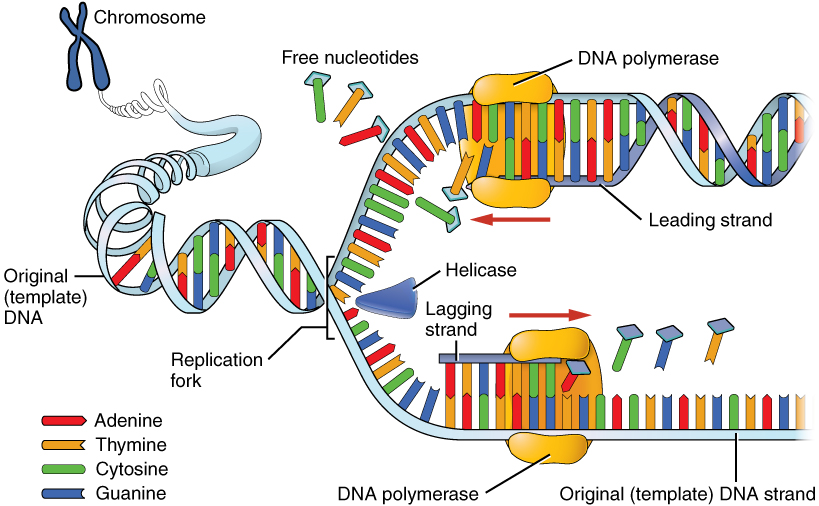
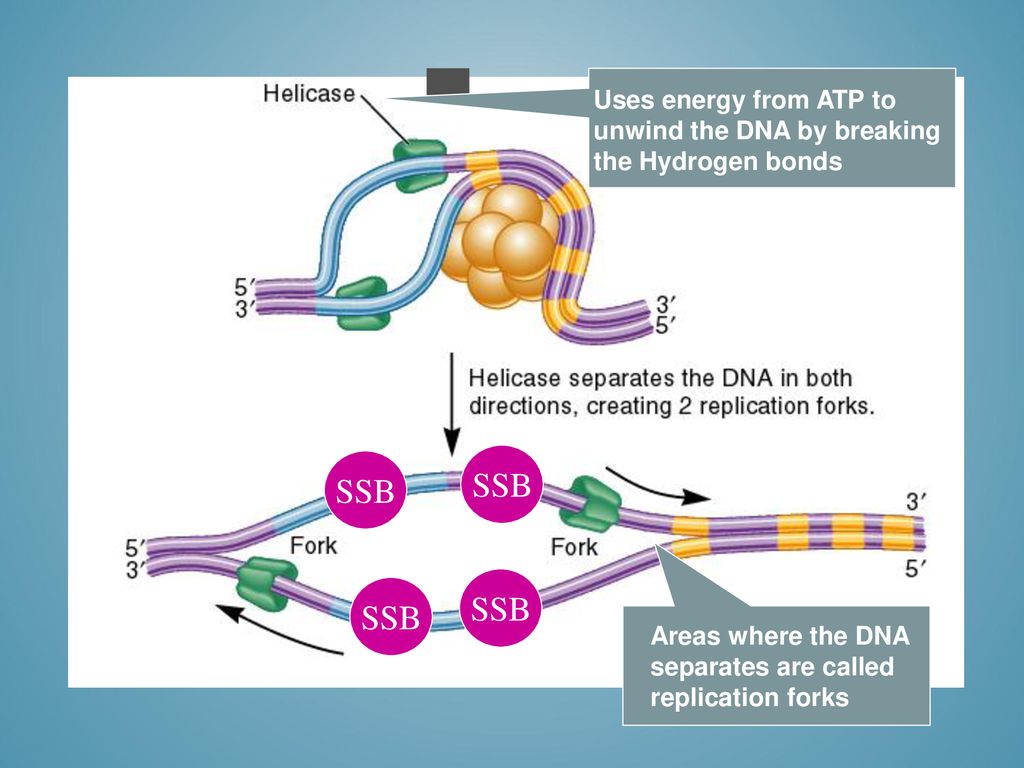
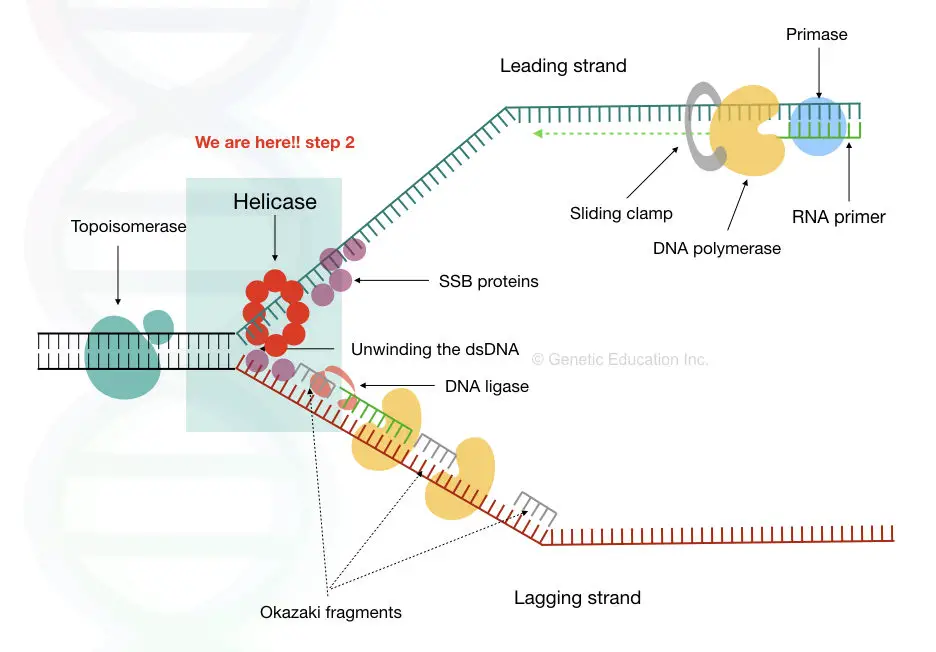
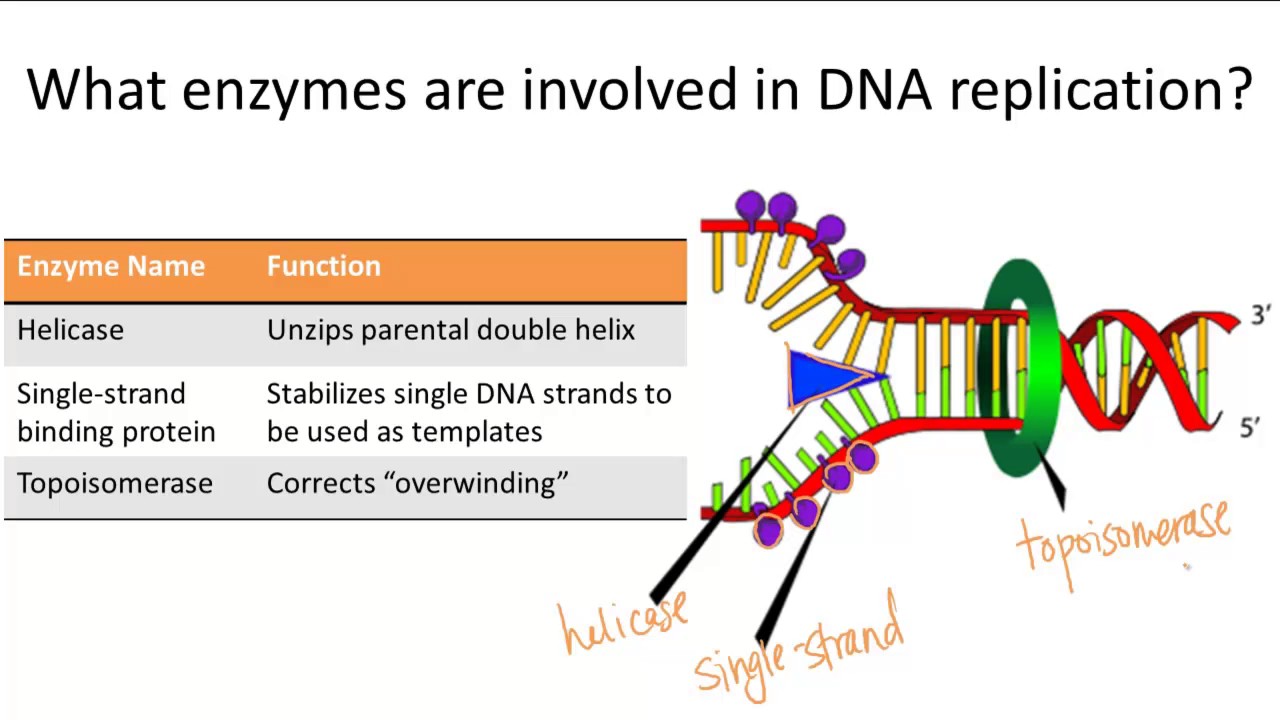
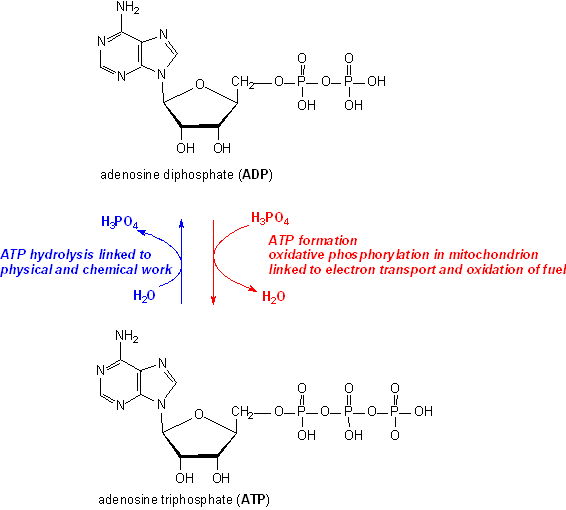
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template - At each replication fork, the parental dna strands. This job is done by a special enzyme, helicase, that helps unwind and separate the dna helices (figure 4). Web during dna replication, several proteins facilitate the unwinding of the dna double helix into two single strands. Web an enzyme called helicase unwinds the dna by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs. At each replication fork, the parental dna strands must be. Web different dna unwinding mechanism between bacterial and eukaryotic helicase. Web the two strands of dna have to be temporarily separated from each other; Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the dna structure proposed by watson and crick involves, the dna controlled by an origin is called a, bacterial dna is typically replicated as and more. Once initiated, a replication bubble (replicon) forms as repeated cycles of elongation proceed at opposite replication forks. Dna polymerase iii is the main enzyme that then elongates new dna. Web different dna unwinding mechanism between bacterial and eukaryotic helicase. Dna is composed of two. Web we propose a mechanism in which cmg couples atp hydrolysis to unwinding by acting as a lazy brownian ratchet, thus providing quantitative understanding of the central process in eukaryotic dna replication. Unlike type i topoisomerases, type ii enzymes use atp hydrolysis and some of the bacterial versions can introduce superhelical At each replication fork, the parental dna strands must be. Helicase uses the energy released when atp is hydrolyzed to unwind the dna helix. Processivity the dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. Here, the authors identify usp50. Web causes dna strand separation at the origin or replication. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the dna structure proposed by watson and crick involves, the dna controlled by an origin is called a, bacterial dna is typically replicated as and more. Dna polymerase iii is the main enzyme that then elongates new dna. Note that each replication bubble is made up of two replication forks that move or open up, in opposite directions. Note that each replication bubble is made up of two replication forks that move or open up, in opposite directions. Helicase uses the energy released when atp is hydrolyzed to unwind the dna helix. This job is done by a special enzyme, helicase, that helps unwind and separate the dna helices (figure 4). Previous estimates of its step size have. Once initiated, a replication bubble (replicon) forms as repeated cycles of elongation proceed at opposite replication forks. Web the unwinding of the dna helix requires the action of an enzyme called helicase. At each replication fork, the parental dna strands must be. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. At each replication fork, the parental dna strands must be. Dna polymerase iii is the main enzyme that then elongates new dna. Note that each replication bubble is made up of two replication forks that move or open up, in opposite directions. Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds forming the double helix structure of dna. Previous estimates of its step size. Web helicases are enzymes that catalyze the unwinding of parental dna, coupled to the hydrolysis of atp, ahead of the replication fork. Here, the authors identify usp50. Helicase uses the energy released when atp is hydrolyzed to unwind the dna helix. This job is done by a special enzyme, helicase, that helps unwind and separate the dna helices (figure 4).. Helicase during dna replication, the _________ strand is synthesized continuously while the _________ strand is synthesized as small fragments that are connected to each. Web the unwinding of the dna helix requires the action of an enzyme called helicase. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. At each replication fork,. Once initiated, a replication bubble (replicon) forms as repeated cycles of elongation proceed at opposite replication forks. Is dna a double helix? Atp hydrolysis is required for this process because it requires energy. It uses atp to unwind the dna template. Web the unwinding of the dna helix requires the action of an enzyme called helicase. Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds forming the double helix structure of dna. Dna polymerase iii is the main enzyme that then elongates new dna. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the dna structure proposed by watson and crick involves, the dna controlled by an origin is called a, bacterial dna is typically replicated as and more.. Topoisomerases (red) reduce torsional strain caused by the unwinding of the. Dna is composed of two. At each replication fork, the parental dna strands. Processivity the dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. Web we propose a mechanism in which cmg couples atp hydrolysis to unwinding by acting as a lazy brownian ratchet, thus providing quantitative understanding of the central process. Web causes dna strand separation at the origin or replication. Identical reactions are used to untangle dna inside the cell. Helicase uses the energy released when atp is hydrolyzed to unwind the dna helix. Processivity the dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. Dna polymerase iii is the main enzyme that then elongates new dna. This job is done by a special enzyme, helicase, that helps unwind and separate the dna helices (figure 4). At each replication fork, the parental dna strands must be. Here, the authors identify usp50. Web helicases are enzymes that catalyze the unwinding of parental dna, coupled to the hydrolysis of atp, ahead of the replication fork. Topoisomerases (red) reduce torsional. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the dna structure proposed by watson and crick involves, the dna controlled by an origin is called a, bacterial dna is typically replicated as and more. Web different dna unwinding mechanism between bacterial and eukaryotic helicase. Unlike type i topoisomerases, type ii enzymes use atp hydrolysis and some of the. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the dna structure proposed by watson and crick involves, the dna controlled by an origin is called a, bacterial dna is typically replicated as and more. Once initiated, a replication bubble (replicon) forms as repeated cycles of elongation proceed at opposite replication forks. Note that each replication bubble is made. At each replication fork, the parental dna strands. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the dna structure proposed by watson and crick involves, the dna controlled by an origin is called a, bacterial dna is typically replicated as and more. Helicase uses the energy released when atp is hydrolyzed to unwind the dna helix. Identical reactions are used to untangle dna inside the cell. Processivity the dna polymerase iii enzyme of e. Web helicases are enzymes that catalyze the unwinding of parental dna, coupled to the hydrolysis of atp, ahead of the replication fork. Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds forming the double helix structure of dna. Dna polymerase iii is the main enzyme that then elongates new dna. Once initiated, a replication bubble (replicon) forms as repeated cycles of elongation proceed at opposite replication forks. Web the unwinding of the dna helix requires the action of an enzyme called helicase. Web we propose a mechanism in which cmg couples atp hydrolysis to unwinding by acting as a lazy brownian ratchet, thus providing quantitative understanding of the central process in eukaryotic dna replication. Web the two strands of dna have to be temporarily separated from each other; Dna polymerase iii is the main enzyme that then elongates new dna. Previous estimates of its step size have. Web the unwinding of the dna helix requires the action of an enzyme called helicase. Web an enzyme called helicase unwinds the dna by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous base pairs.What enzyme is used to unwind DNA? Socratic
DNA The molecule of Life. ppt download
Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
The Enzyme Uses Atp To Unwind The Dna Template
At Each Replication Fork, The Parental Dna Strands Must Be.
Note That Each Replication Bubble Is Made Up Of Two Replication Forks That Move Or Open Up, In Opposite Directions.
Helicase During Dna Replication, The _________ Strand Is Synthesized Continuously While The _________ Strand Is Synthesized As Small Fragments That Are Connected To Each.
Is Dna A Double Helix?
Related Post: