Transcription Template Strand
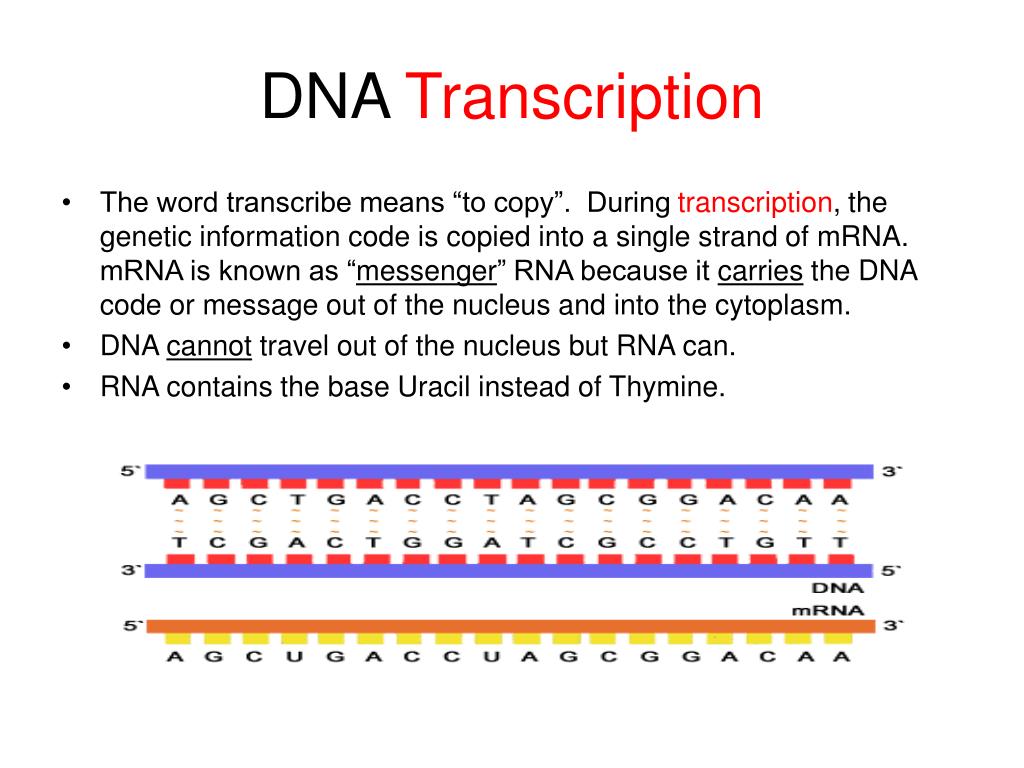
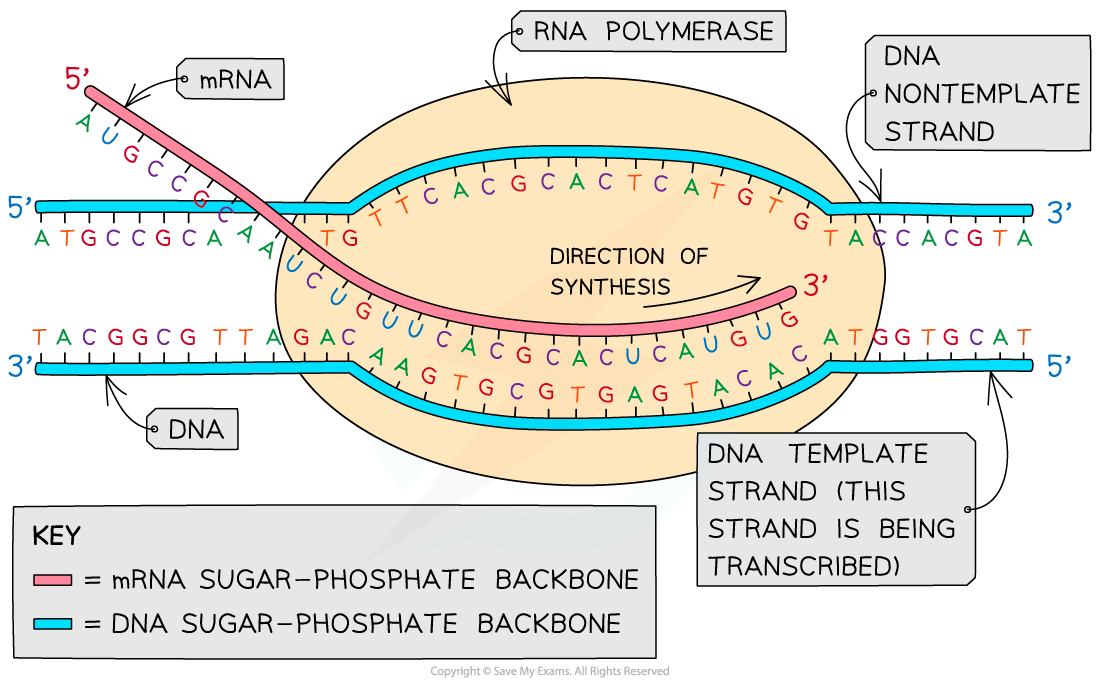
Transcription Template Strand - Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. Rna polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (ntp) precursors, in contrast to dna polymerases, which use deoxyribose nucleotide (dntp) precursors. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web during transcription, rna polymerase reads the template strand and directs the initiation of transcription. Web transcription in prokaryotes (and in eukaryotes) requires the dna double helix to partially unwind in the region of mrna synthesis. Web transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase attaches to the dna template strand and begins assembling a new chain of nucleotides to produce a complementary rna strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. Web transcription occurs when there is a need for a particular gene product at a specific time or in a specific tissue. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web transcription produces rna complementary to one strand of dna. Rna then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses the template dna strand of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. All of the rna in a cell is made by dna transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of dna replication discussed in chapter 5. Translation reads the genetic code in mrna and makes a protein. Web transcription occurs when there is a need for a particular gene product at a specific time or in a specific tissue. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. Web the template strand is read in the 3′ to 5′ direction, which means that rna synthesis takes place in the 5′ to 3′ direction, with the nucleoside triphosphate (ntps) acting as substrates for the enzyme. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Rna then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. Rna polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (ntp) precursors, in contrast to dna polymerases, which use deoxyribose nucleotide (dntp) precursors. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web if you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Rna polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (ntp) precursors, in contrast to dna polymerases, which use deoxyribose nucleotide (dntp) precursors. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. Web it uses dna as a template to make an rna molecule.. Web transcription occurs when there is a need for a particular gene product at a specific time or in a specific tissue. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. Web the template strand. Web during transcription, rna polymerase reads the template strand and directs the initiation of transcription. The nontemplate strand is referred. Web transcription in prokaryotes (and in eukaryotes) requires the dna double helix to partially unwind in the region of mrna synthesis. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Rna then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. The mrna. Web transcription produces rna complementary to one strand of dna. Translation reads the genetic code in mrna and makes a protein. Web transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase attaches to the dna template strand and begins assembling a new chain of nucleotides to produce a complementary rna strand. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding. Web transcription produces rna complementary to one strand of dna. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. Web it uses dna as a. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. During transcription, only one strand of dna is usually copied. Web in transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. Web transcription. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. Rna then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. If you're behind a. All of the rna in a cell is made by dna transcription, a process that has certain similarities to the process of dna replication discussed in chapter 5. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different. Although rna polymerase traverses the. Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. The region of unwinding is called a transcription bubble. Web transcription produces rna complementary to one strand of dna. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase attaches to the dna template strand and begins assembling a new chain of nucleotides to produce a complementary rna strand. Web during transcription, rna polymerase reads the template strand and directs the initiation of transcription. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Rna then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. Web transcription occurs when there is a need for a particular gene product at a specific time or in a specific tissue. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Transcription always proceeds from the same dna strand for each gene, which is called the template strand. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. Translation reads the genetic code in mrna and makes a protein. Although rna polymerase traverses the.Dna Strand That Is Transcribed at Trisha Revis blog
Dna Strand That Is Transcribed at Trisha Revis blog
What Is The Template Strand
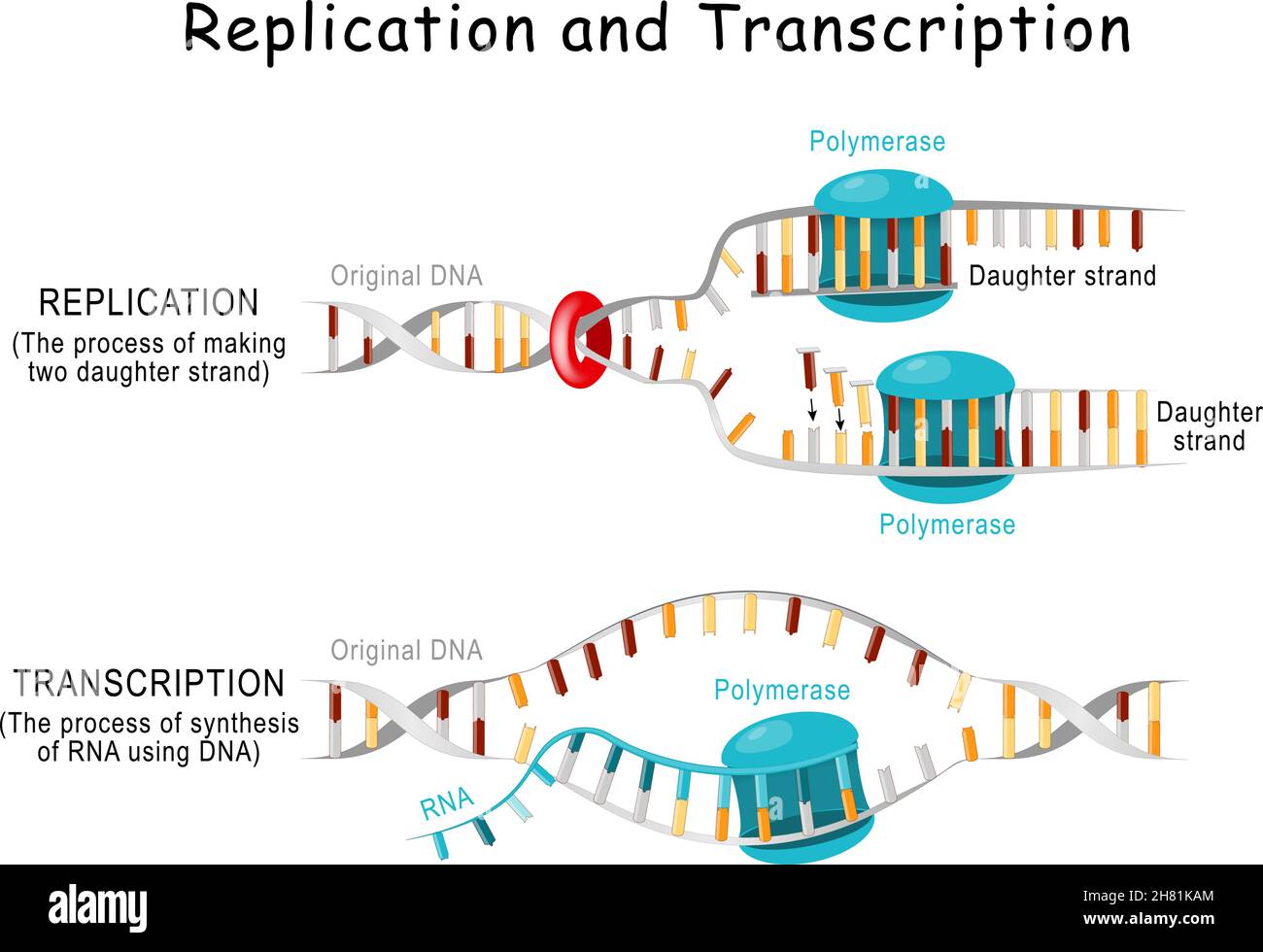
DNA Replication and Transcription. Steps. double helix is unwound. Each
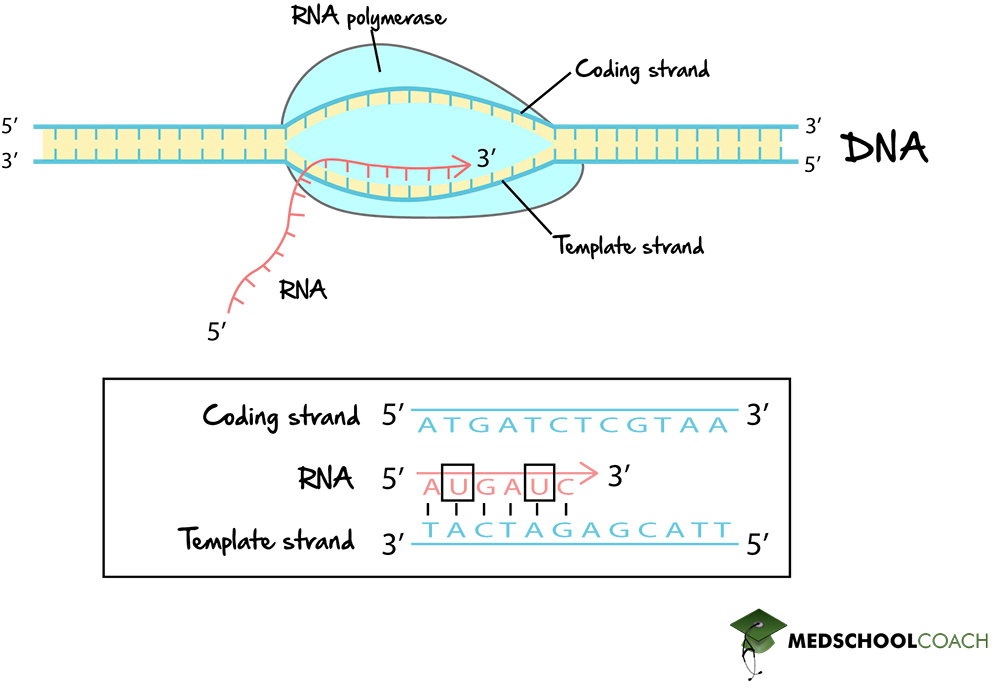
Mechanism of Transcription MCAT Biology MedSchoolCoach
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
PPT DNA Transcription and Translation PowerPoint Presentation, free
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Template And Coding Strand Of Dna
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记4.2.3 Transcription翰林国际教育
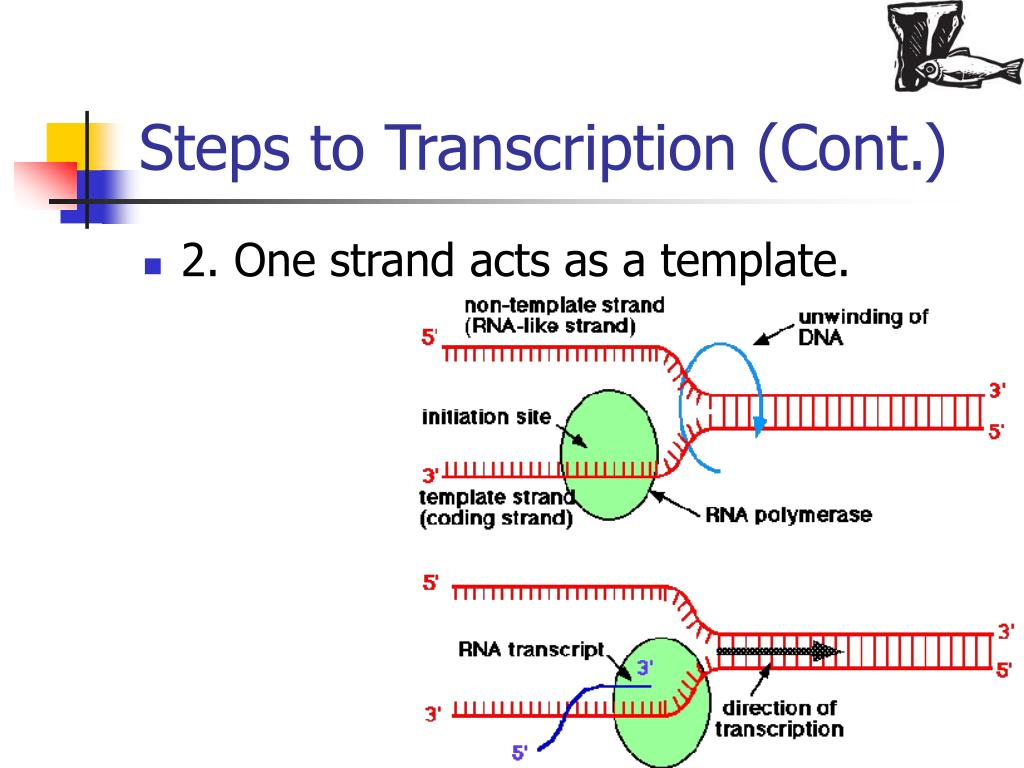
The Region Of Unwinding Is Called A Transcription Bubble.
The Template Strand Acts As A Base For Mrna Transcription.
The Nontemplate Strand Is Referred.
Web The Coding Strand Determines The Correct Nucleotide Sequence Of Mrna.
Related Post: