Postpartum Hemorrhage System Disorder Template
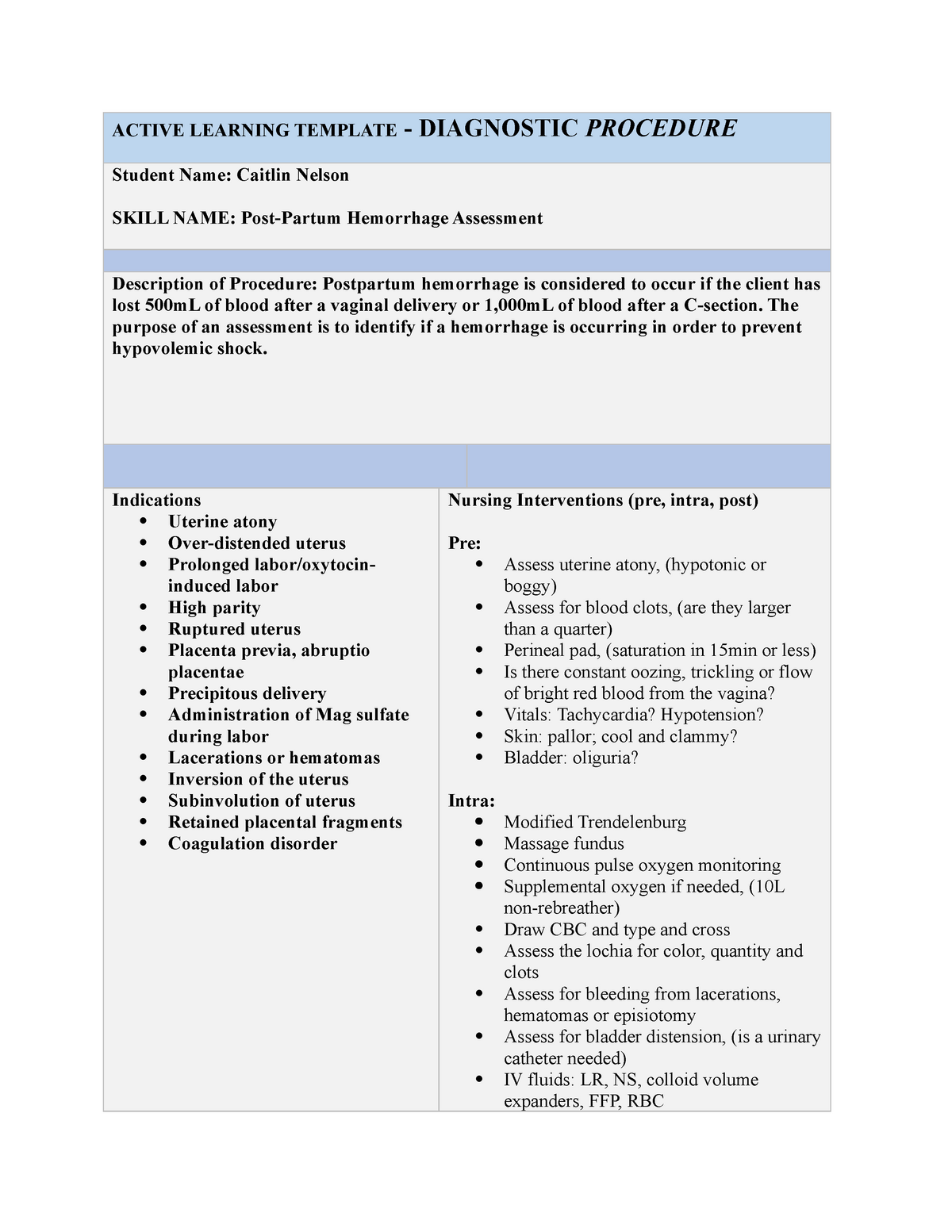
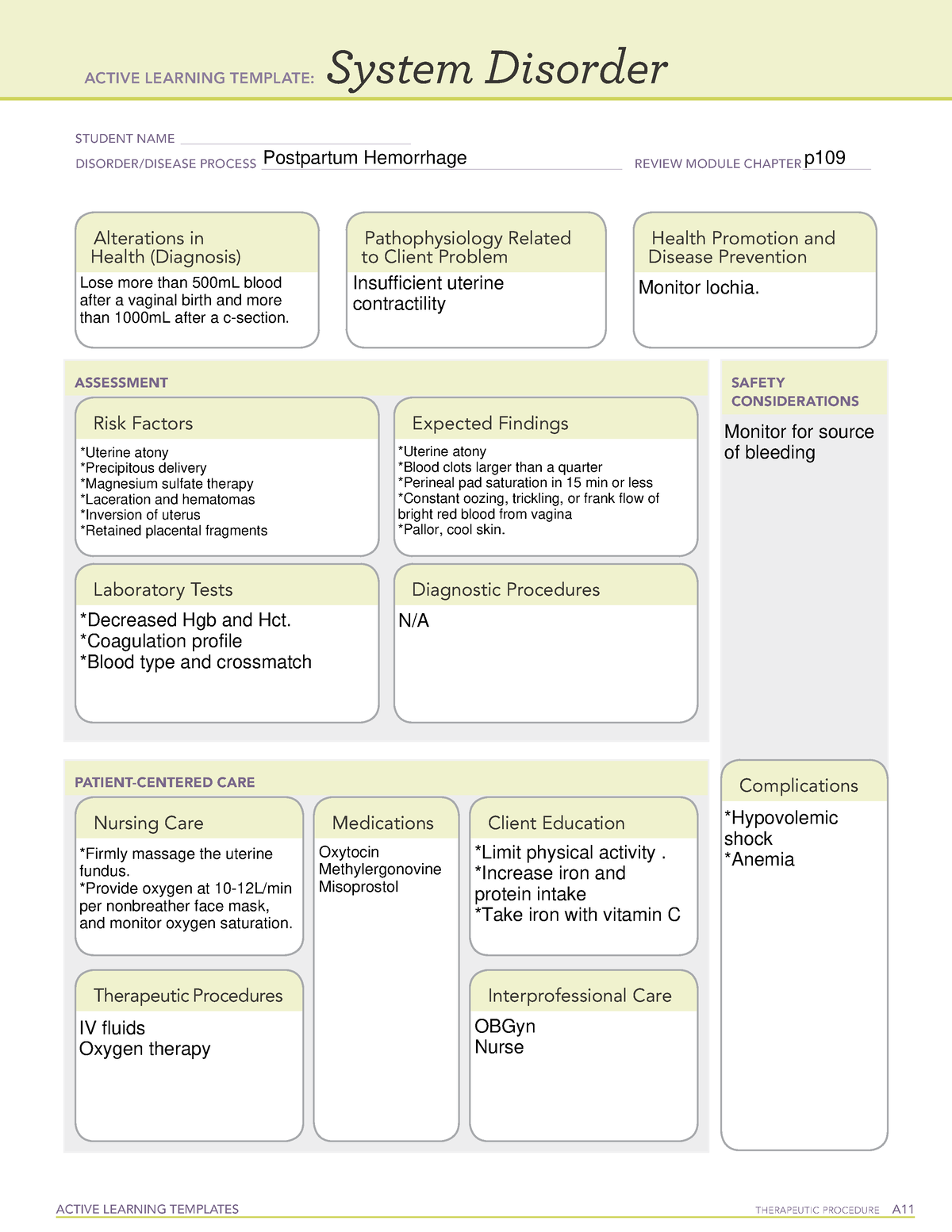
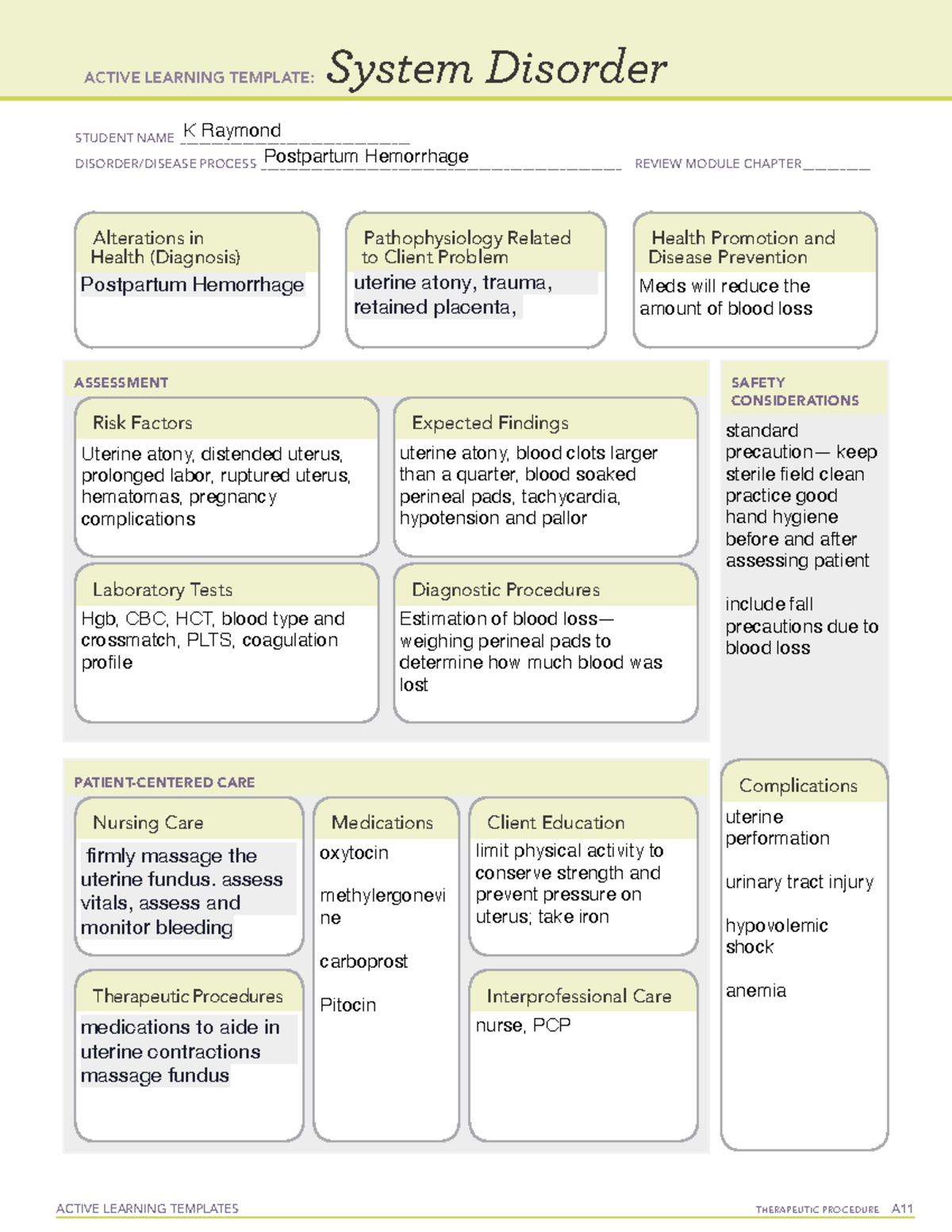
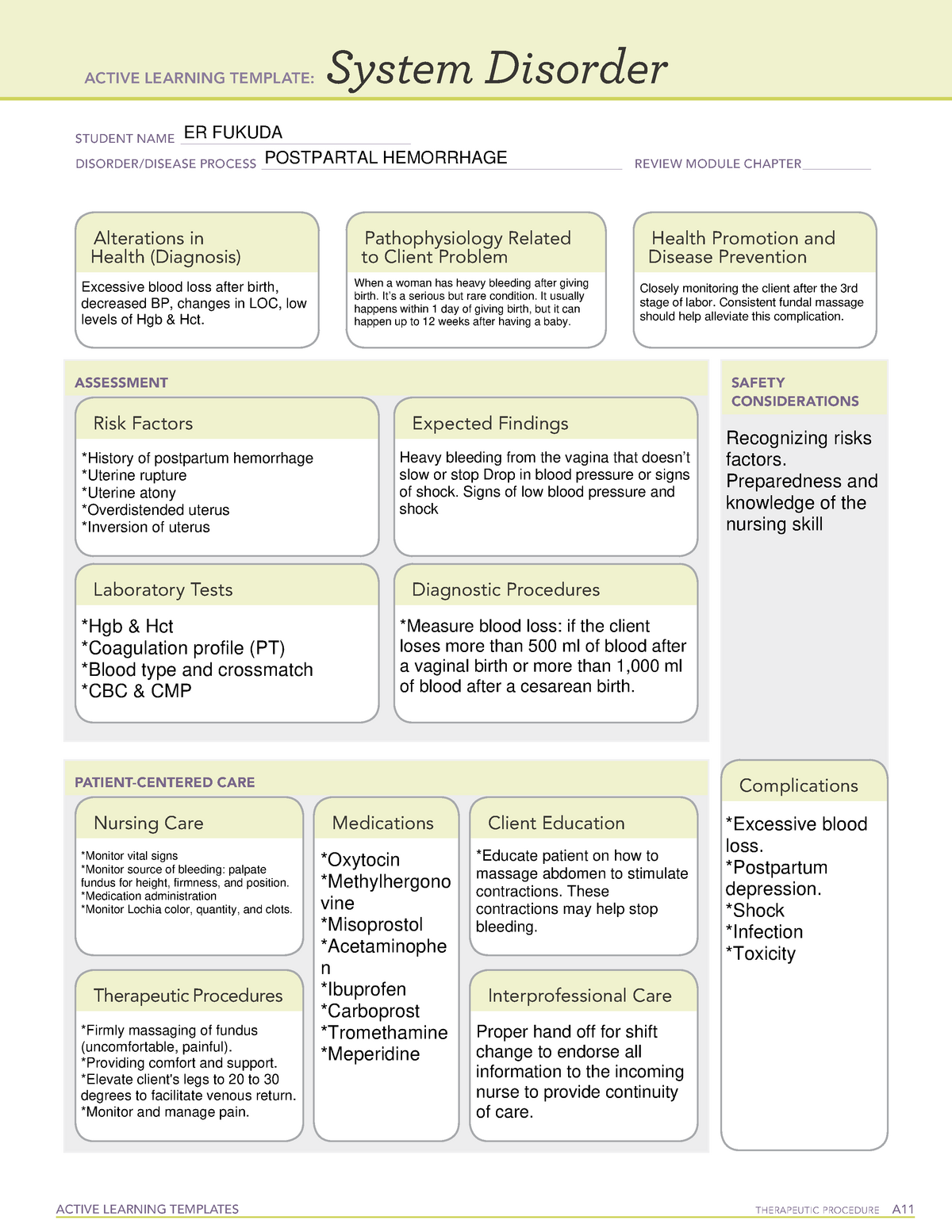
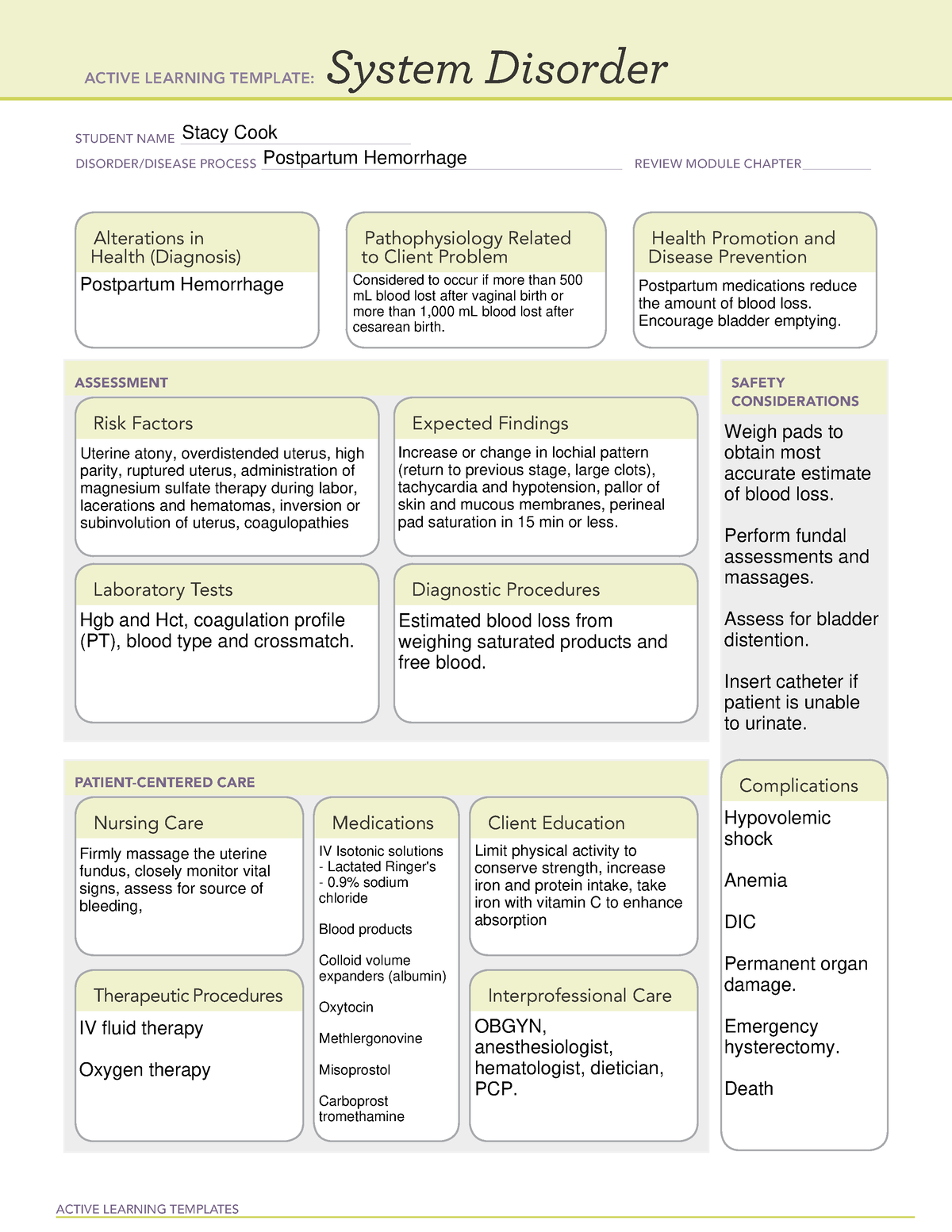
Postpartum Hemorrhage System Disorder Template - Web postpartum hemorrhage (pph) is an obstetric emergency. Uterine atony, overdistende uterus, prolonged labor, oxytocin induced labor, high parity, ruptured uterus, pregnancy complications, lacerations, hematomas. Web the four t's mnemonic can be used to identify and address the four most common causes of postpartum hemorrhage (uterine atony [tone]; Tone (uterine atony, by far the most frequent cause); Treatment depends on etiology of the hemorrhage. Web postpartum hemorrhage (pph) poses a significant risk to maternal health and is characterized by excessive blood loss after delivery. While uterine contractions and the coagulation cascade primarily regulate blood loss, pph can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Web the four ts mnemonic highlights the most common causes of pph: Uterine atony, trauma, retained placenta, Web postpartum hemorrhage ati template obpeds active learning template: Web postpartum haemorrhage (pph) is excessive blood loss that occurs within 24 hours of delivery (primary pph) or >24 hours and up to 12 weeks postpartum (secondary pph). Postpartum hemorrhage is blood loss of > 1000 ml or blood loss accompanied by symptoms or signs of hypovolemia within 24 hours after childbirth. Postpartum hemorrhage firmly massage the uterine fundus. Hgb, cbc, hct, blood type and crossmatch, plts, coagulation profile. Cross matching and blood typing is necessary to replace the blood loss. Uterine atony utilizing manikin in situ postpartum unit hemorrhage in situ labor and delivery unit hemorrhage. Risk stratification for postpartum hemorrhage optimizes care planning and promotes early adoption of preventive measures. Wall charts/job aids estimating blood loss: Estimation of blood loss— weighing perineal pads to determine how much blood was lost. Provide developmental and culturally appropriate education ensure that patient and support understand risks. Wall charts/job aids estimating blood loss: Uterine atony, overdistende uterus, prolonged labor, oxytocin induced labor, high parity, ruptured uterus, pregnancy complications, lacerations, hematomas. Tone (uterine atony), trauma (lacerations or uterine rupture), tissue. Laceration, hematoma, inversion, rupture [trauma]; Web postpartum haemorrhage (pph) is excessive blood loss that occurs within 24 hours of delivery (primary pph) or >24 hours and up to 12 weeks postpartum (secondary pph). System disorder student identifying risk factors for postpartum client: Tone (uterine atony, by far the most frequent cause); Web view postpartum hemorrhage system disorder ati template.pdf from nurs misc at indiana university, purdue university columbus. If the woman is experiencing respiratory distress, administration of oxygen at 4l/min via face mask could be prescribed by the physician. Uterine atony, blood clots larger then a quarter, perineal pad saturation in 15 min or less, tachycardia, hypotension, pallor. Web k raymond postpartum hemorrhage. Uterine atony, overdistende uterus, prolonged labor, oxytocin induced labor, high parity, ruptured uterus, pregnancy complications, lacerations, hematomas. Web view postpartum_hemorrhage.pdf from nur 544 at stony brook university. Nurse staff, midwives, obgyns, anesthesia providers. Risk stratification for postpartum hemorrhage optimizes care planning and promotes early adoption of preventive measures. System disorder postpartum hemorrhage disorder/disease process _ review module chapter _ alterations. Nurse staff, midwives, obgyns, anesthesia providers. Estimation of blood loss— weighing perineal pads to determine how much blood was lost. Web k raymond postpartum hemorrhage. Uterine atony, trauma, retained placenta, Web postpartum hemorrhage is considered to be primary when it occurs within the first 24 hours after delivery and secondary when it occurs between 24 hours and up to 12 weeks after delivery. Web k raymond postpartum hemorrhage. Cross matching and blood typing is necessary to replace the blood loss. Tone (uterine atony, by far the most frequent cause); Quantitative. Postpartum hemorrhage is blood loss of > 1000 ml or blood loss accompanied by symptoms or signs of hypovolemia within 24 hours after childbirth. Web the four t's mnemonic can be used to identify and address the four most common causes of postpartum hemorrhage (uterine atony [tone]; Web the four ts mnemonic highlights the most common causes of pph: Treatment. Tone (uterine atony), trauma (lacerations or uterine rupture), tissue. Hgb, cbc, hct, blood type and crossmatch, plts, coagulation profile. While uterine contractions and the coagulation cascade primarily regulate blood loss, pph can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Web the main causes of postpartum hemorrhage are uterine atony, birth canal trauma, retention of placental remains and coagulation disorders. 10,. System disorder student name_ postpartum hemorrhage 20 disorder/disease. Web postpartum hemorrhage is considered to be primary when it occurs within the first 24 hours after delivery and secondary when it occurs between 24 hours and up to 12 weeks after delivery. While uterine contractions and the coagulation cascade primarily regulate blood loss, pph can lead to severe complications if left. System disorder taleiah jones student name_ postpartum. System disorder kathryn di maggio student name _ postpartum hemorrhage disorder/disease process Uterine atony, overdistende uterus, prolonged labor, oxytocin induced labor, high parity, ruptured uterus, pregnancy complications, lacerations, hematomas. Web postpartum hemorrhage (pph) poses a significant risk to maternal health and is characterized by excessive blood loss after delivery. Quantitative definitions of primary. Trauma (obstetric lacerations/expanding hematomas/uterine rupture); Web postpartum haemorrhage is a major cause of death during pregnancy and early motherhood, accounting for 25% of maternal deaths worldwide, 1 and is the second leading direct cause of maternal deaths in the uk. 2 it is defined as blood loss of more than 500 ml from the female genital tract after delivery of. Tone (uterine atony, by far the most frequent cause); System disorder taleiah jones student name_ postpartum. It offers a visual reference for estimating how much blood a patient has lost. Web clinical and community action to address postpartum hemorrhage model. Hgb, cbc, hct, blood type and crossmatch, plts, coagulation profile. Web the four ts mnemonic highlights the most common causes of pph: Web view postpartum_hemorrhage.pdf from nur 544 at stony brook university. Tone (uterine atony, by far the most frequent cause); Postpartum hemorrhage is blood loss of > 1000 ml or blood loss accompanied by symptoms or signs of hypovolemia within 24 hours after childbirth. Web clinical and community action. If this is to be achieved, maternal deaths related to postpartum haemorrhage (pph) must be. Web management of third stage of labor to prevent hemorrhage. If the woman is experiencing respiratory distress, administration of oxygen at 4l/min via face mask could be prescribed by the physician. While uterine contractions and the coagulation cascade primarily regulate blood loss, pph can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Trauma (obstetric lacerations/expanding hematomas/uterine rupture); Hgb, cbc, hct, blood type and crossmatch, plts, coagulation profile. Tissue (retained products of conception or placenta accreta spectrum disorders); Cross matching and blood typing is necessary to replace the blood loss. Monitor patient and advise support persons to call if any abnormal changes. 10, 12 the causes of postpartum hemorrhage can be summarized by the four “t’s”: Web k raymond postpartum hemorrhage. Provide developmental and culturally appropriate education ensure that patient and support understand risks. Assess vitals, assess and monitor bleeding. And thrombin (acquired or inherited coagulopathy). Web the four ts mnemonic highlights the most common causes of pph: System disorder student identifying risk factors for postpartum client:Ati System Disorder Template Postpartum Hemorrhage Printable Blog
Ati System Disorder Template Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum Hemorrhage System Disorder Template
ATI template Postpartum Hemorrhage ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
Postpartum Hemorrhage System Disorder Template
System disorder postpartum hemorrhage ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
Postpartum Hemorrhage System Disorder Template prntbl
Postpartum Hemorrhage System Disorder Template
Ati System Disorder Template Postpartum Hemorrhage
ATI Postpartum hemorrhage ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES System
Web Postpartum Hemorrhage (Pph) Poses A Significant Risk To Maternal Health And Is Characterized By Excessive Blood Loss After Delivery.
Uterine Atony, Trauma, Retained Placenta,
System Disorder Taleiah Jones Student Name_ Postpartum.
Web Three Sample Postpartum Hemorrhage Scenarios Are Presented In This Document:
Related Post: