Template Strand Dna Replication
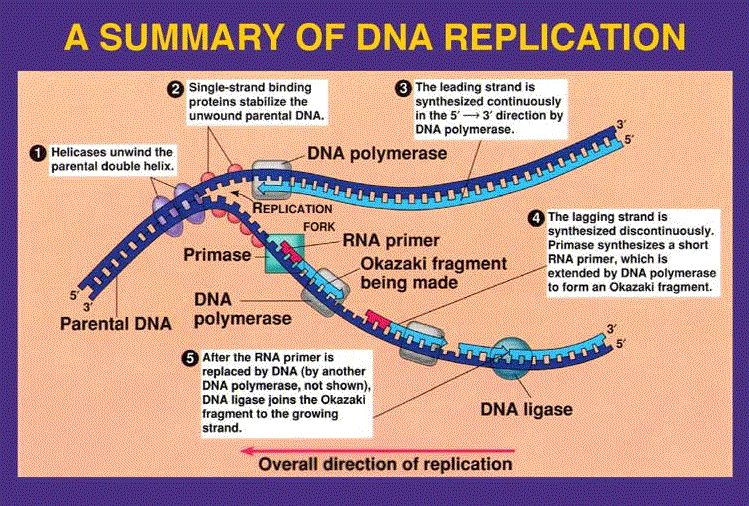
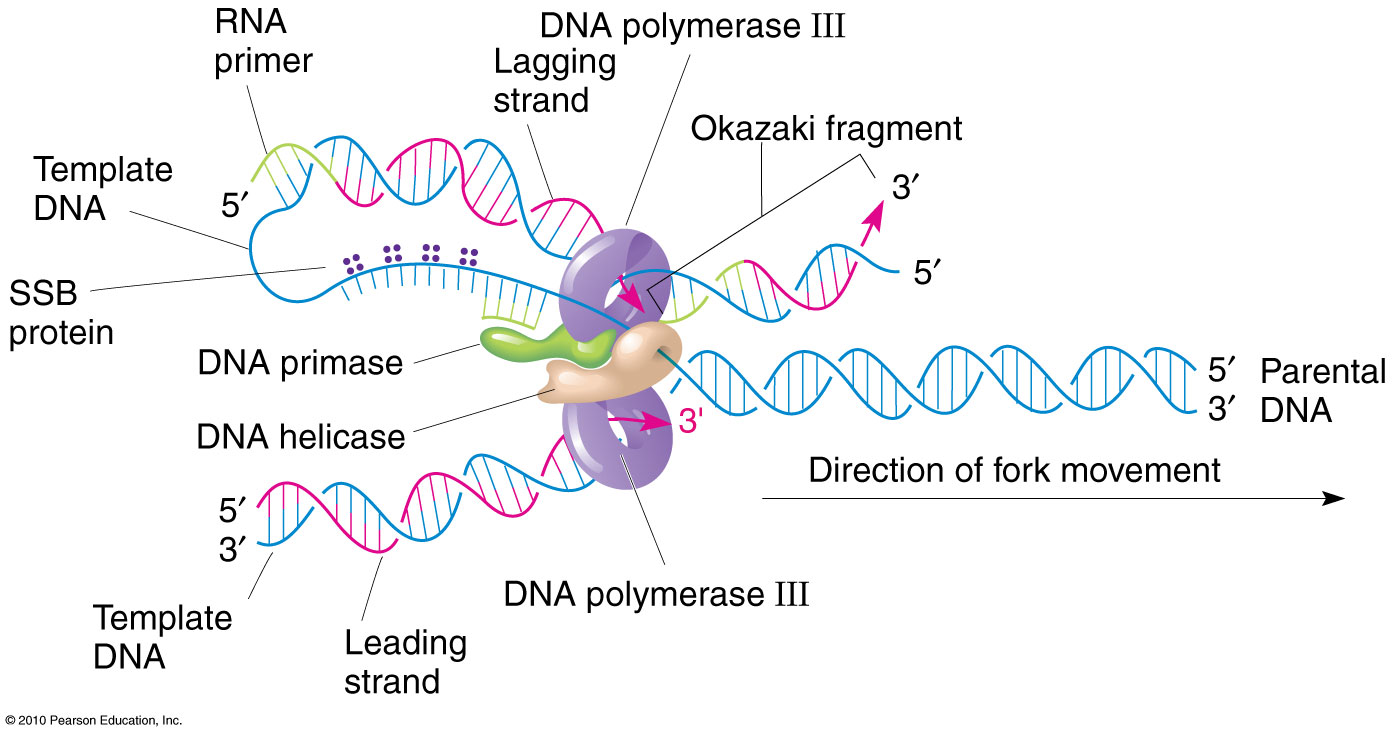
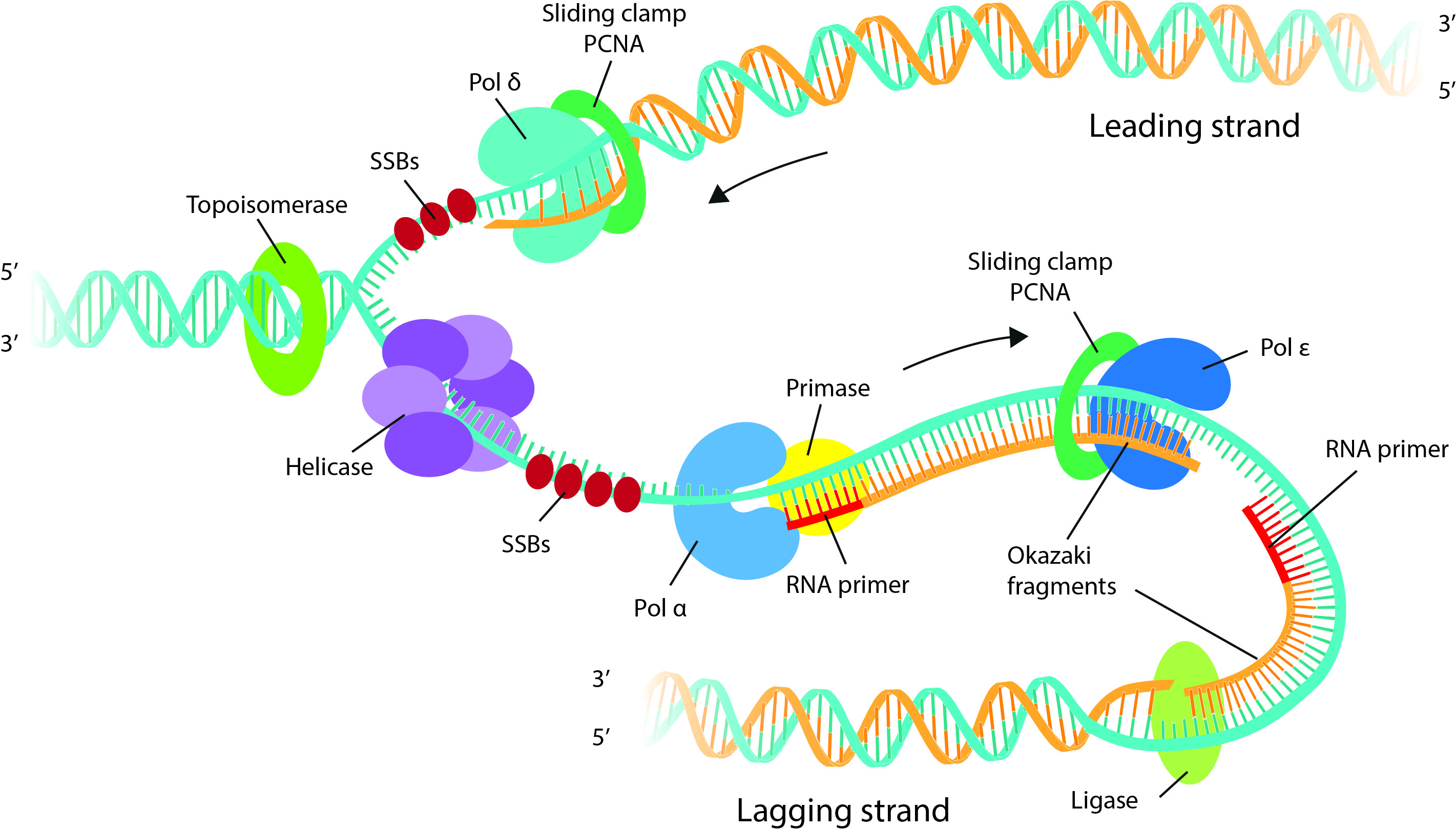
Template Strand Dna Replication - Web this session will explain how dna is replicated prior to cell division. The dna double helix is opened by helicase into individual strands. The opening of the double helix and separation of the dna strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new dna segment. The coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (rna). Web replication occurs in three major steps: Completion of dna replication at the site of the original nick results in full displacement of the nicked strand, which may then. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Web this enzyme unwinds the double helix and exposes each of the two strands so that they can be used as a template for replication. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. It involves denaturation and displacement of the dna strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. The double helix is un'zipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web slipped strand mispairing (ssm, also known as replication slippage) is a mutation process which occurs during dna replication. Web this session will explain how dna is replicated prior to cell division. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. After replication, each dna has one parental or “old” strand, and one daughter or “new” strand. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. The “lagging strand” is synthesized in the direction away from the replication fork and away from the dna helicase unwinds. In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. The coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (rna). After replication, each dna has one parental or “old” strand, and one daughter or “new” strand. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Web this enzyme unwinds the double helix and exposes each of the two strands so that they can be used as a template for replication. Web slipped strand mispairing (ssm, also known as replication slippage) is a mutation process which occurs during dna replication. The dna double helix is opened by helicase into individual strands. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. Web slipped strand mispairing (ssm, also known as replication slippage) is a mutation process which occurs during dna replication. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. After replication, each dna has one parental or “old” strand, and one. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The dna double helix is opened by helicase into individual strands. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. The nontemplate strand is referred. Web collisions of transcription and. It does this by hydrolysing the atp used to form the bonds between the nucleobases, thereby breaking the bond holding the two strands together. The opening of the double helix and separation of the dna strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new dna segment. In this process, dna polymerase uses an original strand as. Web slipped strand mispairing (ssm, also known as replication slippage) is a mutation process which occurs during dna replication. The coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (rna). The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Web one class of proteins required for replication binds to dna polymerases, increasing. Web this session will explain how dna is replicated prior to cell division. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. The double helix is un'zipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Topoisomerase relieves the tension further down the double helix.. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. Topoisomerase relieves the tension further down the double helix. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. The opening of the double helix and separation of the dna strands, the priming of the template strand, and. Web replication occurs in three major steps: Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. American enzymologist and nobel prize winner arthur. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new. In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. The “lagging strand” is synthesized in the direction away from the replication fork and away from. Web this session will explain how dna is replicated prior to cell division. The dna double helix is opened by helicase into individual strands. It involves denaturation and displacement of the dna strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each. Web this session will explain how dna is replicated prior to cell division. The dna double helix is opened by helicase into individual strands. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Topoisomerase relieves the tension further down the double helix. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. The opening of the double helix and separation of the dna strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new dna segment. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web slipped strand mispairing (ssm, also known as replication slippage) is a mutation process which occurs during dna replication. Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. Web one class of proteins required for replication binds to dna polymerases, increasing the activity of the polymerases and causing them to remain bound to the template dna so that they continue synthesis of a new dna strand. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. It does this by hydrolysing the atp used to form the bonds between the nucleobases, thereby breaking the bond holding the two strands together. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices.Replication of DNA summary A Level H1 and H2 Biology
Dna Template
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial
Dna Replication Template
Replication Britannica
The Nucleus and DNA Replication Anatomy and Physiology I
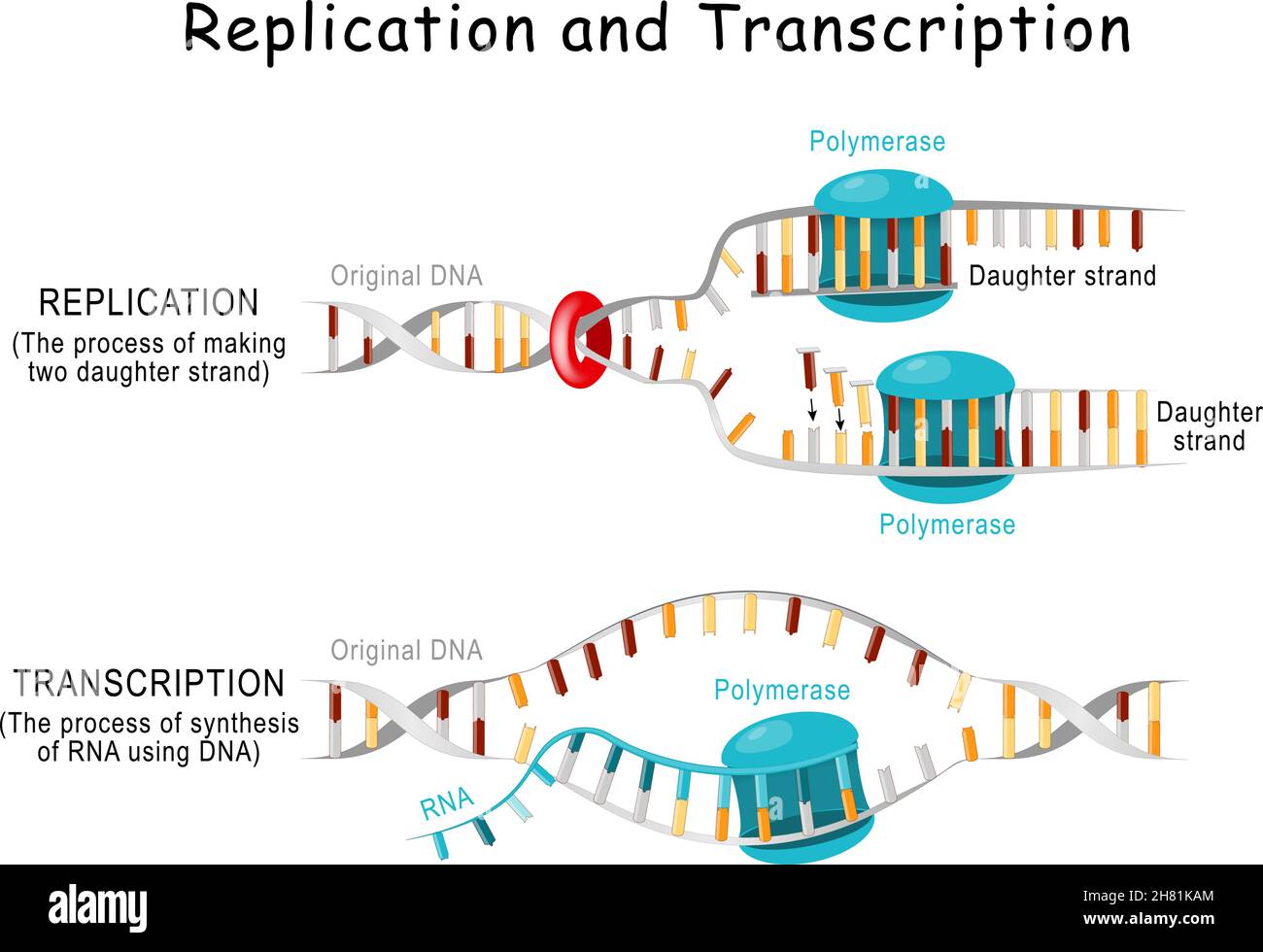
DNA Replication and Transcription. Steps. double helix is unwound. Each
DNA Replication Lagging Strand
Dna Replication Template
The Coding Strand Serves As A Template For Producing Complementary Rna.
The New Strand Will Be Complementary To The Parental Or “Old” Strand.
The Nontemplate Strand Is Referred.
The Coding Strand Is The Dna Strand Whose Base Sequence Is Similar To Its Primary Transcript (Rna).
Related Post: