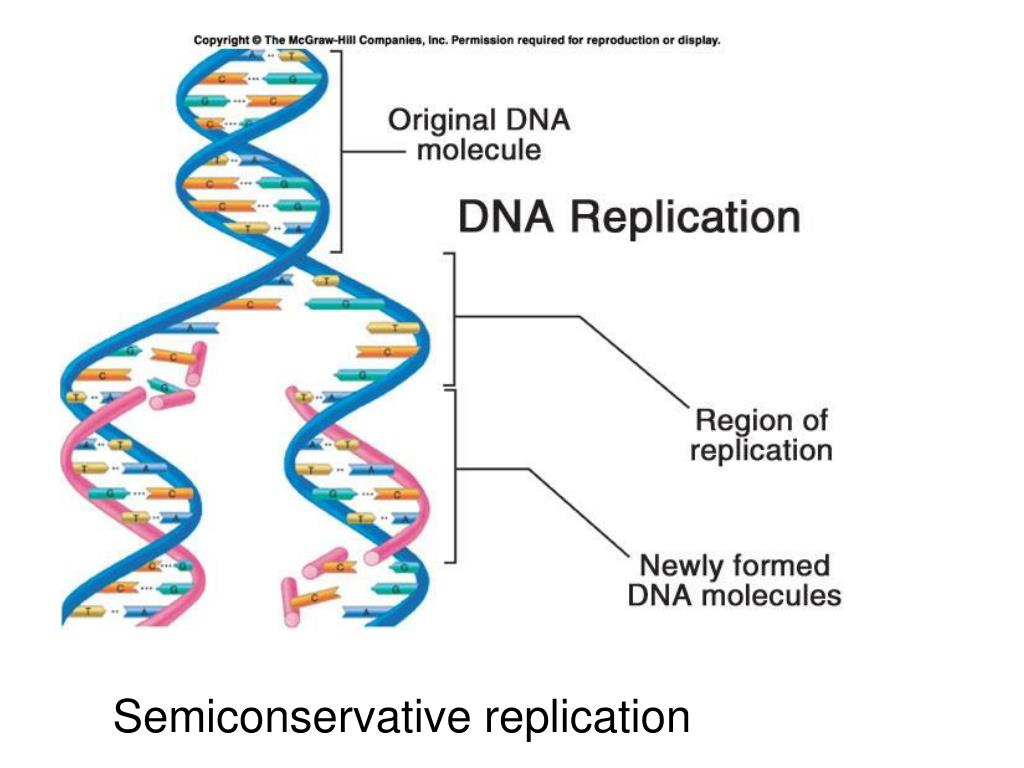
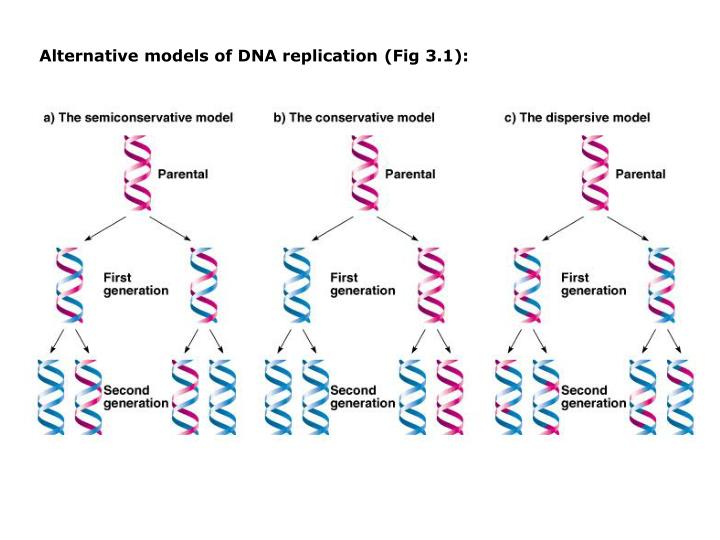
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template What Is The Template
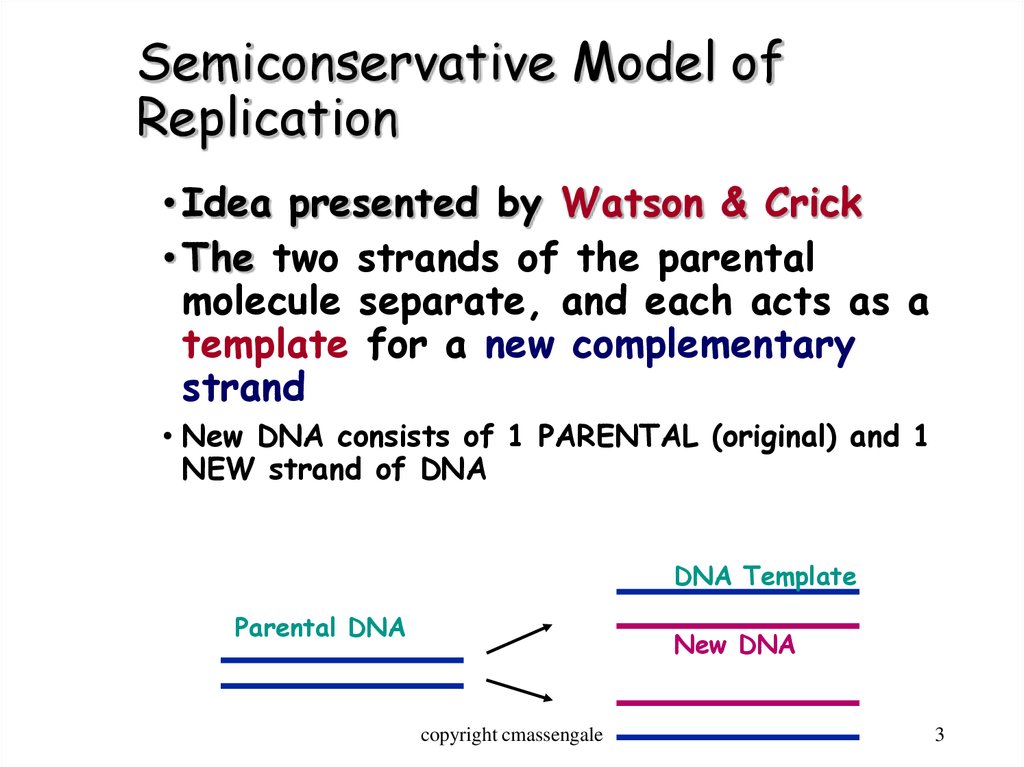
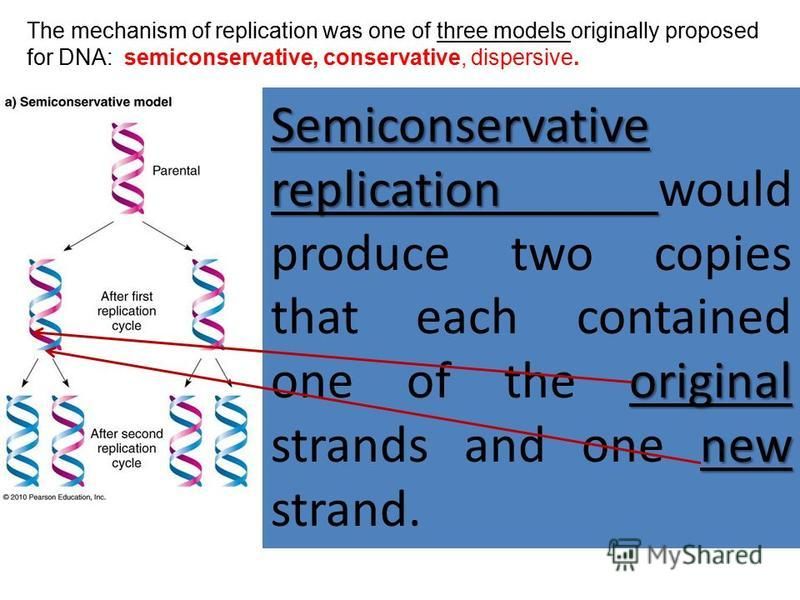
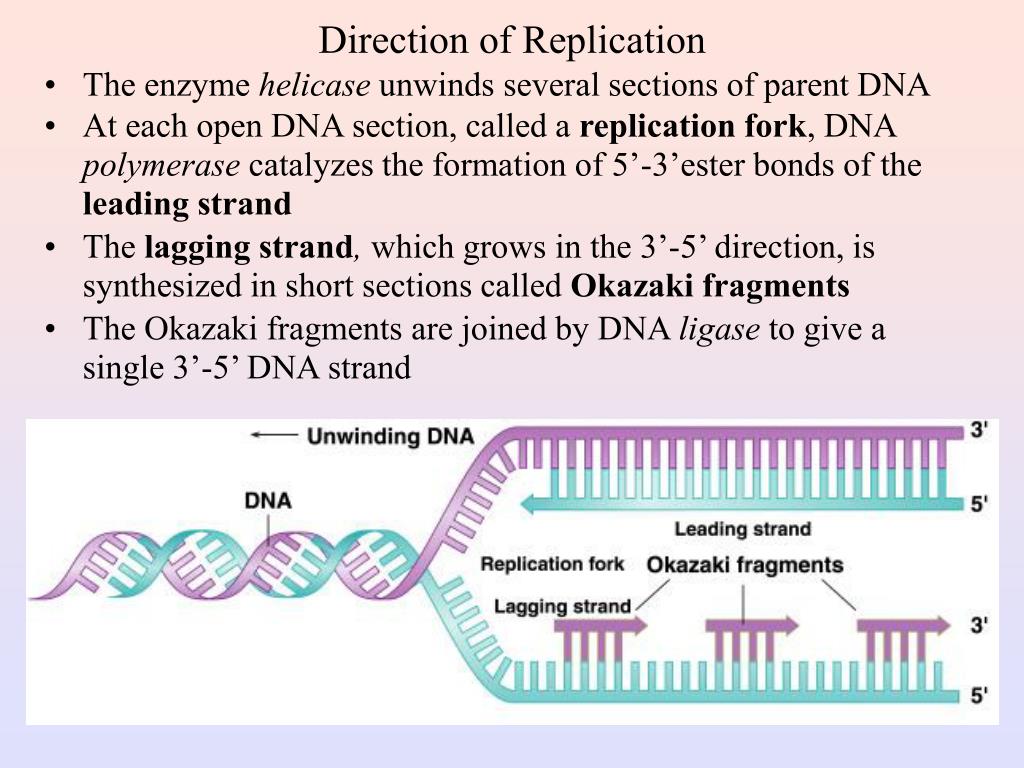
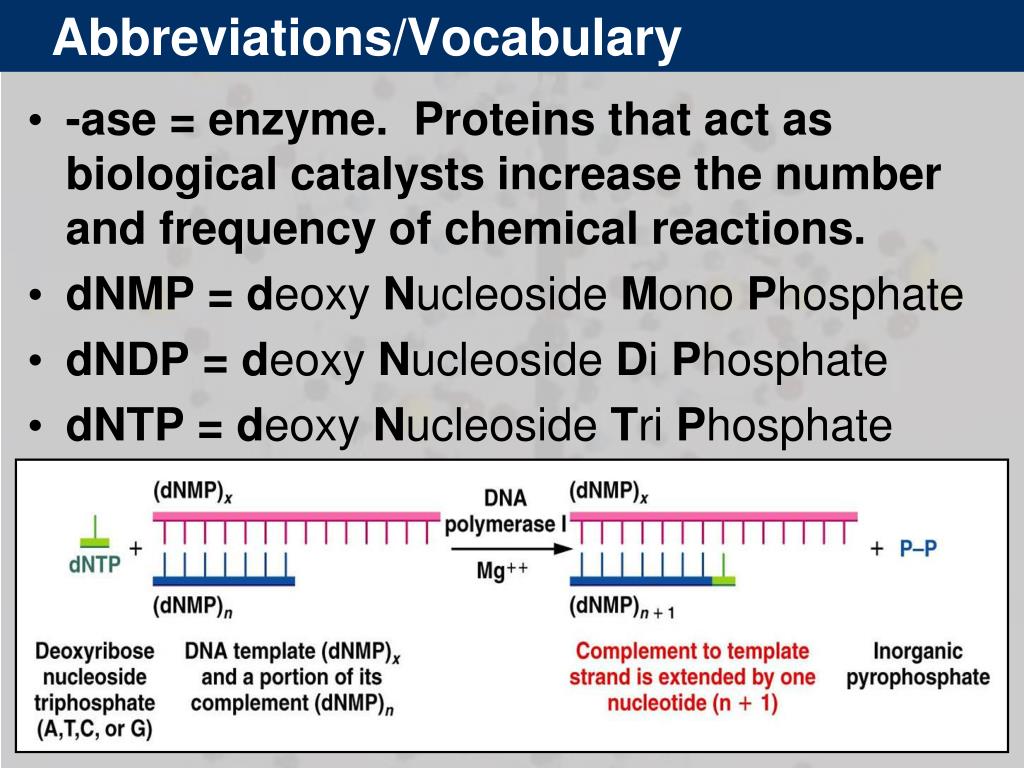
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template What Is The Template - The semiconservative model of dna replication is shown. Prokaryotic replication does not require a primer. Dna polymerase contains the template needed. Web in semiconservative replication, the 'template' refers to one strand of the dna molecule. This results in the formation of two identical copies of the original double stranded molecule. Web in semiconservative replication, the double helix splits into two separate strands. As discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. Single stranded binding proteins dna polymerase one strand of the dna molecule an rna molecule. During dna replication, a double stranded dna molecule separate, and each strand is used as a template for the synthesis of a new strand. What is the template?, what joins dna segments into a continuous strand?, after dna replication is completed and more. What is the template?, what is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in dna replication?, what is a major difference between eukaryotic dna replication and prokaryotic dna replication?. Web in semiconservative replication, the 'template' refers to one strand of the dna molecule. Prokaryotic replication does not require a primer. This is called semiconservative replication since one old strand of dna is paired with one new strand to produce the daughter dna molecule. Web according to the semiconservative replication model, which is illustrated in figure 1, the two original dna strands (i.e., the two complementary halves of the double helix) separate during. What is the template?, what joins dna segments into a continuous strand?, after dna replication is completed and more. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like semiconservative replication involves a template. Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of. Web semiconservative replication involves a template. Your solution’s ready to go! Web our community brings together students, educators, and subject enthusiasts in an online study community. During dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. One strand of the dna molecule This strand serves as a pattern for creating a new, complementary dna strand, resulting in two dna molecules, each with one original and one new strand. What is the template?, what is the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in dna replication?, what is a major difference between eukaryotic dna replication and prokaryotic dna replication?. What is a dna template? Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like semiconservative replication involves a template. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like question semiconservative replication involves a template. Web according to the semiconservative replication model, which is illustrated in figure 1, the two original dna strands (i.e., the two complementary halves of the double helix) separate during. Dna replication occurs on multiple origins of replication along the dna template strands. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like semiconservative replication involves a template. Semiconservative replication involves a dna template. This strand serves as a pattern for creating a new, complementary dna strand, resulting in two dna molecules, each with one original and one new strand. What is a dna template? What is the template?, what is a major. Prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of. Web according to the semiconservative replication model, which is illustrated in figure 1, the two original dna strands (i.e., the two complementary halves of the double helix) separate during. This strand serves as a pattern for creating a new, complementary dna strand, resulting in two dna molecules, each with one original and one. Web dna replication occurs by synthesizing new strands of dna using existing strands as a template. Web according to the semiconservative replication model, which is illustrated in figure 1, the two original dna strands (i.e., the two complementary halves of the double helix) separate during. Web in one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during. The two new double helices each contain an original template strand and a newly synthesized daughter strand, which is why this process is. This is called semiconservative replication since one old strand of dna is paired with one new strand to produce the daughter dna molecule. What is the template?, what joins dna segments into a continuous strand?, after dna. Single stranded binding proteins dna polymerase one strand of the dna molecule an rna molecule. What is the template?, what is a major difference between eukaryotic dna replication and prokaryotic dna replication? Gray indicates the original dna strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized dna. Dna polymerase contains the template needed. During the replication process, an entirely new strand of dna. What is the template?, what joins dna segments into a continuous strand?, after dna replication is completed and more. Web in one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during dna replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. What is a dna template? Prokaryotic replication does not. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like question semiconservative replication involves a template. This strand serves as a pattern for creating a new, complementary dna strand, resulting in two dna molecules, each with one original and one new strand. This is called semiconservative replication since one old strand of dna is paired with one new strand to. Web semiconservative replication involves a template. Dna polymerase contains the template needed. Web in semiconservative replication, the 'template' refers to one strand of the dna molecule. Web in one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during dna replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. This strand. Web in conservative replication, the parental dna remains together, and the newly formed daughter strands are together. Your solution’s ready to go! Web our community brings together students, educators, and subject enthusiasts in an online study community. Web in one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during dna replication, and each strand serves as a. Web in one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during dna replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Your solution’s ready to go! During dna replication, a double stranded dna molecule separate, and each strand is used as a template for the synthesis of a new. What is a dna template? What is the template?, what is a major difference between eukaryotic dna replication and prokaryotic dna replication? What is the template?, what joins dna segments into a continuous strand?, after dna replication is completed and more. Single stranded binding proteins dna polymerase one strand of the dna molecule an rna molecule. Web in conservative replication, the parental dna remains together, and the newly formed daughter strands are together. The semiconservative model of dna replication is shown. Dna polymerase contains the template needed. This strand serves as a pattern for creating a new, complementary dna strand, resulting in two dna molecules, each with one original and one new strand. Semiconservative replication involves a dna template. Web in one model, semiconservative replication, the two strands of the double helix separate during dna replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied; Web our community brings together students, educators, and subject enthusiasts in an online study community. All dna molecules in all organisms replicate. Gray indicates the original dna strands, and blue indicates newly synthesized dna. The two new double helices each contain an original template strand and a newly synthesized daughter strand, which is why this process is. Your solution’s ready to go! This is called semiconservative replication since one old strand of dna is paired with one new strand to produce the daughter dna molecule.Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template. What Is The Template
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template What Is The Template
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template. What Is The Template
SOLVED Semiconservative replication involves a template. What is the
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template. What Is The Template
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template What Is The Template
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template. What Is The Template
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template. What Is The Template
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template. What Is The Template
Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template What Is The Template
During Dna Replication, A Double Stranded Dna Molecule Separate, And Each Strand Is Used As A Template For The Synthesis Of A New Strand.
Prokaryotic Chromosomes Have A Single Origin Of.
Web Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Question Semiconservative Replication Involves A Template.
What Is The Template?, What Is The Difference Between The Leading Strand And The Lagging Strand In Dna Replication?, What Is A Major Difference Between Eukaryotic Dna Replication And Prokaryotic Dna Replication?.
Related Post: