Template Dna Strand
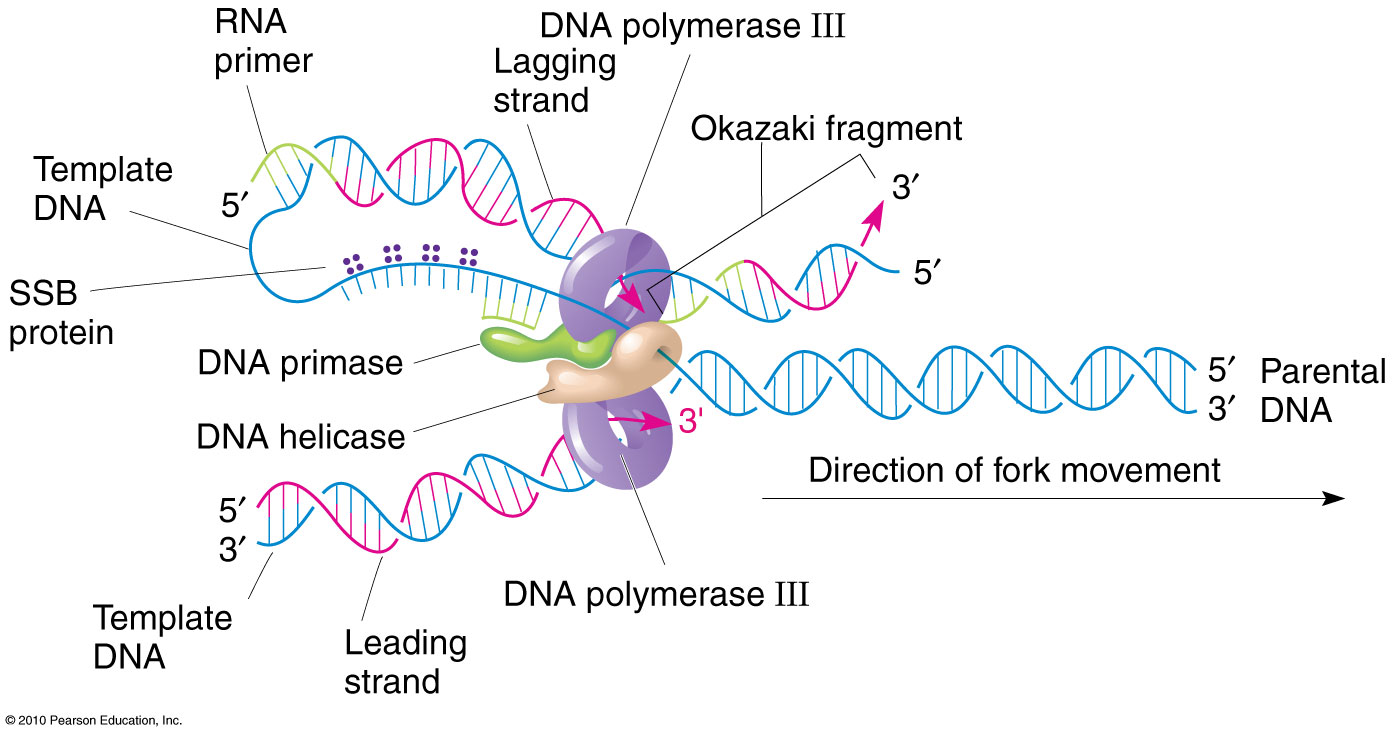
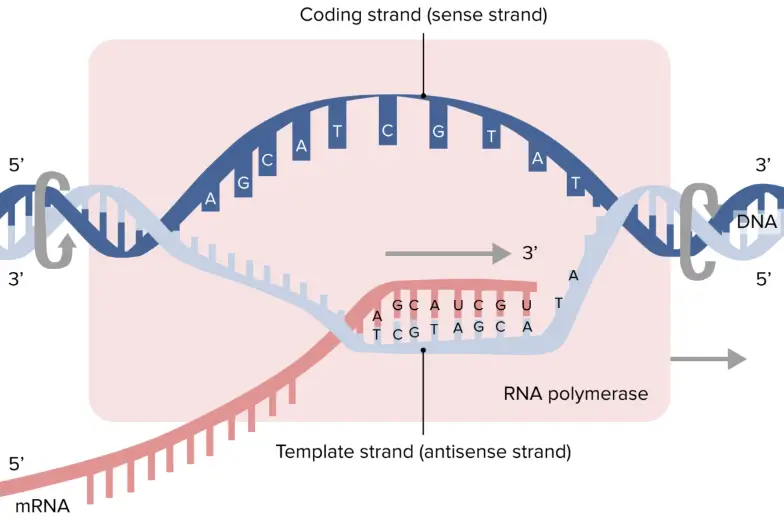
Template Dna Strand - Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or informational strand. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. All of the rna in a cell is made by dna transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of dna replication discussed in chapter 5. Web the cosegregation of 'immortal' template dna strands and their link with the asymmetry apparatus has important implications for stem cell biology and cancer. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. It is the transfer of genetic instructions in dna to messenger rna (mrna). The double helix is un'zipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Difference between coding strand and template strand. Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Ester falconer, mark hills, ulrike naumann, steven s s poon, elizabeth a chavez,. Difference between coding strand and template strand. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. All of the rna in a cell is made by dna transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of dna replication discussed in chapter 5. Understand the difference between template and coding strands. After replication, each dna has one parental or “old” strand, and one daughter or “new” strand. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To initiate rna synthesis, the two dna strands unwind at specific sites along the dna molecule. Ist, kann von gen zu gen verschieden sein. All of the rna in a cell is made by dna transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of dna replication discussed in chapter 5. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Both coding and template strands are distinct strands of a dna structure. After replication, each dna has one parental or “old” strand, and one daughter or “new” strand. Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Yet in theory, the chemical strings could represent just about any sequence of information. Web what is the dna template strand? Figure below shows how this occurs. All of the rna in a cell is made by dna transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of dna replication discussed in chapter 5. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Ribonucleotides are. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web what is the dna template strand? Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Web what is the dna template strand? Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web dna acts as a codebase for living organisms, providing molecular templates for biological structures and processes. Welcher der beiden stränge der m. Wird gelegentlich auch als codogener. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Ist, kann von gen. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Ester falconer, mark hills, ulrike naumann, steven s s. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). Ester falconer, mark hills, ulrike naumann, steven s s poon, elizabeth a chavez,. Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make. Learn what is meant by a template strand and a coding strand. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Welcher der beiden stränge der m. Wird gelegentlich auch als codogener strang bezeichnet. Web what is the dna template strand? Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Ribonucleotides are attracted to the uncoiling region of the dna. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Web the cosegregation of 'immortal' template dna strands and their link with the asymmetry apparatus has important implications for stem cell biology and cancer. This template strand is. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Figure below shows how this occurs. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. All of the rna in a cell is made by dna transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of dna replication discussed in chapter 5. Wird gelegentlich auch als codogener strang bezeichnet. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. Ribonucleotides are attracted to the uncoiling region of the dna. Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or informational strand. Yet in theory, the chemical strings could represent just about any sequence of information. Ist, kann von gen zu gen verschieden sein. Web the cosegregation of 'immortal' template dna strands and their link with the asymmetry apparatus has important implications for stem cell biology and cancer. To initiate rna synthesis, the two dna strands unwind at specific sites along the dna molecule. After replication, each dna has one parental or “old” strand, and one daughter or “new” strand. Both coding and template strands are distinct strands of a dna structure. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand.Template Strand Of Dna
Template And Coding Strand Of Dna
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
DNA Transcription Steps and Mechanism • Microbe Online
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
How To Identify Template Strand Of Dna
Dna Template
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
It Is The Transfer Of Genetic Instructions In Dna To Messenger Rna (Mrna).
Web One Strand Of The Dna, The Template Strand (Or Noncoding Strand), Is Used As A Template For Rna Synthesis.
Web In Transcription, An Rna Polymerase Uses Only One Strand Of Dna, Called The Template Strand, Of A Gene To Catalyze Synthesis Of A Complementary, Antiparallel Rna Strand.
Web A Dna Template Strand Generally Refers To The Strand Which Is Used By The Enzyme Dna Polymerases And Rna Polymerases To Attach With The Complementary Bases During The Process Of Replication Of Dna Or At The Time Of Transcription Of Rna Respectively.
Related Post: