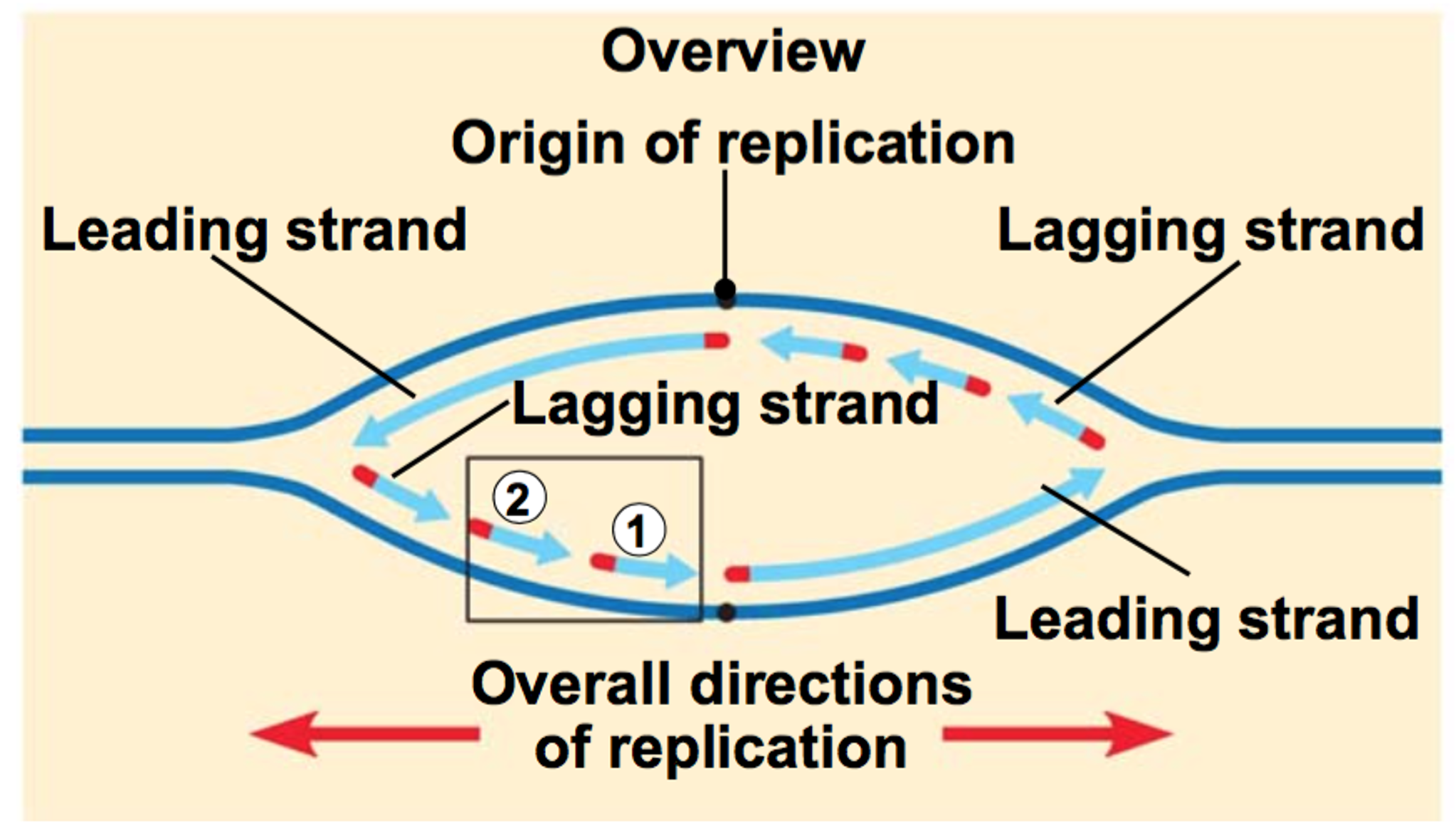
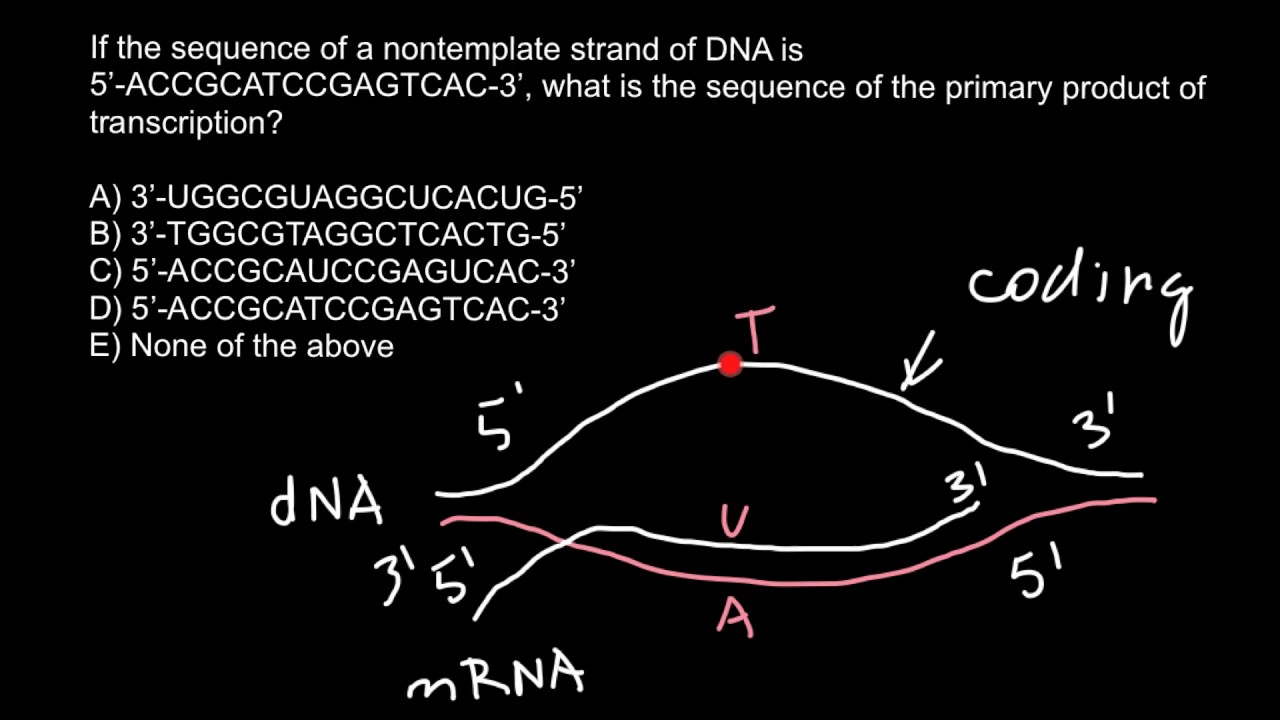
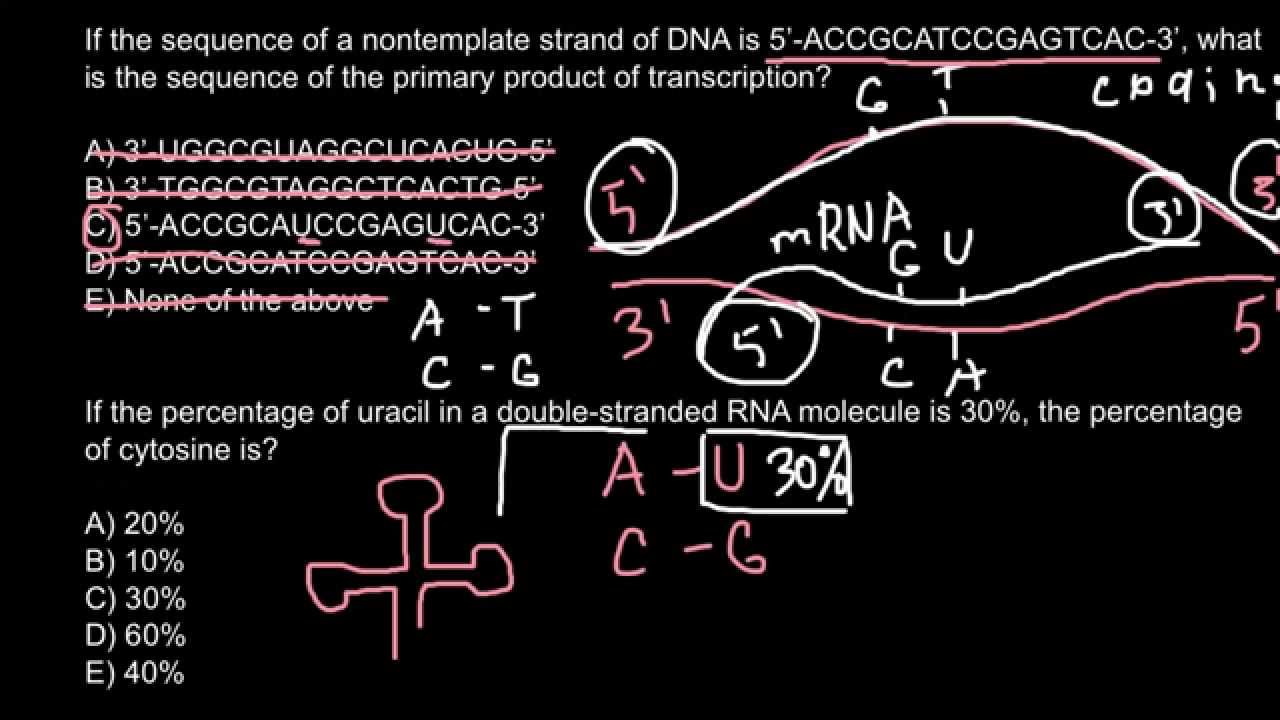
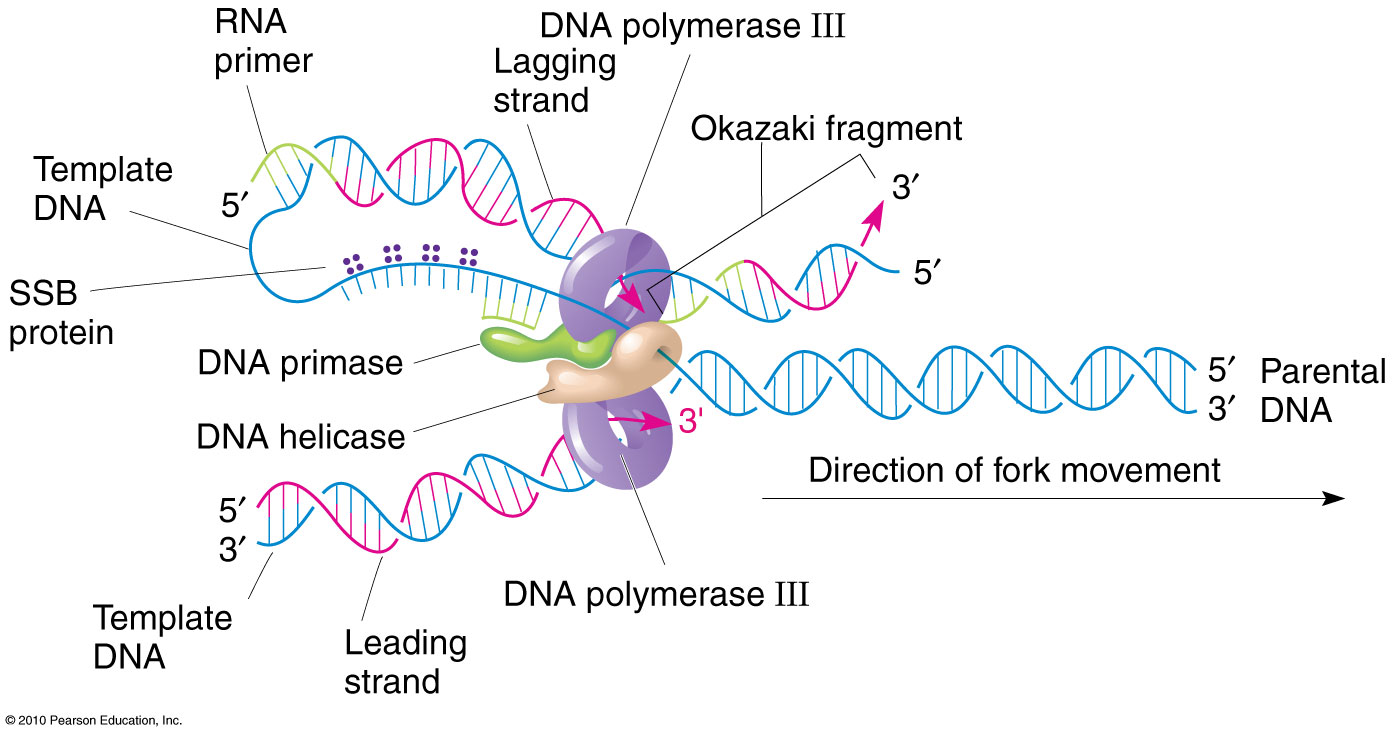
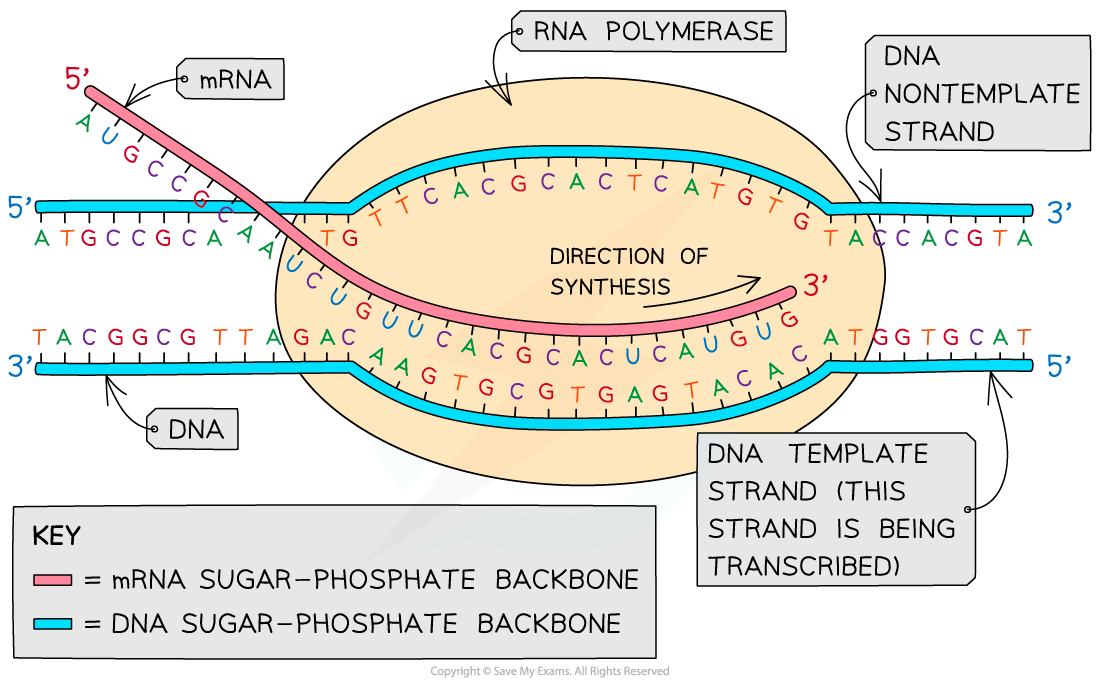
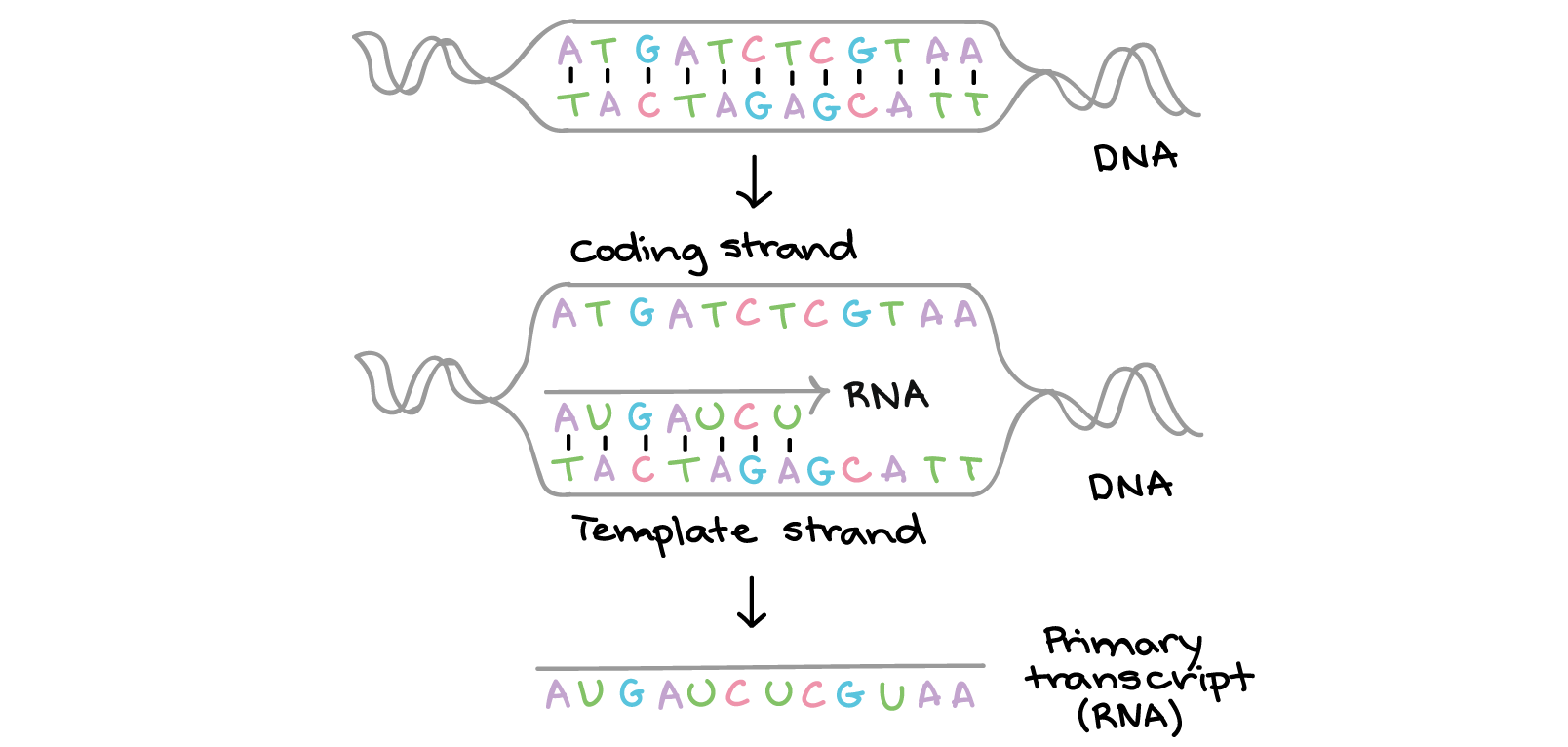
Template Strands
Template Strands - Only the nucleotide complementary to the template nucleotide at that position is added to the new strand. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. During transcription, both strands of the gene being transcribed have different names and different roles. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. Wird gelegentlich auch als codogener strang bezeichnet. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web the choice of template strand for each gene is therefore determined by the location and orientation of the promoter. Welcher der beiden stränge der m. Web the template strand specifies which of the four dna nucleotides (a, t, c, or g) is added at each position along the new chain. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or informational strand. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web rna polymerases end transcription at sequences called terminators. Ist, kann von gen zu gen verschieden sein. If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c). Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. The nontemplate strand is referred. Welcher der beiden stränge der m. In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web during transcription, the template strand, also known as the ‘minus’ or ‘antisense’ strand, is generated by rna polymerase itself in the case of prokaryotes, or by a transcription factor with helicase activity in case of eukaryotes. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c). Ribonucleotides are attracted to the uncoiling region of the dna. Web the template strand specifies which of the four dna nucleotides (a, t, c, or g) is added at each position along the new chain. The strand that actually serves as the template on which rna is polymerized is properly referred to as the template strand. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is. Ist, kann von gen zu gen verschieden sein. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. During transcription, both strands of the gene being transcribed have different names and different roles. The nontemplate strand is referred. Web. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web rna polymerases end transcription at sequences called terminators. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied.. Web during transcription, the template strand, also known as the ‘minus’ or ‘antisense’ strand, is generated by rna polymerase itself in the case of prokaryotes, or by a transcription factor with helicase activity in case of eukaryotes. The coding strand has a coding sequence of nucleotides that serves as a master blueprint for our protein. Web the template strand specifies. During transcription, both strands of the gene being transcribed have different names and different roles. Ist, kann von gen zu gen verschieden sein. It can be used to detect sister chromatid exchange and other chromosomal. If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c). In transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the. Although rna polymerase traverses the. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web the template strand specifies which of the four dna nucleotides (a, t, c, or g) is added at each position along the new chain. Web during transcription, the template strand, also known as the ‘minus’ or ‘antisense’ strand, is generated by rna polymerase itself in the. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. Welcher der beiden stränge der m. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding. Web during transcription, the template strand, also known as the ‘minus’ or ‘antisense’ strand, is generated by rna polymerase itself in the case of prokaryotes, or by a transcription factor with helicase activity in case of eukaryotes. Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna. To initiate rna synthesis, the two dna strands unwind at specific sites along the dna molecule. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. In transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand,. In transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web the template strand specifies which of the four dna nucleotides (a, t, c, or g) is added at each position along the new chain. During transcription, both strands of the gene being. After replication, each dna has one parental or “old” strand, and one daughter or “new” strand. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Only the nucleotide complementary to the template nucleotide at that position is added to the new strand. Web rna polymerases end transcription at sequences called terminators. Web the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis, i.e., if adenine (a) is encoded in the template strand, uracil (u) will be encoded in the newly synthesized rna. Ribonucleotides are attracted to the uncoiling region of the dna. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand). It can be used to detect sister chromatid exchange and other chromosomal. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). If guanine (g) is encoded in the template strand, then cytosine (c). The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. During transcription, both strands of the gene being transcribed have different names and different roles. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Ist, kann von gen zu gen verschieden sein.Heredity DNA Structure, Composition, Britannica
How To Identify Template Strand Of Dna
Dna Coding And Template Strands
Dna Coding And Template Strands
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
Template And Coding Strand
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记4.2.3 Transcription翰林国际教育
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Variations sciencesavers
How To Identify Template Strand Of Dna
Web The Main Difference Between Template And Coding Strand Is That Template Strand Only Serves As The Template For Transcription Whereas Coding Strand Contains The Exact Same Sequence Of Nucleotides In The Mrna Except Thymine.
Wird Gelegentlich Auch Als Codogener Strang Bezeichnet.
The Nontemplate Strand Is Referred.
Web The Choice Of Template Strand For Each Gene Is Therefore Determined By The Location And Orientation Of The Promoter.
Related Post: