Hospital Sliding Scale Insulin Protocol Printable
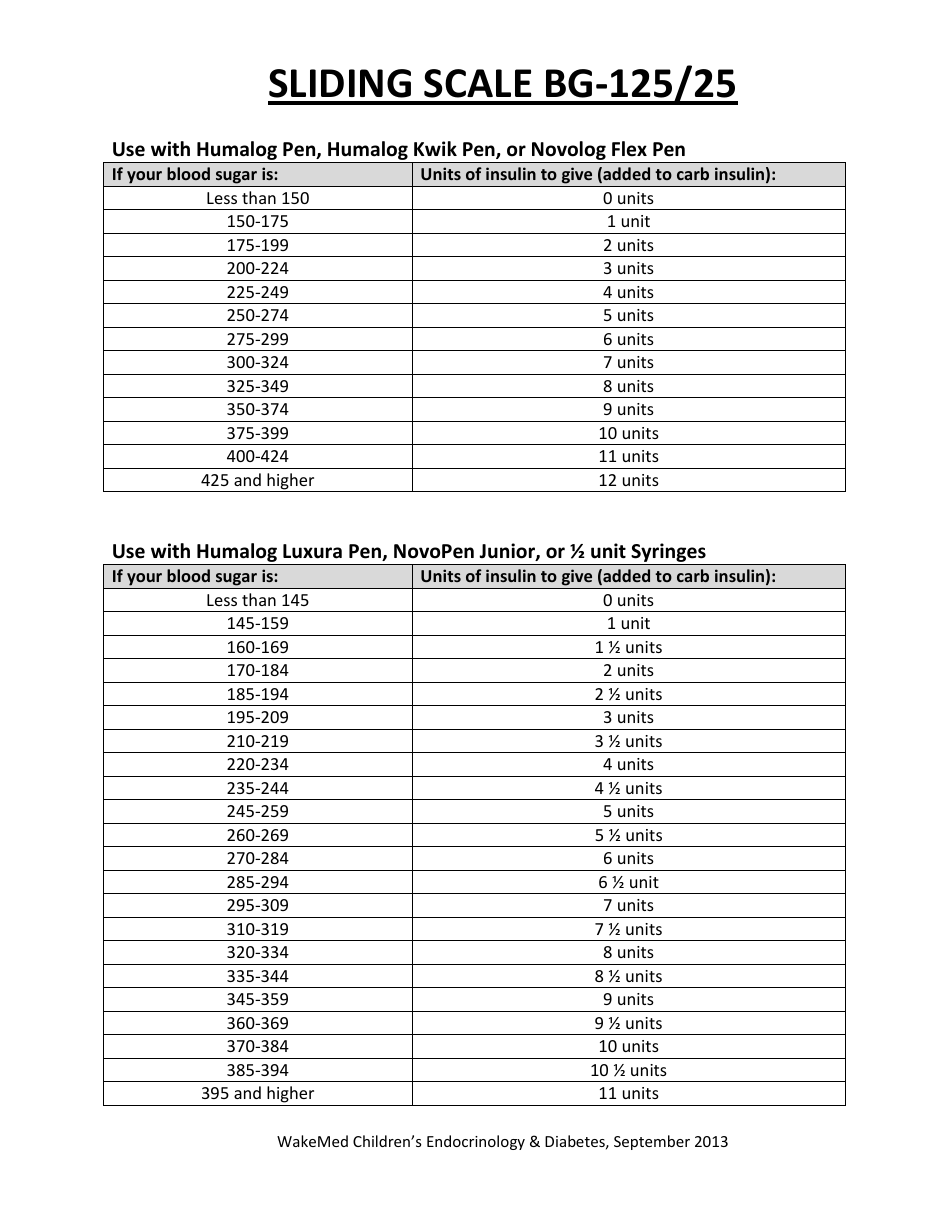
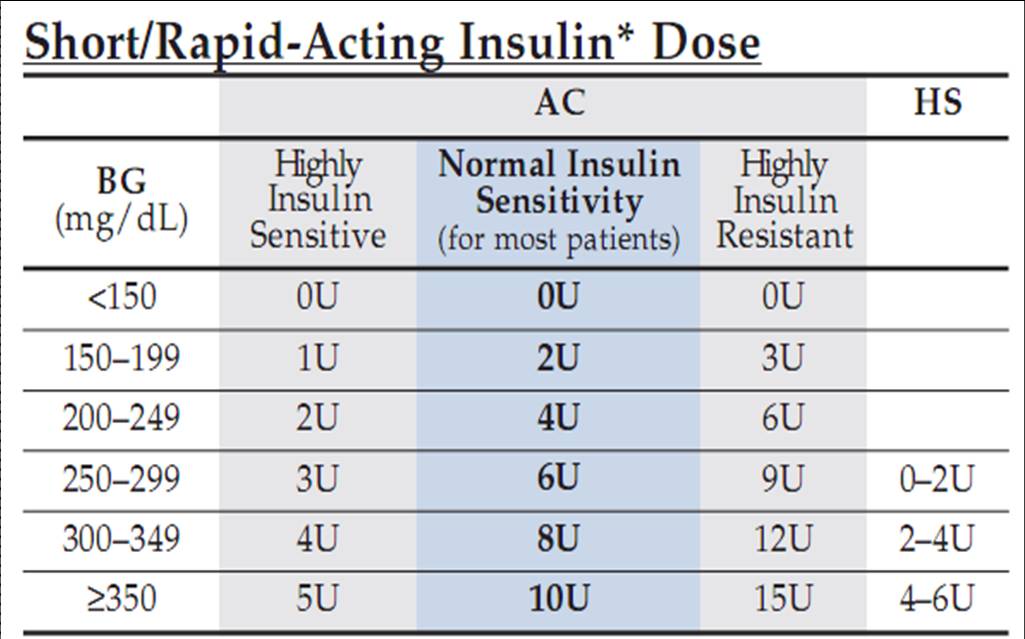
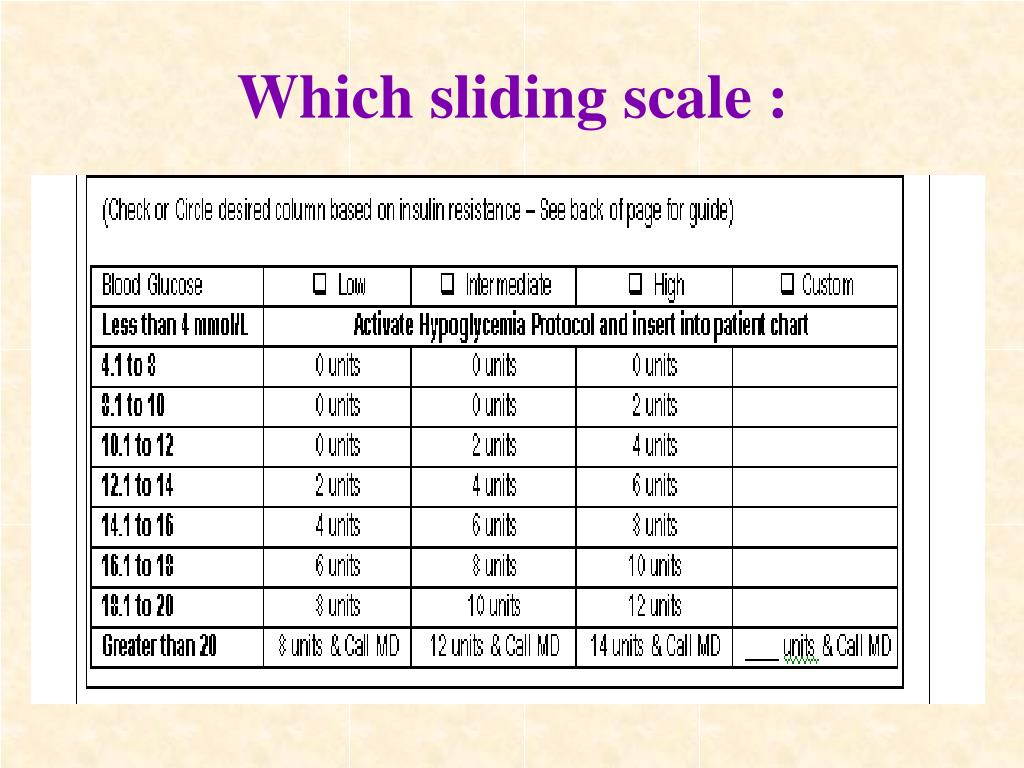
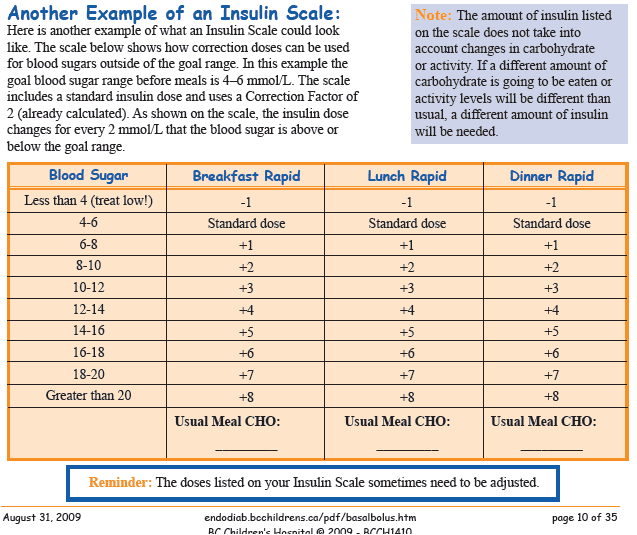
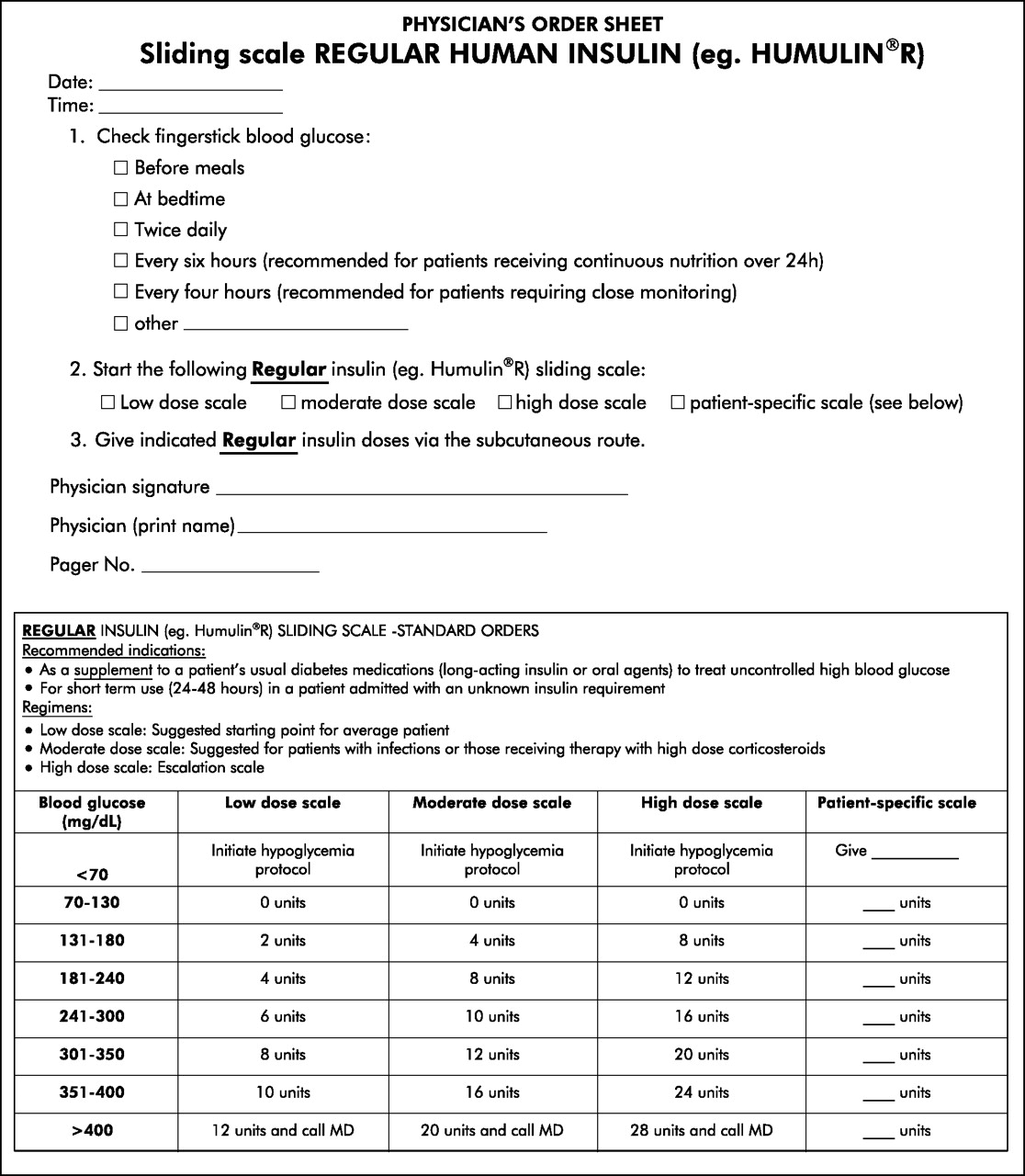
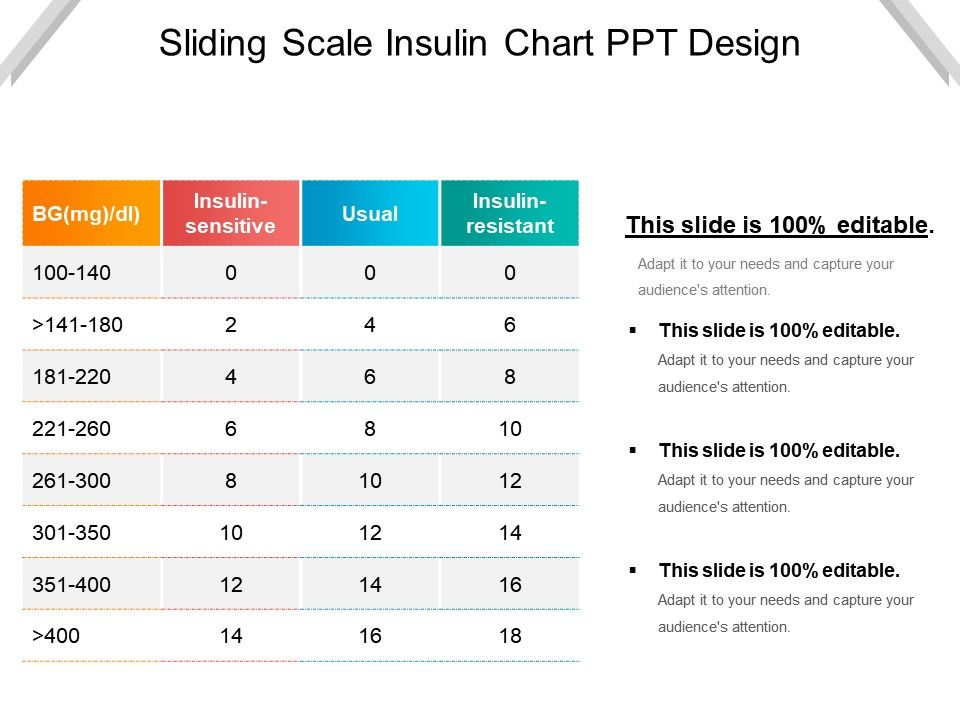
Hospital Sliding Scale Insulin Protocol Printable - Hypoglycemia management protocol should be adopted and implemented. Web sliding scale insulin regular guidelines. A recommended sliding scale is on the back of the nsw adult subcutaneous insulin prescribing chart. Less than/equal to 70 treat hypoglycemia per nursing protocol. Most importantly, patients with type 1. Web high dose sliding scale. Administer 12 units subcut, notify provider, and repeat poc blood sugar check in 30 minutes. Web sliding scale insulin therapy is one way a person with diabetes can work out how much insulin to take before a meal without causing negative effects on the body. Web correction only (sliding scale) insulin program. Web an insulin regimen with basal and correction components is necessary for all hospitalized patients with type 1 diabetes, with the addition of prandial insulin if the patient is eating. Therefore, ssi without basal insulin must be distinguished from ssi with basal and premeal bolus in cases where ssi is only used to combat breakthrough hyperglycemia. Basal insulin, prandial insulin, correction‐dose insulin, and sliding scale insulin (ssi). Continue to repeat 10 units subcut and poc blood sugar checks every 2 hour until blood glucose is less than 300 mg/dl. Web in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin may be used to augment therapy with oral glycemic medications or as insulin replacement therapy. Web four strategies are used to achieve glycaemic control in hospitalised diabetic people: Check patient’s blood sugar before meals, at bedtime, and as needed for symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. The main difference between these strategies is the intervention. Web the main goals in patients with diabetes needing hospitalization are to minimize disruption of the metabolic state, prevent adverse glycemic events (especially hypoglycemia), return the patient to a stable glycemic balance as quickly as possible, and ensure a smooth transition to outpatient care. Continue to repeat 10 units subcut and poc blood sugar checks every 90 minutes until blood glucose is less than 300 mg/dl. Continue to repeat 10 units subcut and poc blood sugar checks every 30 minutes until blood glucose is less than 300 mg/dl, then resume normal poc blood sugar check and insulin aspart sliding scale. Web sliding scale insulin therapy is one way a person with diabetes can work out how much insulin to take before a meal without causing negative effects on the body. Web sliding scale insulin regimens approximate daily insulin requirements. Therefore, ssi without basal insulin must be distinguished from ssi with basal and premeal bolus in cases where ssi is only used to combat breakthrough hyperglycemia. 0nce blood sugar is less than 300 mg/dl, repeat poc blood sugar in 4 hours, then resume normal Continue to repeat 10 units subcut and poc blood sugar checks every 2 hour until blood glucose is less than 300 mg/dl. The main difference between these strategies is the intervention. Web insulin aspart (high dose insulin aspart sliding scale) 0−14 units, subcut, inj, ac & nightly, prn glucose levels − see parameters blood glucose <70 and patient is symptomatic; Check patient’s blood sugar before meals, at bedtime, and as needed for symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Administer 14 units subcut, notify provider, and repeat poc blood sugar check in 90 minutes. Web sliding scale insulin regular guidelines. Web variable rate intravenous insulin infusion (vriii), formerly known as sliding scale has been used for decades to achieve normo glycaemia in hospitals. This medication has been associated with patient falls. Blood glucose (mg/dl) low dose: Web sliding scale insulin regimens approximate daily insulin requirements. If a patient is fasting, specify that the sliding scale is to be given “q6h”. Continue to repeat 10 units subcut and poc blood sugar checks every 90 minutes until blood glucose is less than 300 mg/dl. Greater than 351 20 units. D50w iv and recheck bgm in 30 minute. The american diabetes association suggests. Administer 14 units subcut, notify provider, and repeat poc blood sugar check in 90 minutes. Web four strategies are used to achieve glycaemic control in hospitalised diabetic people: Continue to repeat 10 units subcut and poc blood sugar checks every 2 hour until blood glucose is less than 300 mg/dl. 0nce blood sugar is less than 300 mg/dl, repeat poc blood sugar in 4 hours, then resume normal A recommended sliding scale is on the. No difference in outcomes was seen (umpierrez, 2007). It is a very useful tool when used in the right context and has been shown to improve outcomes. Web insulin aspart (high dose insulin aspart sliding scale) 0−14 units, subcut, inj, ac & nightly, prn glucose levels − see parameters blood glucose <70 and patient is symptomatic; Administer 14 units subcut,. Note insulin pens cost more than insulin vials. These strategies are used to maintain optimal glucose levels (fasting and postprandial). Web sliding scales are insulin lispro subcutaneous. The main difference between these strategies is the intervention. Therefore, ssi without basal insulin must be distinguished from ssi with basal and premeal bolus in cases where ssi is only used to combat. These strategies are used to maintain optimal glucose levels (fasting and postprandial). Basal insulin, prandial insulin, correction‐dose insulin, and sliding scale insulin (ssi). It is a very useful tool when used in the right context and has been shown to improve outcomes. Web consider insulin pen if able for patients with vision, dexterity or cognition difficulties or for patient convenience.. Administer 10 units subcut, notify provider, and repeat poc blood sugar check in 2 hour. Web sliding scale insulin regimens approximate daily insulin requirements. Web consider insulin pen if able for patients with vision, dexterity or cognition difficulties or for patient convenience. Hypoglycemia management protocol should be adopted and implemented. Blood glucose (mg/dl) low dose: Higher sliding scale doses may be required for those who are usually on large insulin. Therefore, the 2018 cpgs recommendations are: Web the main goals in patients with diabetes needing hospitalization are to minimize disruption of the metabolic state, prevent adverse glycemic events (especially hypoglycemia), return the patient to a stable glycemic balance as quickly as possible, and ensure a. 0nce blood sugar is less than 300 mg/dl, repeat poc blood sugar in 4 hours, then resume normal Continue to repeat 10 units subcut and poc blood sugar checks every 2 hour until blood glucose is less than 300 mg/dl. Less than/equal to 70 treat hypoglycemia per nursing protocol. Check patient’s blood sugar before meals, at bedtime, and as needed. Administer 12 units subcut, notify provider, and repeat poc blood sugar check in 30 minutes. These strategies are used to maintain optimal glucose levels (fasting and postprandial). If a patient is fasting, specify that the sliding scale is to be given “q6h” and not “before meals”. Web the sole use of sliding scale insulin in the inpatient hospital setting is. Hypoglycemia management protocol should be adopted and implemented. Web high dose sliding scale. Web in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin may be used to augment therapy with oral glycemic medications or as insulin replacement therapy. Initiate hypoglycemic protocol and call physician; Web sugar check and insulin aspart sliding scale. These strategies are used to maintain optimal glucose levels (fasting and postprandial). Web the main goals in patients with diabetes needing hospitalization are to minimize disruption of the metabolic state, prevent adverse glycemic events (especially hypoglycemia), return the patient to a stable glycemic balance as quickly as possible, and ensure a smooth transition to outpatient care. Administer 12 units subcut, notify provider, and repeat poc blood sugar check in 30 minutes. Web the sole use of sliding scale insulin in the inpatient hospital setting is strongly discouraged. A recommended sliding scale is on the back of the nsw adult subcutaneous insulin prescribing chart. Web correction only (sliding scale) insulin program. Higher sliding scale doses may be required for those who are usually on large insulin. Web chart supplemental insulin on a sliding scale. Check patient’s blood sugar before meals, at bedtime, and as needed for symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Web an insulin regimen with basal and correction components is necessary for all hospitalized patients with type 1 diabetes, with the addition of prandial insulin if the patient is eating. 2 purpose in an acute setting, the options for controlling blood glucose are limited.Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Download Printable PDF Templateroller
Printable Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Download
Printable Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Download
Printable Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Download
Printable Humalog Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Dosage
Printable Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Download
Printable Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Novolog
Use of a standardized protocol to decrease medication errors and
Printable Sliding Scale Insulin Chart Download
Humalog Kwikpen Printable Humalog Sliding Scale Insulin Char
Estimate The Total Daily Dose (Tdd) Of Insulin, Starting With 1 Unit Insulin For Every 10 Grams Of Carb.
Web Sliding Scales Are Insulin Lispro Subcutaneous.
These Goals Are Not Always Easy To Achieve.
Most Importantly, Patients With Type 1.
Related Post: