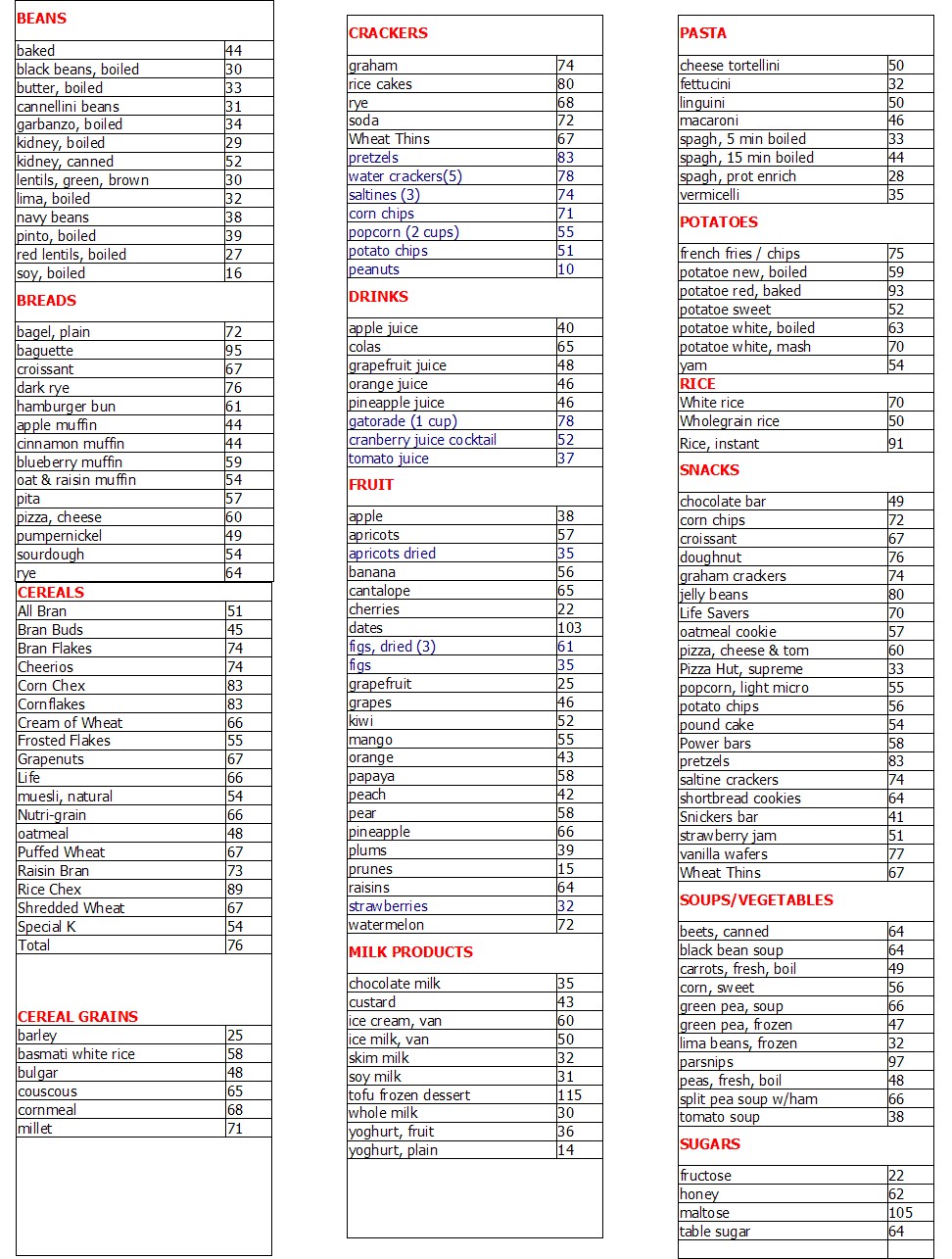
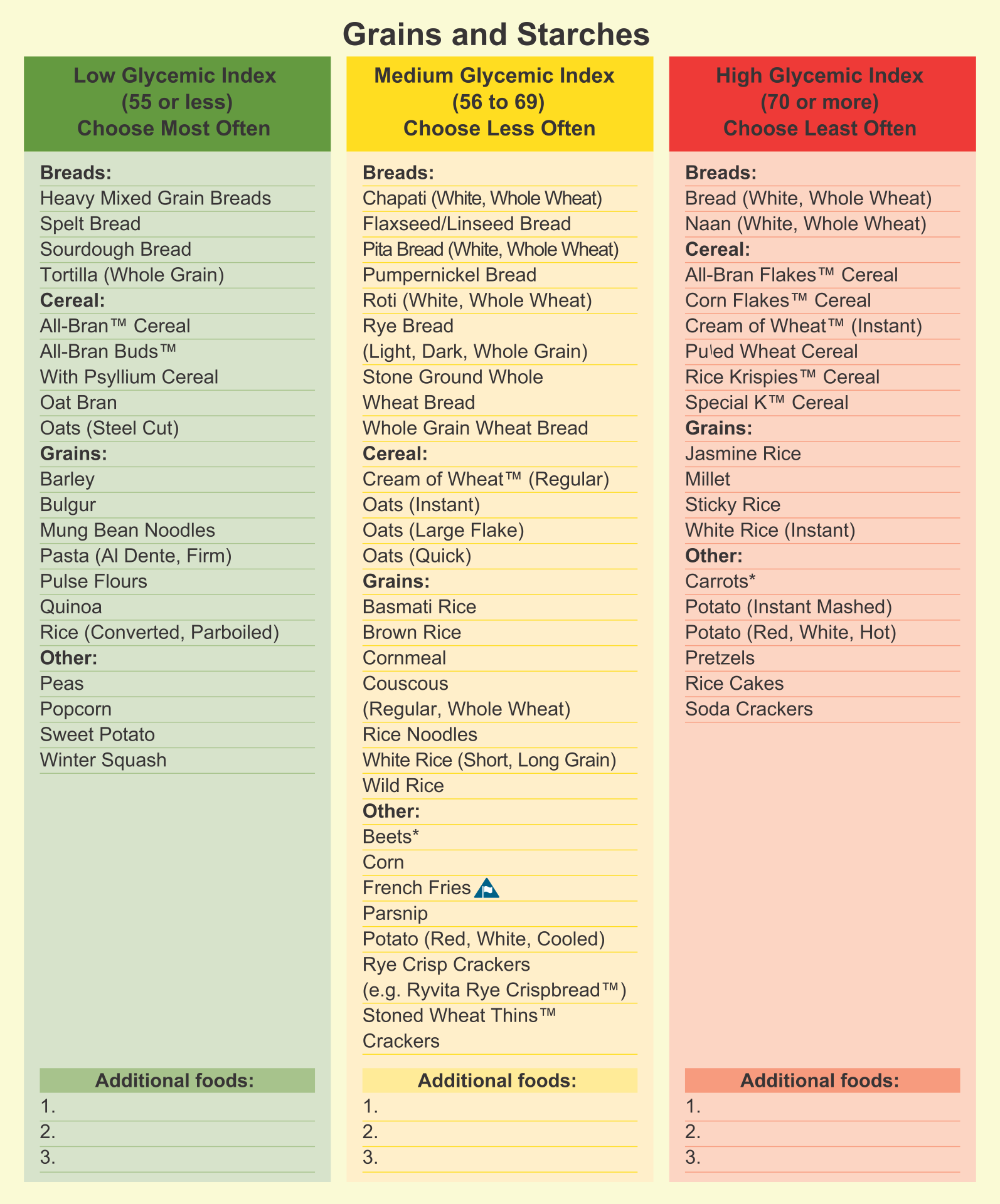
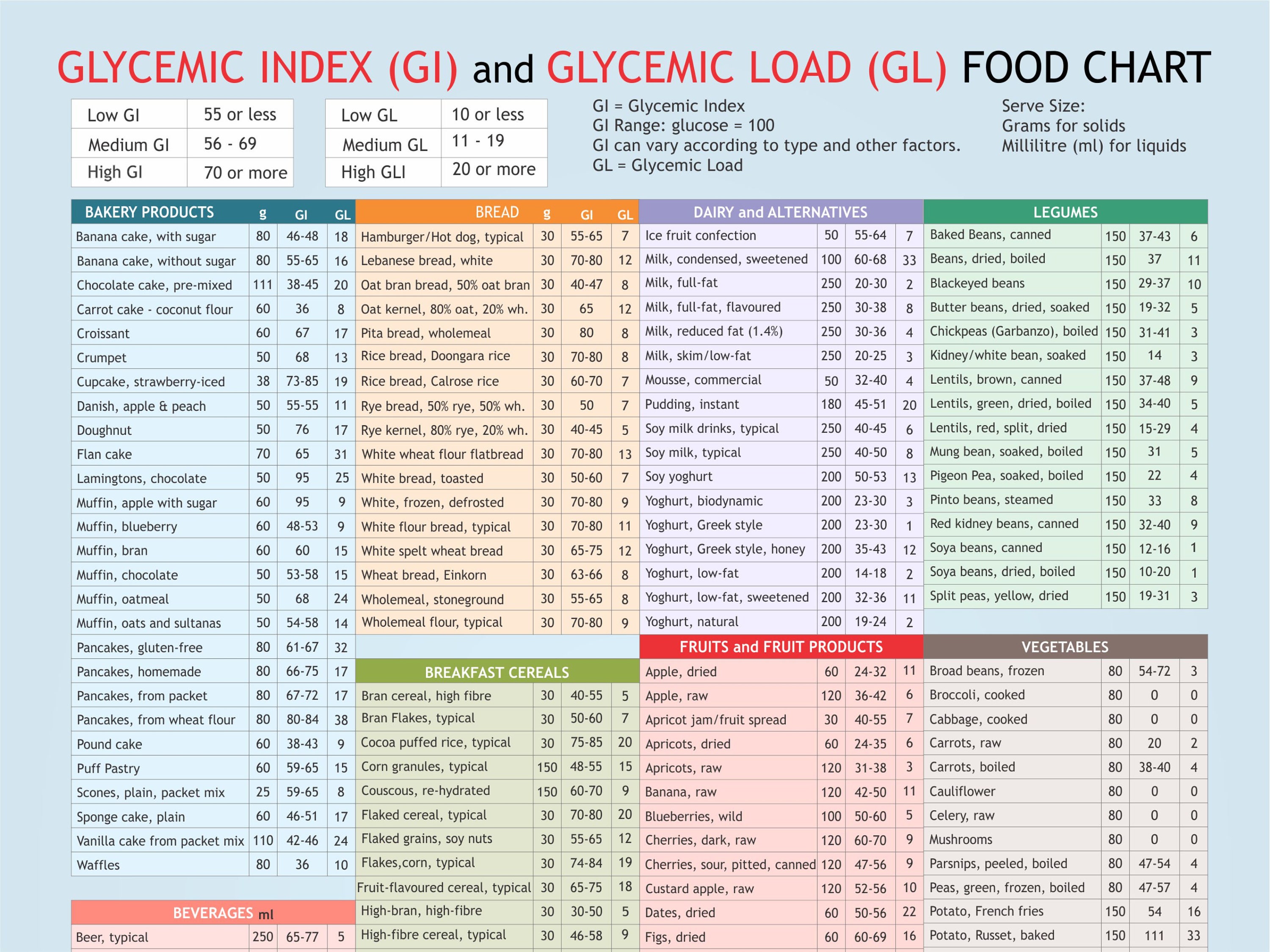
Printable Glycemic Index Food Chart
Printable Glycemic Index Food Chart - This article explains the glycemic index and how it works. Understanding the gi values of specific foods can help reduce harmful spikes in blood sugar, as sugars and carbohydrates are broken down and your metabolism releases insulin to aid in digestion. “the glycemic index is used to classify foods that contain carbohydrates, their potential for raising blood sugar and how quickly they raise your blood sugar,” says endocrinologist alexander williams, md. Web to help you understand how the foods you are eating might impact your blood glucose level, here is an abbreviated chart of the glycemic index and glycemic load, per serving, for more than 100 common foods. The glycemic index of a food refers to the effect the food has on the body’s blood sugar levels. Web learn more about the glycemic index, which foods tend to cause a spike in blood sugar (or not) and the limitations of this measurement. Web the glycemic index classifies foods that contain carbohydrates according to their potential to raise blood sugar. Gi chart for 600+ common foods that is updated constantly. A low gi is a sign of better quality. Foods with a high gi increase blood sugar higher and faster than foods with a low gi. Web the best choices are fresh, frozen and canned vegetables and vegetable juices without added salt (sodium), fat or sugar such as: Blood sugar levels are raised after a person eats foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and starches). Web the glycemic index (gi) is a measure of how fast a food raises the blood sugar level. A low gi is a sign of better quality. Foods with a higher gi value are more likely to spike your blood sugar than foods with a lower gi. Eating foods with a lower gi may result in a more gradual rise in your blood sugar level. Web the glycemic index, or gi, uses a scale of numbers from 1 to 100 to rank carbohydrate foods by how quickly a serving size of each raises blood sugar. Folks trying to manage blood sugar, lose weight, or just aiming for a healthier diet often find navigating food choices tricky. High glycemic foods result in a quick spike in insulin and blood sugar (also known as blood glucose). This article explains the glycemic index and how it works. Low glycemic foods slow down sugar absorption, helping in maintaining stable glucose levels. Foods with a high gi increase blood sugar higher and faster than foods with a low gi. Web glycemic index chart. Understanding the gi values of specific foods can help reduce harmful spikes in blood sugar, as sugars and carbohydrates are broken down and your metabolism releases insulin to aid in digestion. Eating foods with a lower gi may result in a more gradual rise in your blood sugar level. Web the glycemic index, or gi, uses a scale of numbers from 1 to 100 to rank carbohydrate foods by how quickly a serving size of each raises blood sugar. Blood sugar levels are raised after a person eats foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and starches). A low gi is a sign of better quality. They are grouped according to range and food type. Work with your registered dietitian to find ways to substitute high gi foods for foods in the medium and/or low gi category. Work with your registered dietitian to find ways to substitute high gi foods for foods in the medium and/or low gi category. The glycemic index (gi) is a measure of the effect carbohydrates have on blood glucose levels. Web the glycemic index (gi) chart for carbohydrates fruits: Web the glycemic index charts below lists common foods followed by their serving. Low glycemic foods have a slower, smaller effect. Web the glycemic index classifies foods that contain carbohydrates according to their potential to raise blood sugar. “the glycemic index is used to classify foods that contain carbohydrates, their potential for raising blood sugar and how quickly they raise your blood sugar,” says endocrinologist alexander williams, md. Complete up to date table. We have put together a glycemic index food chart. Gi chart for 600+ common foods that is updated constantly. Web below you will find a printable glycemic index chart in pdf format, featuring over 100 different foods and their corresponding gi values. Web the glycemic index charts below lists common foods followed by their serving size and glycemic index number,. The glycemic index of a food refers to the effect the food has on the body’s blood sugar levels. High glycemic foods result in a quick spike in insulin and blood sugar (also known as blood glucose). Foods with a higher gi value are more likely to spike your blood sugar than foods with a lower gi. The glycemic index. One way of looking at a healthy diet is considering where foods fall on the glycemic index. Low glycemic foods slow down sugar absorption, helping in maintaining stable glucose levels. Foods are categorized as low gi (55 or less), medium gi (56 to 69) and high gi (70 or more). Web learn more about the glycemic index, which foods tend. This article explains the glycemic index and how it works. A low gi is a sign of better quality. Web glycemic index chart. Web below you will find a printable glycemic index chart in pdf format, featuring over 100 different foods and their corresponding gi values. We have put together a glycemic index food chart. Web glycemic index chart. Web below you will find a printable glycemic index chart in pdf format, featuring over 100 different foods and their corresponding gi values. Web the glycemic index chart below uses a scale of 1 to 100 for glycemic index and 1 to 50 for glycemic load values, glucose having the highest gi value of 100 and. Low glycemic foods have a slower, smaller effect. We have put together a glycemic index food chart. Foods with a high gi increase blood sugar higher and faster than foods with a low gi. Work with your registered dietitian to find ways to substitute high gi foods for foods in the medium and/or low gi category. High glycemic foods result. Eating foods with a lower gi may result in a more gradual rise in your blood sugar level. The glycemic index (gi) is a measure of the effect carbohydrates have on blood glucose levels. High glycemic foods result in a quick spike in insulin and blood sugar (also known as blood glucose). Web learn more about the glycemic index, which. High glycemic foods result in a quick spike in insulin and blood sugar (also known as blood glucose). Foods with a high gi increase blood sugar higher and faster than foods with a low gi. It is a sign of the quality of carbohydrates in the food. Web learn more about the glycemic index, which foods tend to cause a. High glycemic foods result in a quick spike in insulin and blood sugar (also known as blood glucose). Low glycemic foods have a slower, smaller effect. Web the glycemic index classifies foods that contain carbohydrates according to their potential to raise blood sugar. Eating foods with a lower gi may result in a more gradual rise in your blood sugar level. They are grouped according to range and food type. Web the glycemic index charts below lists common foods followed by their serving size and glycemic index number, according to the gi database compiled by the university of sydney and cited by the usda. Web learn more about the glycemic index, which foods tend to cause a spike in blood sugar (or not) and the limitations of this measurement. One way of looking at a healthy diet is considering where foods fall on the glycemic index. Web below you will find a printable glycemic index chart in pdf format, featuring over 100 different foods and their corresponding gi values. For instance a food with a glycemic index of 30 doesn’t raise the blood glucose that much at all , but gi doesn’t consider how big the serving size is or how much you eat. Because carbohydrates, or carbs, such as rice, pasta, bread, and fruit, raise blood sugar more, and more quickly, than fats or proteins do. Understanding the gi values of specific foods can help reduce harmful spikes in blood sugar, as sugars and carbohydrates are broken down and your metabolism releases insulin to aid in digestion. Web this page provides a comprehensive gi index chart and their corresponding glycemic index and glycemic load values for easy reference. Web the glycemic index (gi) chart for carbohydrates fruits: Blood sugar levels are raised after a person eats foods containing carbohydrates (sugars and starches). “the glycemic index is used to classify foods that contain carbohydrates, their potential for raising blood sugar and how quickly they raise your blood sugar,” says endocrinologist alexander williams, md.Printable Pdf Printable Glycemic Index Chart
Full Glycemic Index Food List Printable Chart
Printable Glycemic Index Food Chart
Full Glycemic Index Food List Printable Chart
Glycemic Index Chart 6 Free Templates in PDF, Word, Excel Download
Full Glycemic Index Food List Printable Chart
Full Glycemic Index Food List Printable Chart
Free Printable Glycemic Index Food Chart
Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load, Food List Chart, Printable Planner
List Of Glycemic Index Foods Printable
Web What Is Glycemic Index?
Web The Glycemic Index Is A Great Measure Of How Much A Certain Food Will Effect Your Insulin Levels.
Web Glycemic Index Chart.
Web The Glycemic Index, Or Gi, Uses A Scale Of Numbers From 1 To 100 To Rank Carbohydrate Foods By How Quickly A Serving Size Of Each Raises Blood Sugar.
Related Post: