Template Strand To Mrna
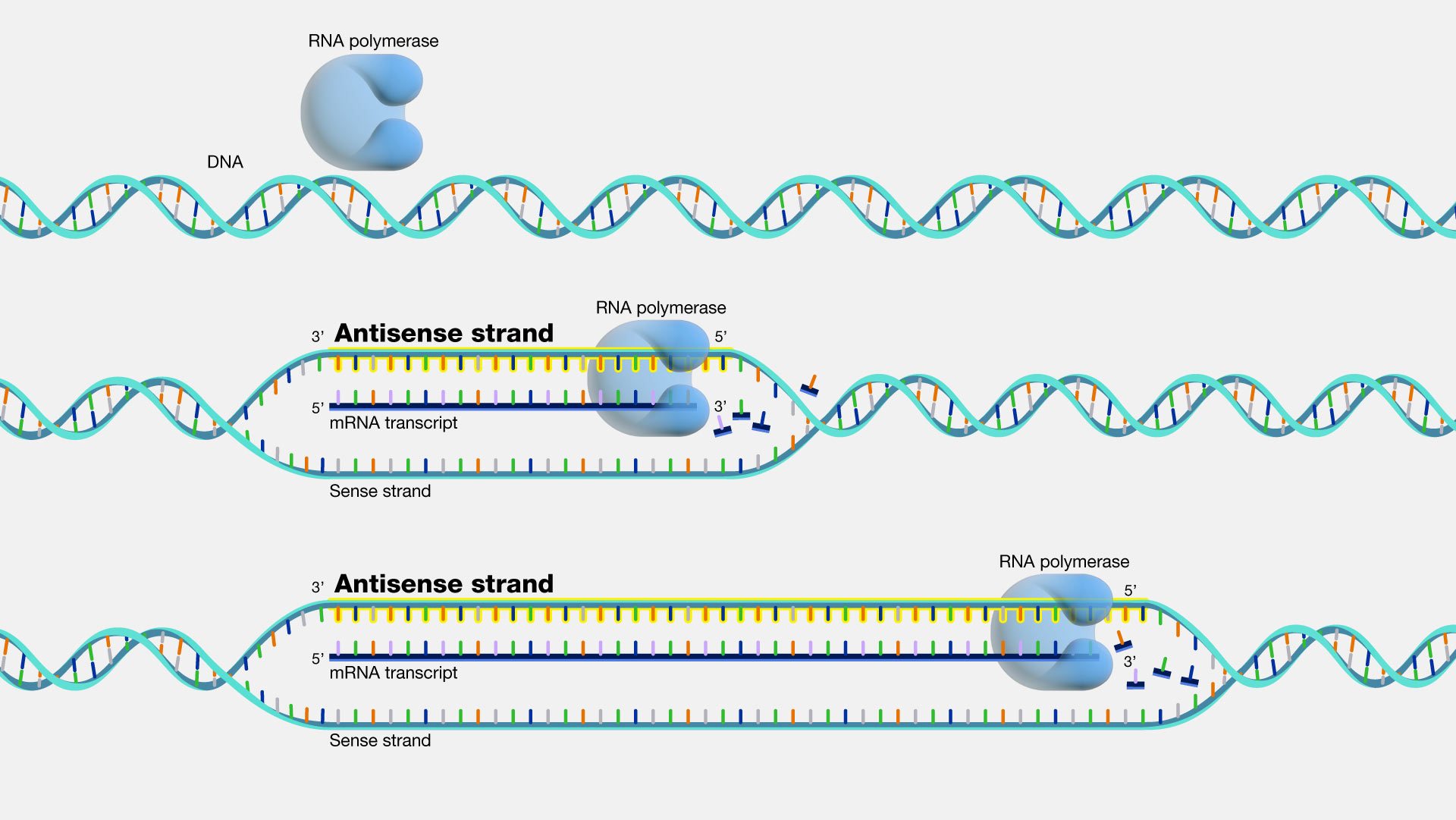
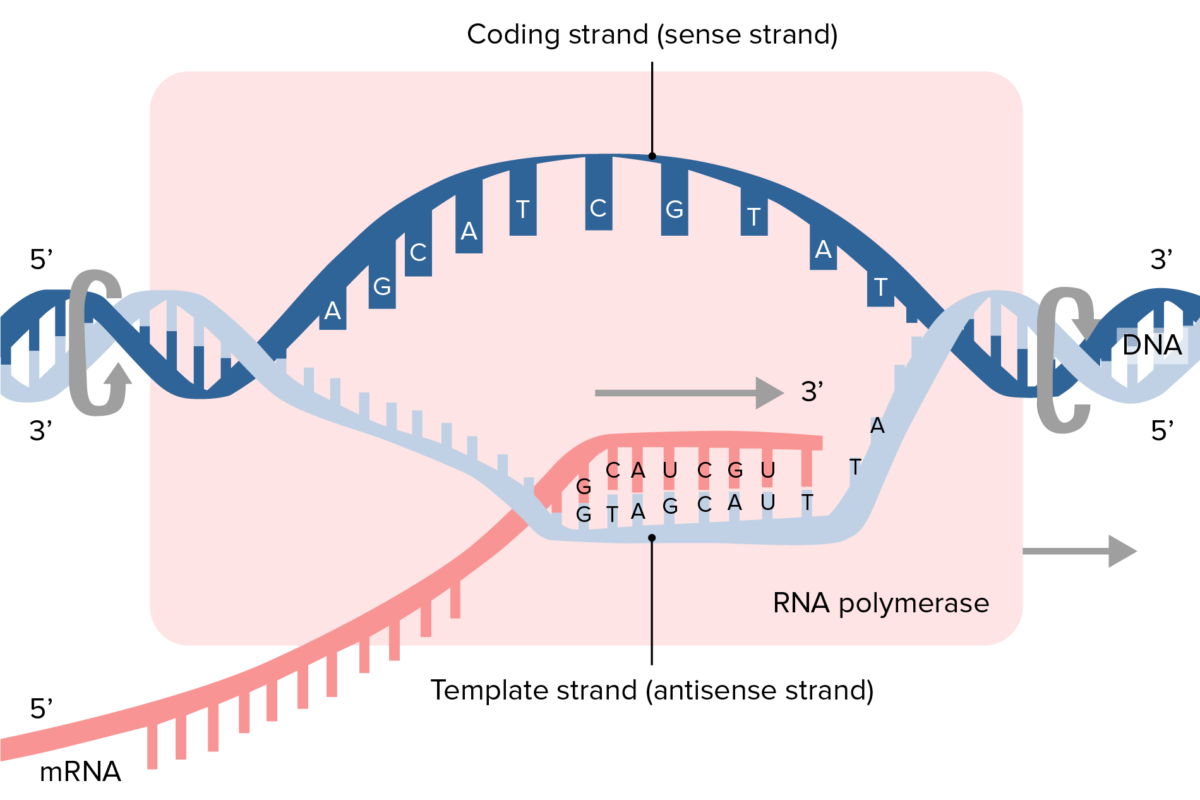
Template Strand To Mrna - The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized. Web the rna polymerase follows the template strand and uses it to assemble an mrna molecule, that is the mirrored image of the template strand. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of. Then, a process called translation uses this mrna. Web to manufacture protein molecules, a cell must first transfer information from dna to mrna through the process of transcription. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains. Web learn how dna is converted to rna in the process of transcription, and how rna polymerase and promoters are involved. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Then, a process called translation uses this mrna. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template. The second copy is transcribed from the complementary (sense) strand to. Utrs are thought to be particularly important. It is also known as sense strand (plus. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. A dna molecule is double stranded. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of. Web translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Utrs are thought to be particularly important. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and translate the mrna to a polypeptide. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Web learn how dna is converted to rna in the process of transcription, and how rna polymerase and promoters are involved. Web learn how dna is converted to rna in the process of transcription, and how rna polymerase and promoters are involved. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand. Web learn how dna is converted to rna in the process of transcription, and how rna polymerase and promoters are involved. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template. Utrs are thought to be particularly important. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template. Web the rna polymerase follows the template strand and uses it to assemble an mrna molecule, that is the mirrored image of the template strand. Web translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Web in transcription, an rna. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and translate the mrna to a polypeptide. Web the original copy is transcribed from the usual template (transcribed) strand to make mrna; Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. See diagrams and. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template. It is the transfer of genetic instructions in dna to messenger rna (mrna). Web the original copy is transcribed from the usual template (transcribed) strand to make mrna; Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains. Web one strand. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and translate the mrna to a polypeptide. Web to manufacture protein molecules, a cell must first transfer information from dna to mrna through the process of transcription. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. Utrs are thought to be particularly important. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. It is also known as sense strand (plus. Web an enzyme called rna. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web learn how dna is converted to rna in the process of transcription, and how rna polymerase and promoters are. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. See diagrams and examples of prokaryotic and. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and translate the mrna to a. Web an enzyme called rna polymerase reads the template dna strand to produce an mrna molecule. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Web transcription is the first part of the central dogma of molecular biology: The second copy is transcribed from the complementary (sense) strand to. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web the rna polymerase follows the template strand and uses it to assemble an mrna molecule, that is the mirrored image of the template strand. Web the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of. It is also known as sense strand (plus. Utrs are thought to be particularly important. It is the transfer of genetic instructions in dna to messenger rna (mrna). Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different mrna. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized. A dna molecule is double stranded. Then, a process called translation uses this mrna. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis.Mrna Template Strand
Protein Synthesis Anatomy and Physiology I
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
Mrna Template Strand
Gene Expression Transcription Agriculture, and Biotechnology
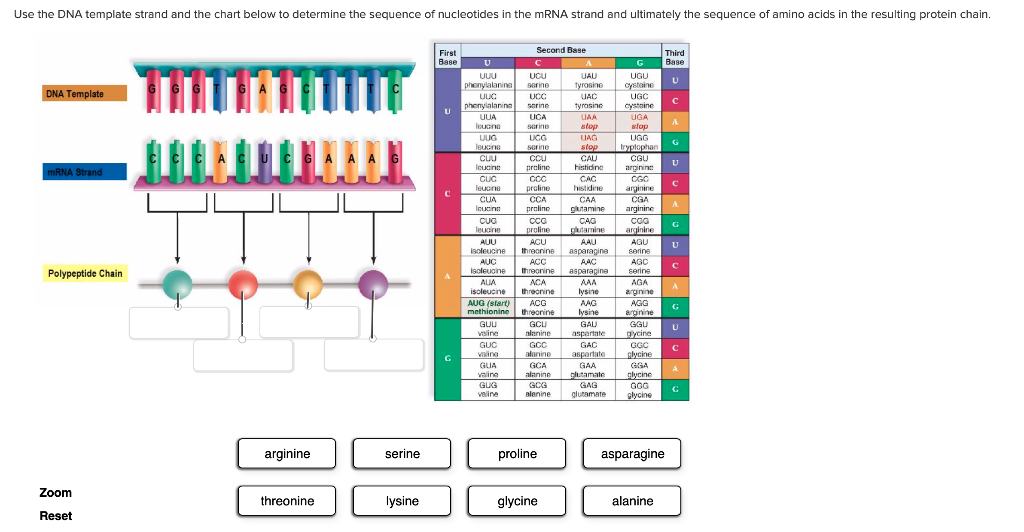
Mrna Sequence Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Mrna Template Strand
Template Strand Mrna
What Is The Template Strand
Coding Strand Template Strand Mrna
Web Translates Dna Or Mrna To The Other And A Protein Strand (Amino Acids).
Web The Coding Strand Determines The Correct Nucleotide Sequence Of Mrna.
Web The Mrna Product Is Complementary To The Template Strand And Is Almost Identical To The Other Dna Strand, Called The Nontemplate Strand, With The Exception That Rna Contains.
Web In Transcription, An Rna Polymerase Uses Only One Strand Of Dna, Called The Template Strand, Of A Gene To Catalyze Synthesis Of A Complementary, Antiparallel Rna Strand.
Related Post: