Template Strand And Non Template Strand
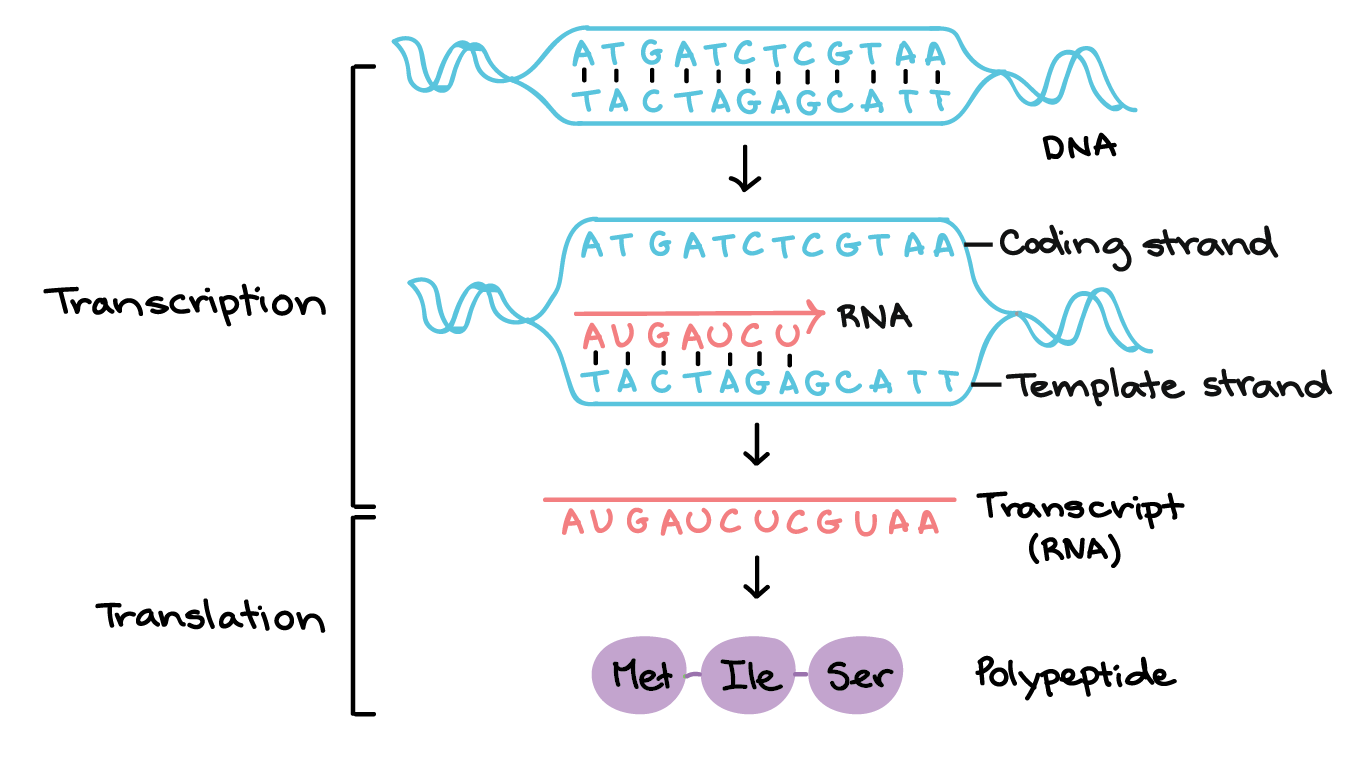
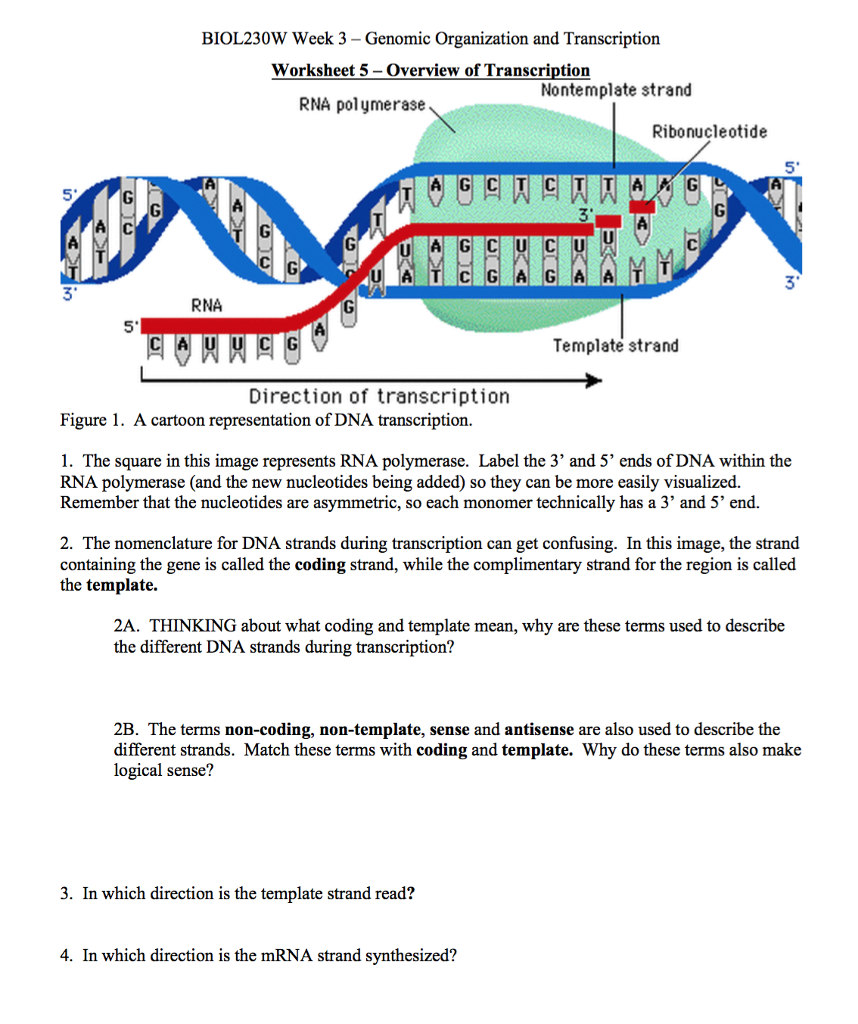
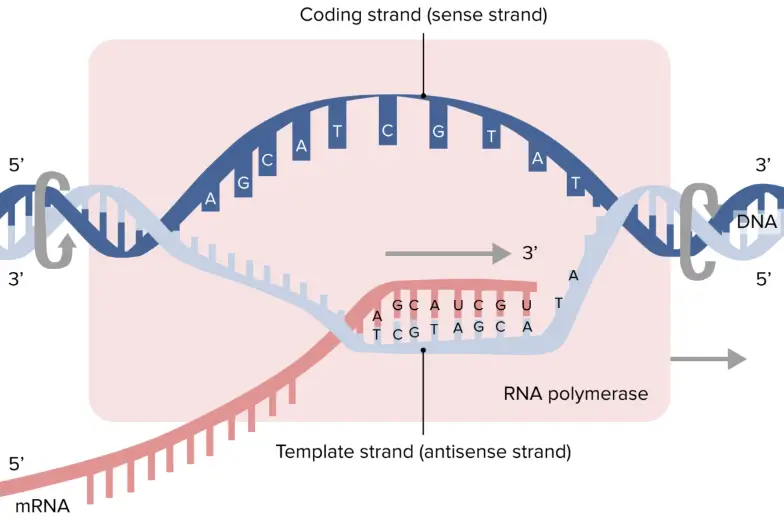
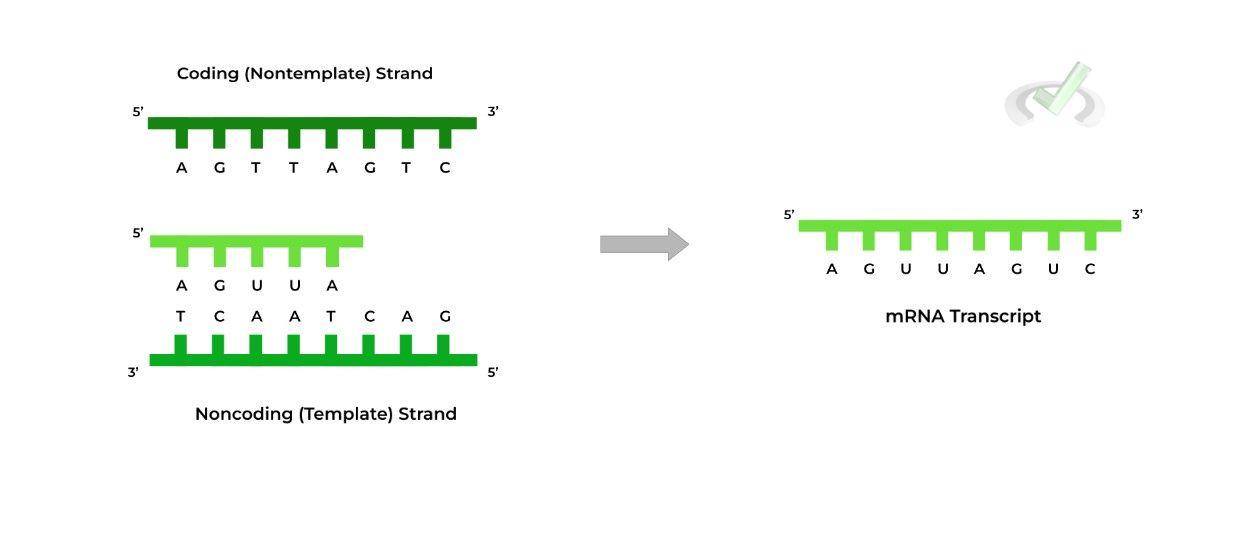
Template Strand And Non Template Strand - The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. The coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Web my book keeps giving different indicators as to whether the promoters are on the coding or template strand. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and matches the. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. The coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. Web my book keeps giving different indicators as to whether the promoters are on the coding or template strand. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. Web template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. During elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c) will be encoded in the rna. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e.,. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis,. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary. If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c) will be encoded in the rna. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. Web template strand functions as a base. The coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. The main difference between sense and antisense strand is in their serving as the template for the transcription. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas. Although rna polymerase traverses the. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and matches the. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web rna is synthesized by using the template. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of. This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and matches the. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). It is also known as. If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c) will be encoded in the rna. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna. Although rna polymerase traverses the. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. It. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web let’s say you have the following dna sequence fragment: The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. The coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. It can make a copy of itself during mrna synthesis. The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. This structural difference ensures that the rna transcript is synthesized in the correct orientation and matches the. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c) will be encoded in the rna. Web the coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction.Gene Expression Transcription Agriculture, and Biotechnology
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Dna Template Vs Coding Strand
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Template vs. Nontemplate (Noncoding vs. Coding strand of DNA) YouTube
Template Vs Non Template Strand Web It Is Presented In The 5' To 3
RNA Transcription Fundamentals and Key Terms on the MCAT MCAT Mastery
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
During Elongation, An Enzyme Called Rna Polymerase Proceeds Along The Dna Template Adding Nucleotides By Base Pairing.
Web Template Strand Functions As A Base For The Rna Synthesis.
As Transcription Proceeds, Rna Polymerase Traverses The Template Strand And Uses Base Pairing Complementarity With The Dna Template To Create An Rna Copy (Which Elongates During The Traversal).
This Template Strand Is Called The Noncoding Strand.
Related Post: