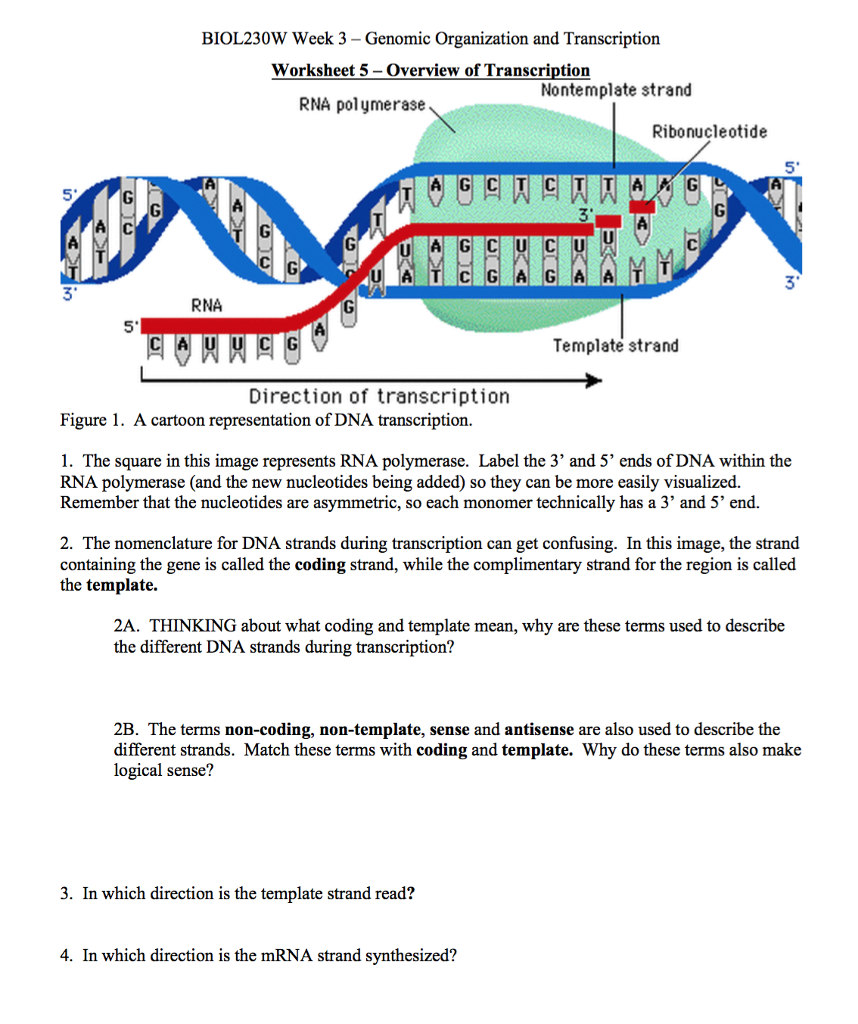
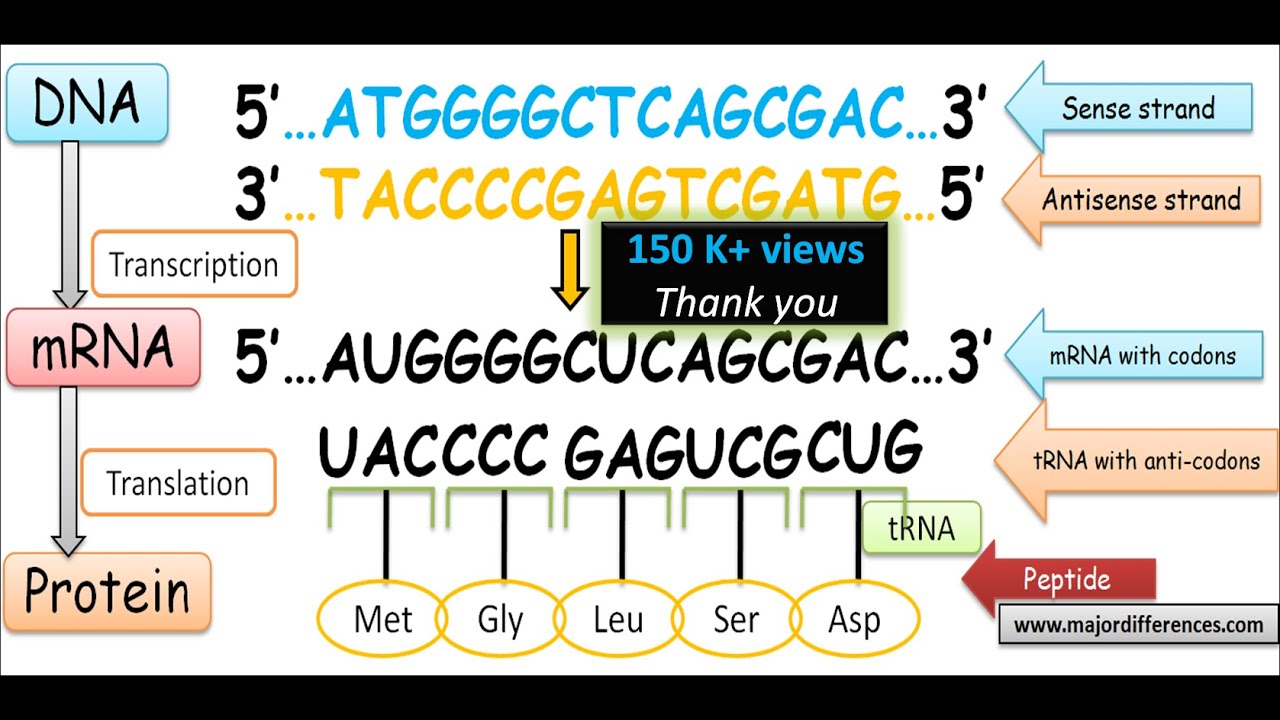
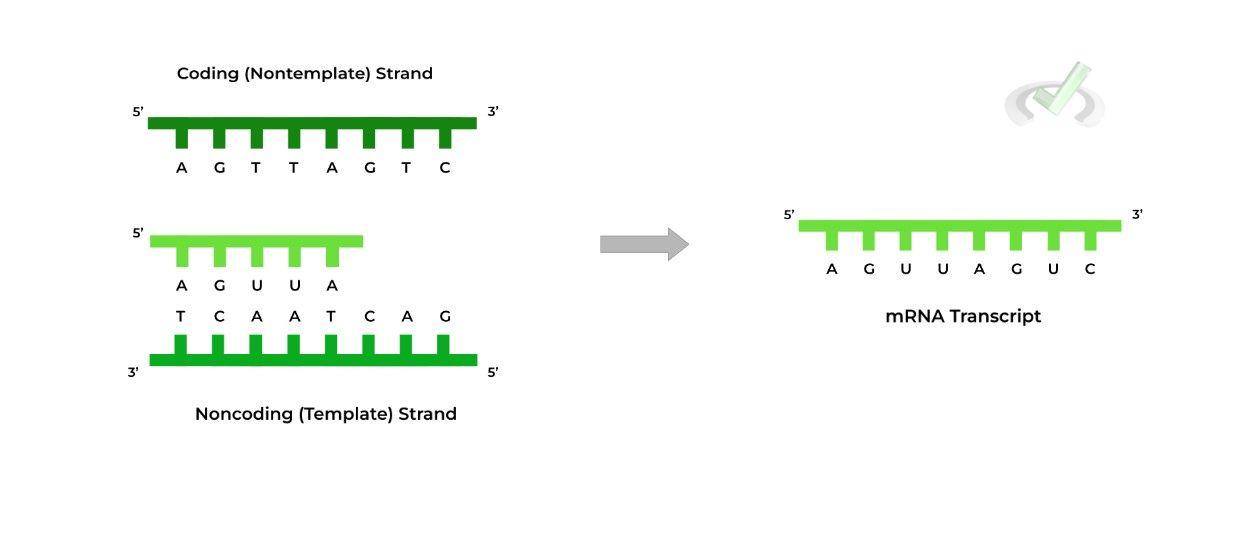
Template And Nontemplate Strand
Template And Nontemplate Strand - Web the nontemplate strand is the dna strand that is not used as a template during transcription. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplatestrand. Web the template strand is also called the antisense strand or the positive strand. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different mrna. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and matches the. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web the template strand is also called the antisense strand or the positive strand. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplatestrand. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web the template strand is also called the antisense strand or the positive strand. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web transcription in prokaryotes (and in eukaryotes) requires the dna double helix to partially unwind in the region of mrna synthesis. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. Web my book keeps giving different indicators as to whether the promoters are on the coding or template strand. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are. Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. Web sometimes genes. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different mrna. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplatestrand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web the nontemplate strand is the dna strand that. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then. Web transcription uses one of the two. Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. It has the same nucleotide sequence as the mrna, except that thymine (t) in dna is replaced by uracil (u) in rna. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Transcription always. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. Web my book keeps giving different indicators as to whether the promoters are on the. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in. Web my book keeps giving different indicators as to whether the promoters are on the coding or template strand. Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. This strand is called the template strand. Web template strand functions as a base for the. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. The region of unwinding is called a transcription bubble. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and matches the. Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand.What Direction Is The Template Strand Read
Dna Template Vs Coding Strand
Dna Coding And Template Strands
RNA Transcription Fundamentals and Key Terms on the MCAT MCAT Mastery
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Variations sciencesavers
Template And Nontemplate Strand
How To Identify Template Strand Of Dna
Web The Template Strand Is Also Called The Antisense Strand Or The Positive Strand.
Web Transcription Uses One Of The Two Exposed Dna Strands As A Template;
Web The Coding Strand Determines The Correct Nucleotide Sequence Of Mrna.
It Has The Same Nucleotide Sequence As The Mrna, Except That Thymine (T) In Dna Is Replaced By Uracil (U) In Rna.
Related Post: