Xsl Apply Templates
Xsl Apply Templates - Web if you don't have any, then no template rules other than match=/ will get triggered. This supports the recursiveness of xslt application which is matching the (possible) recursiveness of the processed xml. Calls a matching template for each node in the set. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched by an attribute of the element. It adds a select attribute along with the template to specify the order of child nodes to process the current task with the help of the xslt processor. Available in xslt 1.0 and later versions. For play nodes that match the condition, your template is applied. Causes navigation from the current element, usually but not necessarily to process its children. It has to match a node that you elect to. Its select attribute contains an xpath expression telling the xslt processor which nodes to process at that point in the output tree. This is useful for processing the same information in multiple ways. Causes navigation from the current element, usually but not necessarily to process its children. The match attribute is used to associate a template with an xml element. For a template rule to get triggered, it can't just match a node in the input. It has to match a node that you elect to. Its select attribute contains an xpath expression telling the xslt processor which nodes to process at that point in the output tree. Web if you don't have any, then no template rules other than match=/ will get triggered. Match=/ defines the whole document). The value of the match attribute is an xpath expression (i.e. If we add a select attribute to the element, it will process only the child elements that matches the value of the attribute. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched by an attribute of the element. But for those that don't match the condition, a default template (identity transform) is applied instead. Web if you don't have any, then no template rules other than match=/ will get triggered. Available in all saxon editions. Web i am fairly new to xslt 3.0 and have a problem that requires it's use. This tag is used to direct the processor to apply templates on node elements of xml. It has to match a node that you elect to. The match attribute can also be used to define a template for the entire xml document. If we add a select attribute to the element, it will process only the child elements that matches the value of the attribute. Available in xslt 1.0 and later versions. The value of the match attribute is an xpath expression (i.e. I have to basically merge the t3. If we add a select attribute to the element it will process only the. It applies a template rule to the current child nodes. This supports the recursiveness of xslt application which is matching the (possible) recursiveness of the processed xml. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched by an attribute of the element. It has to match a node that you elect to. Web in your solution, you are transforming all nodes. Web i am fairly new to xslt 3.0 and have a problem that requires it's use. Causes navigation from the current element, usually but. Web if you don't have any, then no template rules other than match=/ will get triggered. Match=/ defines the whole document). Web the xslt apply template tag is used to apply the appropriate templates in the context of the selected node. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched by an attribute of the element. Causes navigation. Match=/ defines the whole document). This tag is used to direct the processor to apply templates on node elements of xml. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched by an attribute of the element. This supports the recursiveness of xslt application which is matching the (possible) recursiveness of the processed xml. For play nodes that match. I have to basically merge the t3. Web in your solution, you are transforming all nodes. Causes navigation from the current element, usually but not necessarily to process its children. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched by an attribute of the element. This supports the recursiveness of xslt application which is matching the (possible) recursiveness. Web in your solution, you are transforming all nodes. Calls a matching template for each node in the set. Its select attribute contains an xpath expression telling the xslt processor which nodes to process at that point in the output tree. But for those that don't match the condition, a default template (identity transform) is applied instead. This tag is. Its select attribute contains an xpath expression telling the xslt processor which nodes to process at that point in the output tree. Web the xslt apply template tag is used to apply the appropriate templates in the context of the selected node. It adds a select attribute along with the template to specify the order of child nodes to process. It applies a template rule to the current child nodes. Its select attribute contains an xpath expression telling the xslt processor which nodes to process at that point in the output tree. It adds a select attribute along with the template to specify the order of child nodes to process the current task with the help of the xslt processor.. Web i am fairly new to xslt 3.0 and have a problem that requires it's use. Web the <<strong>xsl</strong>:template> element is used to build templates. Web it means select all element children and apply the templates that match them. so if there is, for example, a child tag meh and a template for any element matching meh (or a more. If we add a select attribute to the element, it will process only the child elements that matches the value of the attribute. Causes navigation from the current element, usually but not necessarily to process its children. Web if you don't have any, then no template rules other than match=/ will get triggered. It applies a template rule to the. The match attribute can also be used to define a template for the entire xml document. Available in all saxon editions. Calls a matching template for each node in the set. Causes navigation from the current element, usually but not necessarily to process its children. Think of it this way: This tag is used to direct the processor to apply templates on node elements of xml. The value of the match attribute is an xpath expression (i.e. For play nodes that match the condition, your template is applied. Specifies a particular mode for this template, which can be matched by an attribute of the element. Web if you don't have any, then no template rules other than match=/ will get triggered. This supports the recursiveness of xslt application which is matching the (possible) recursiveness of the processed xml. But for those that don't match the condition, a default template (identity transform) is applied instead. Web the <<strong>xsl</strong>:template> element is used to build templates. Web the xslt apply template tag is used to apply the appropriate templates in the context of the selected node. If we add a select attribute to the element, it will process only the child elements that matches the value of the attribute. It has to match a node that you elect to.Xsl Apply Templates
xslapplytemplates ⚡️ XSLT 3.1 with examples
Xsl Apply Templates
Xsl Apply Templates
Using XSLT and XPath to Transform XML Documents ppt download
Xsl Apply Templates
Xsl Apply Template
Xsl Apply Template
Xsl Apply Templates
Xsl Apply Templates
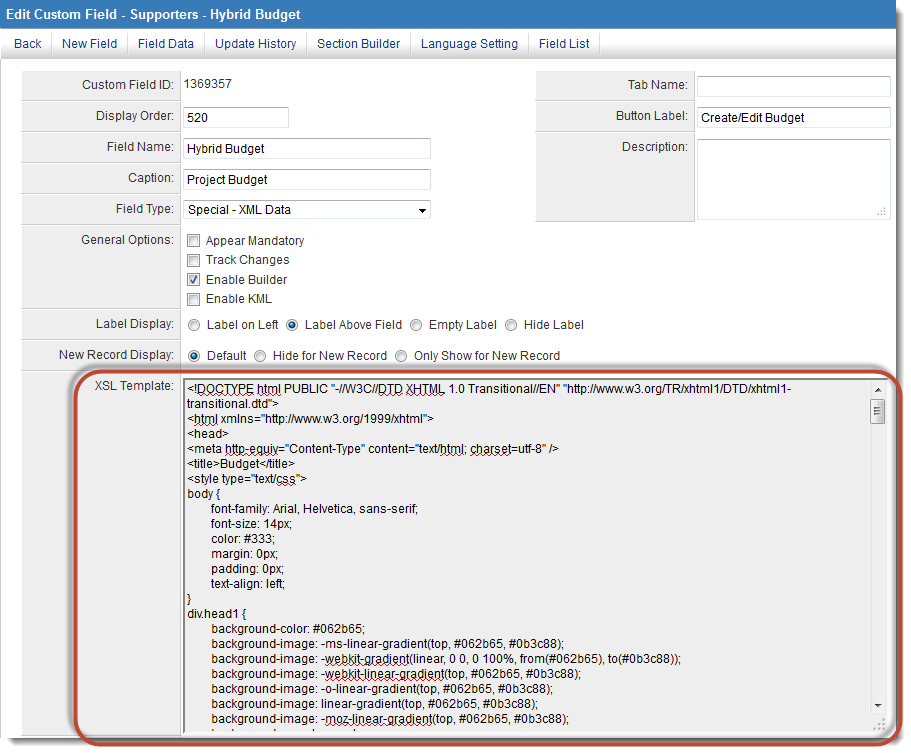
It Adds A Select Attribute Along With The Template To Specify The Order Of Child Nodes To Process The Current Task With The Help Of The Xslt Processor.
Web It Means Select All Element Children And Apply The Templates That Match Them. So If There Is, For Example, A Child Tag Meh And A Template For Any Element Matching Meh (Or A More General Match), It Would Apply That Template For That Child Element.
Its Select Attribute Contains An Xpath Expression Telling The Xslt Processor Which Nodes To Process At That Point In The Output Tree.
It Applies A Template Rule To The Current Child Nodes.
Related Post: