What Is The Template Strand
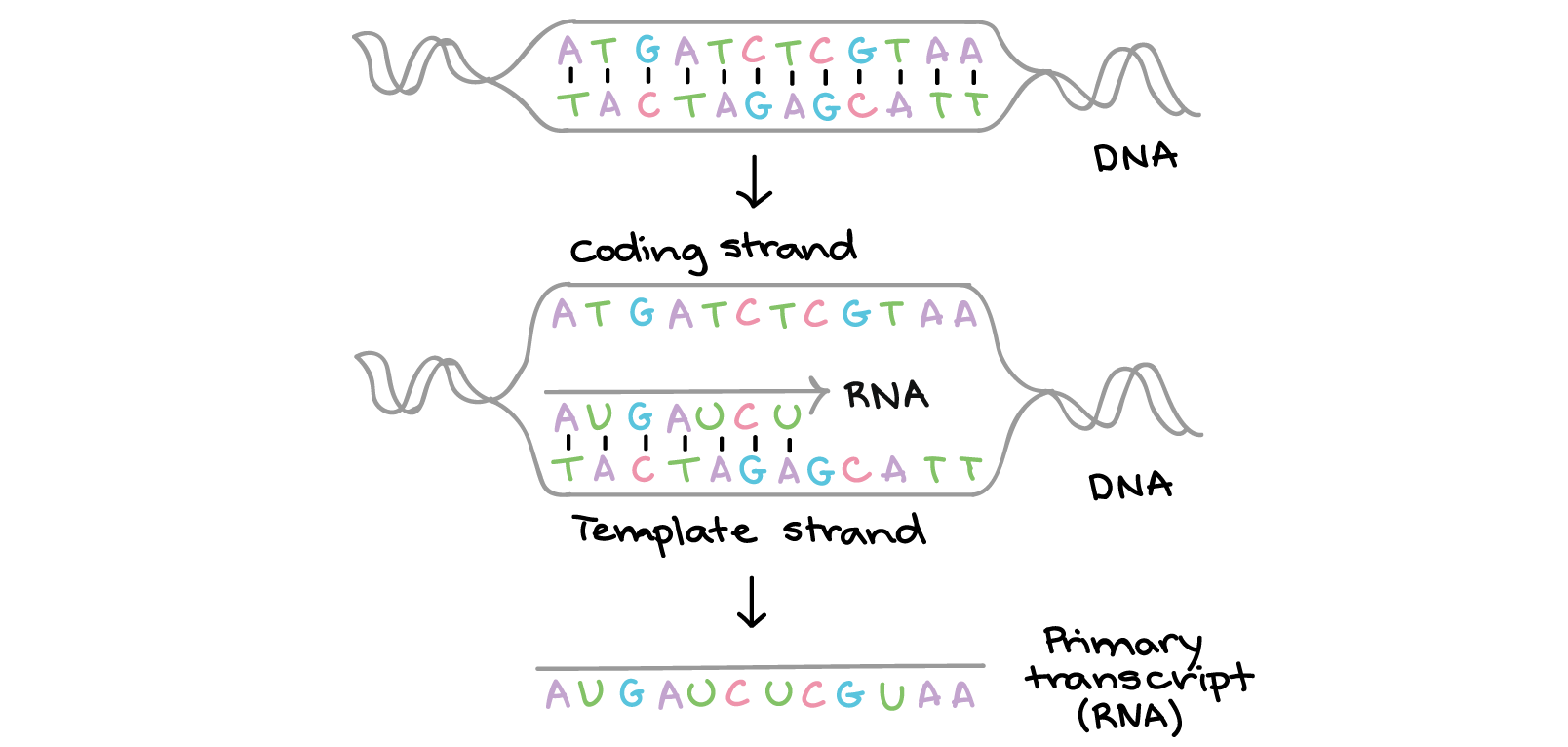
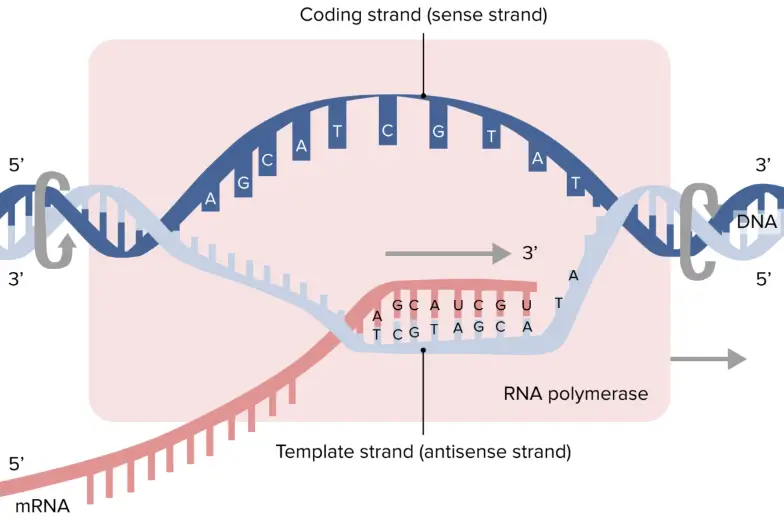
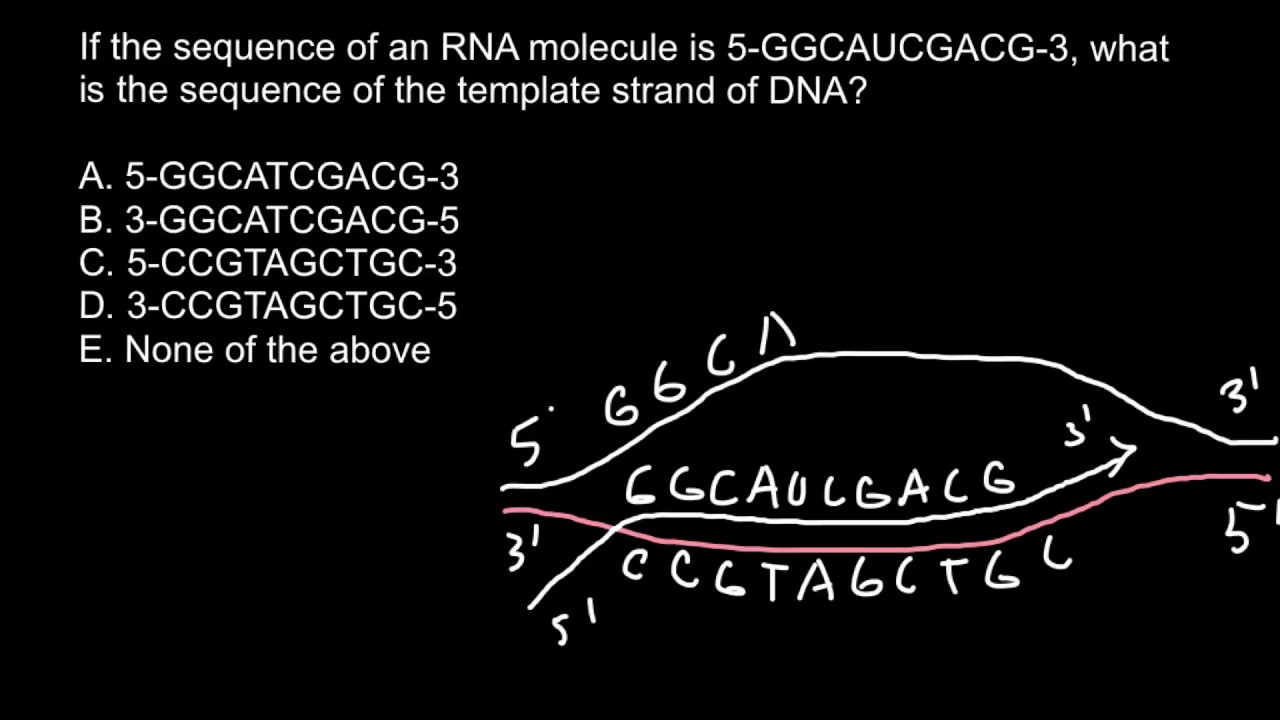
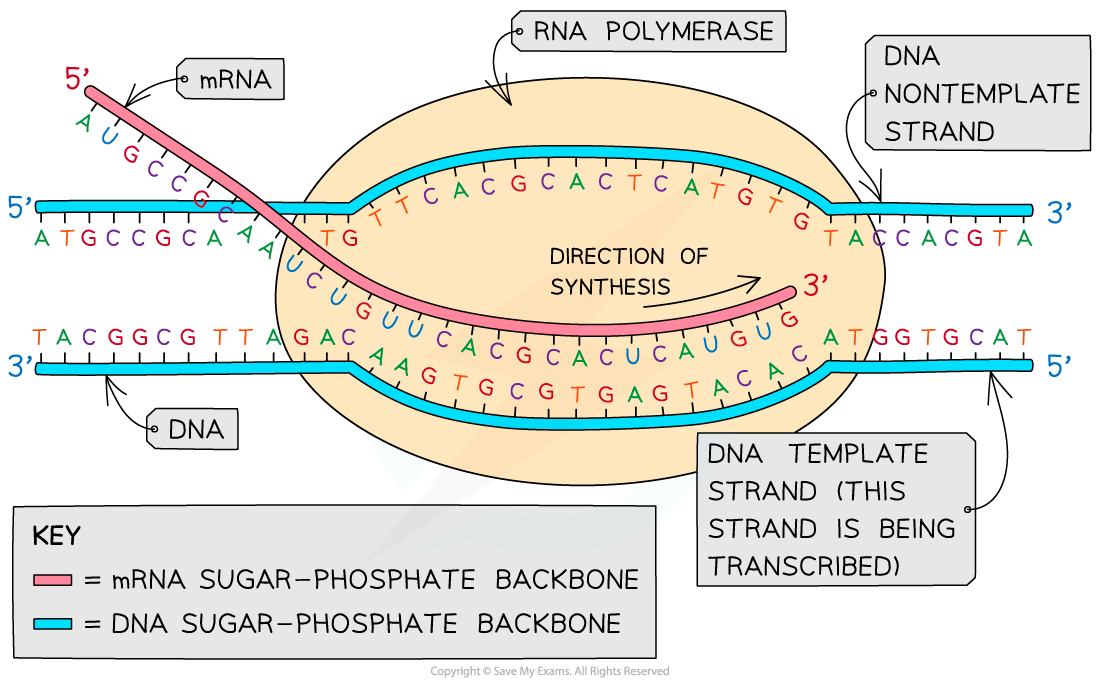
What Is The Template Strand - Adenine and guanine are classified as purines, while cytosine and thymine are classified as pyrimidines. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. It provides the sequence of nucleotides that are complementary to the rna being synthesized. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web the choice of template strand for each gene is therefore determined by the location and orientation of the promoter. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web dna is a template, transcribed and translated by a common set of mechanisms into just two different kinds of molecule. To initiate rna synthesis, the two dna strands unwind at specific sites along the dna molecule. (rna, or ribonucleic acid, is chemically similar to dna, except for three main. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. Web the template strand specifies which of the four dna nucleotides (a, t, c, or g) is added at each position along the new chain. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or informational strand. Because of this commonality, molecular biologists tend to use a standard set of tools to determine how information in dna encodes the biological functions of rna and proteins. Ribonucleotides are attracted to the uncoiling region of the dna. Web all of the nucleotides have the same sugar group and phosphate group, but different nitrogenous bases. The two strands of dna follow strict rules. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different mrna. Web the coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. It provides the sequence of nucleotides that are complementary to the rna being synthesized. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. Only the nucleotide complementary to the template nucleotide at that position is added to the new strand. To initiate rna synthesis, the two dna strands unwind at specific sites along the dna molecule. The nitrogenous bases in dna are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Web the template strand specifies which of the four dna nucleotides (a, t, c, or g) is added at each position along the new chain. Web during transcription, a portion of the cell's dna serves as a template for creation of an rna molecule. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build. The strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception. Sense strand contains the exact nucleotide sequence to the mrna which encodes for a functional protein. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand. In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. Web during transcription, a portion of the cell's dna serves as a template for creation of an. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. A always pairs with t, and g with c. Web the dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while. Only the nucleotide complementary to the template nucleotide at that position is added to the new strand. Web the template strand is the dna strand that serves as a guide for rna synthesis during transcription. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web the template strand is the dna strand that serves as a guide for rna synthesis during. Web sometimes genes overlap, and in some of those cases each strand of dna is copied, but each for a different mrna. Web chemical modification of dna is a common strategy to improve the properties of oligonucleotides. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Only the nucleotide complementary to the template nucleotide at that position is added. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Adenine and guanine. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and translate the mrna to a polypeptide. Adenine and guanine are classified as purines, while cytosine and thymine are classified as pyrimidines. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand). By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and translate the mrna to a polypeptide. The strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. In conservative replication, the parental. Web all of the nucleotides have the same sugar group and phosphate group, but different nitrogenous bases. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Web the template strand specifies which of the four dna nucleotides (a, t, c, or g) is added at each position along the new chain. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web chemical modification of dna is a common strategy to improve the properties of oligonucleotides. (rna, or ribonucleic acid, is chemically similar to dna, except for three main. Only the nucleotide complementary to the template nucleotide at that position is added to the new strand. Adenine and guanine are classified as purines, while cytosine and thymine are classified as pyrimidines. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Ribonucleotides are attracted to the uncoiling region of the dna. Web the template strand is the dna strand that serves as a guide for rna synthesis during transcription. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The template strand acts as a base for mrna transcription. Web during transcription, a portion of the cell's dna serves as a template for creation of an rna molecule. It is also known as sense strand (plus strand) or coding strand.Template Strand Mrna
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
What Is A Template Strand
How To Identify Template Strand Of Dna
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
What Is The Template Strand
Difference Between Template Strand And Coding Strand Printable Word
How To Identify Template Strand Of Dna
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记4.2.3 Transcription翰林国际教育
Web The Coding Strand Determines The Correct Nucleotide Sequence Of Mrna.
This Pairing Is Indispensable For Accurate Replication And Transcription.
In Conservative Replication, The Parental Dna Is Conserved, And The Daughter Dna Is Newly Synthesized.
Web The Dna Sequence That Is Transcribed To Make Rna Is Called The Template Strand, While The Complementary Sequence On The Other Dna Strand Is Called The Coding Or Informational Strand.
Related Post: