strand
Template And Coding Strand Of Dna
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
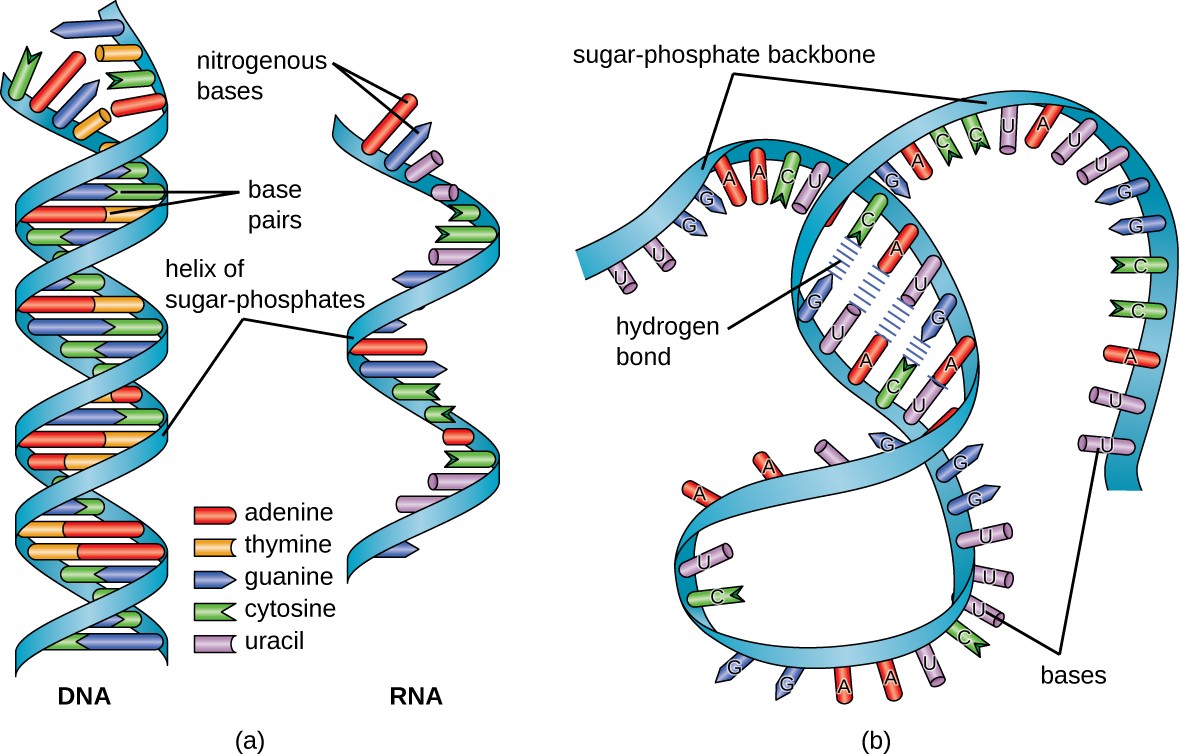
Mrna Structure Diagram
Dna Rna Mrna Explained at Michael Kidwell blog
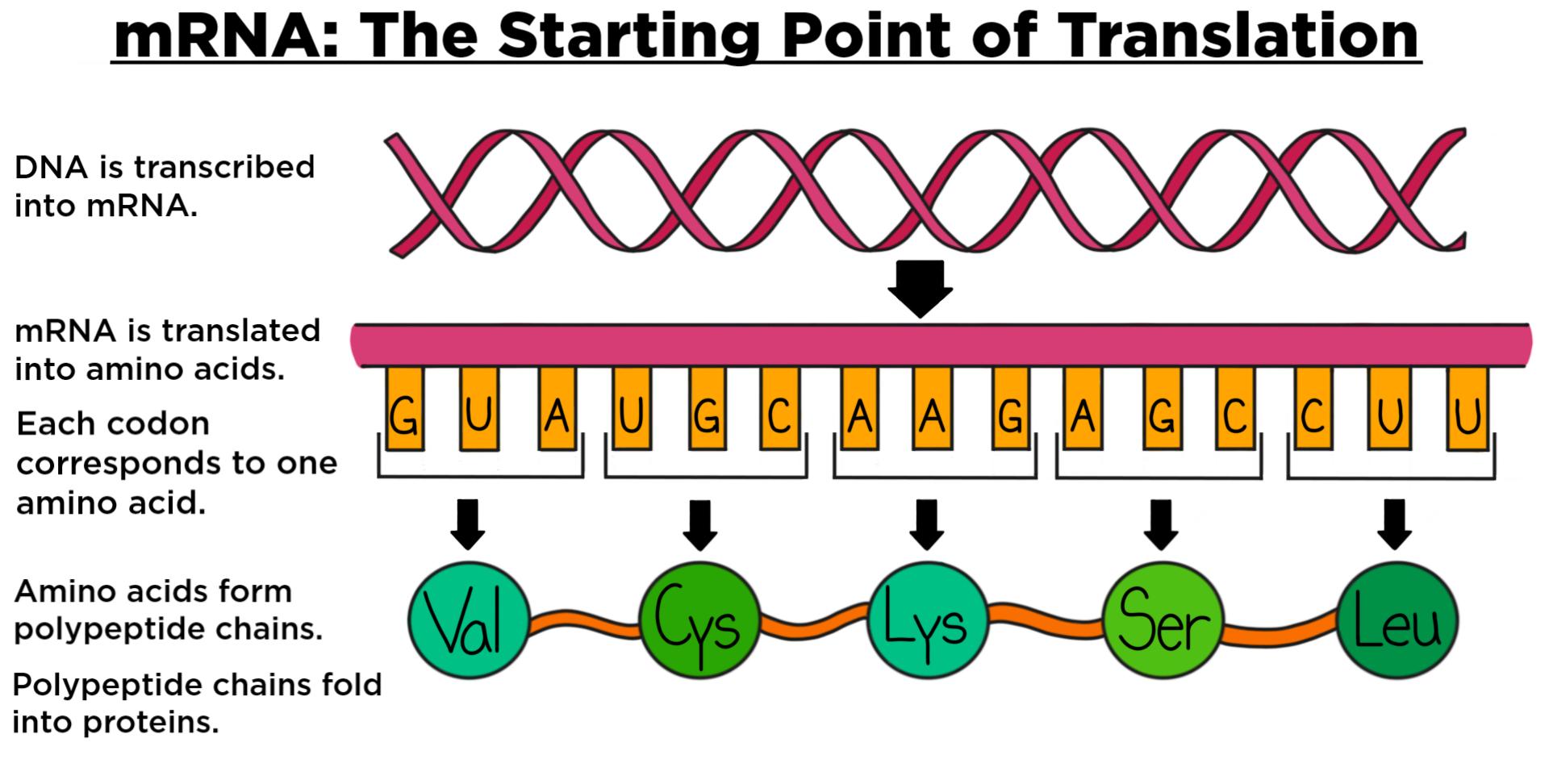
Protein Synthesis Anatomy and Physiology I
What Is The Template For Mrna
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
Template Strand Mrna
Web Rna Is Synthesized By Using The Template Strand Of Dna As A Guide For Complementary Base Pairing.
Web Transcription Always Proceeds From One Of The Two Dna Strands, Which Is Called The Template Strand.
Web In Transcription, An Rna Polymerase Uses Only One Strand Of Dna, Called The Template Strand, Of A Gene To Catalyze Synthesis Of A Complementary, Antiparallel Rna Strand.
The Coding Strand Provides A Reference For The Formation Of Mrna With A Similar Sequence, While The Template Strand Guides The Rna Polymerase To Synthesize A Complementary Rna Strand.
Related Post: